Resistance Spot Welding: Definition, Construction, Working Principle, Applications, Defects, Advantages, and Disadvantages [PDF]
Resistance Spot Welding Operation is used for joining the plates of railway tracks, fuel tanks, domestic radiators, etc.
In the last session, we had discussed the gas welding process and arc welding process and whereas in today's session, we will discuss Resistance Spot Welding along with its Definition, Construction, Working Principle, Applications, Defects, Advantages, and Disadvantages
Definition of Resistance Spot Welding:
The heat required for melting and joining of the plates obtained through the electrical resistance of the circuit, in the form of spots (nugget) is called Resistance Spot welding Operation.
Types of Resistance Welding:
Resistance Welding operation is classified as follows.
Resistance Spot Welding:
It is the simplest type of welding, where the two sheets are melted and joined by the application of force and electrical energy at the same time leading to the generation of heat and the formation of a spot that joins two metal sheets.
Resistance Seam welding:
It is also known as continuous spot welding in which a roller forms an electrode.
Projection Welding:
It is similar to spot welding in which a dimple can be generated on the workpieces where there are welded.
In this article, we can discuss in detail Resistance Spot Welding Operation.
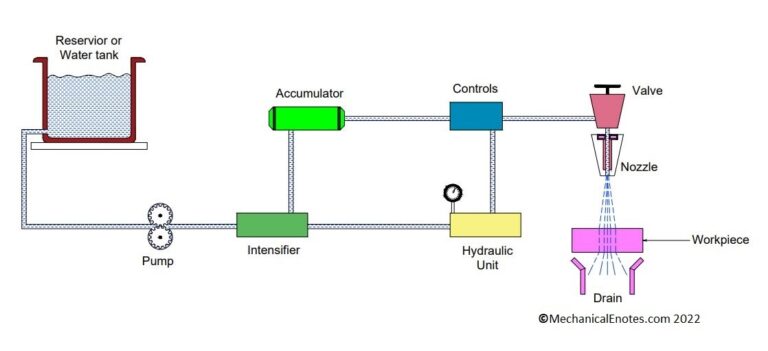
Resistance Spot Welding Diagram:
The diagram of the Resistance Spot Welding operation is shown below.
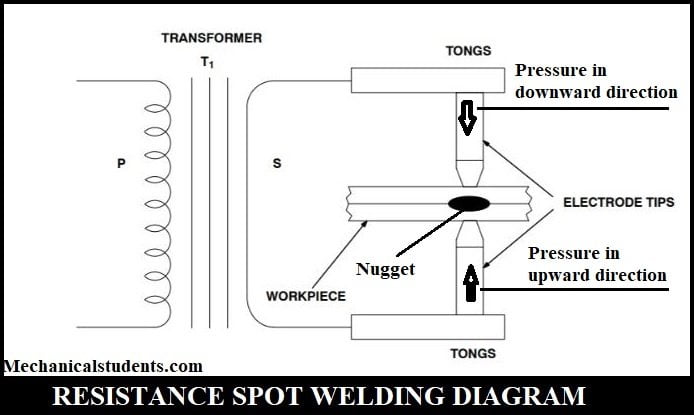
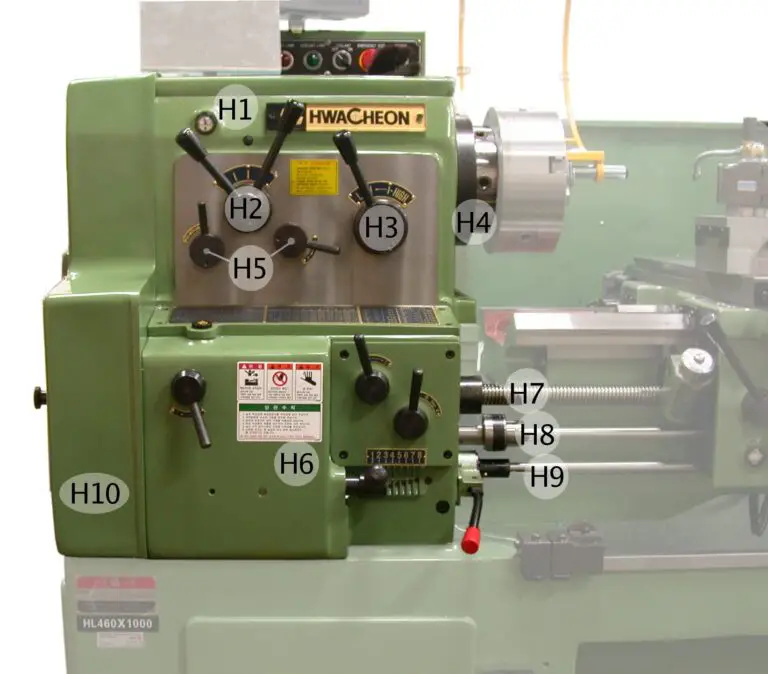
Construction of Resistance Spot Welding:
The Resistance Spot welding setup consists of a transformer, workpieces, two copper electrodes, and two tongs.
Depending upon the requirement, the transformer will be used either to step up or step down the voltage.
The power supply will be passed through the two Tongs to the electrodes.
The most commonly used electrode materials in resistance welding are Copper(Cu), Tungsten, Copper-Tungsten Alloy, etc.
Due to the application of pressure on the tongs, the heat is generated between the workpieces due to the passage of current and the formation of spot or nugget takes place.
Thereby a joint is formed between two workpieces.
Working Principle of Resistance Spot Welding:
Resistance Spot Welding working on the following concept:
- In a Resistance Spot Welding process, in which two or more metal sheets are joined together by means of spot welds.
- The workpieces to be welded are pressed between the tips of Copper electrodes and high current at low voltages is passed through the workpieces.
- Due to the resistance offered by the workpieces ( sheet metal ) to the flow of current, the temperature at the contact surfaces rises to fusion point and the weld is formed in the form of a nugget.
- A nugget is a weld formed in between the workpieces.
- No filler material is used in the Resistant spot welding Process.
- The operation is repeated ‘n’ no. of times to get the spot weld at the desired location.
Applications of Resistance Spot Welding:
Resistance Spot Welding is Used for:
- Joining of vehicle body parts
- Fuel tanks
- Railway tracks
- Pipes of gas oil and water pipelines
- Domestic radiators
- Turbine blades
Defects of Resistance Spot Welding:
The defects of Resistance Spot Welding are as follows.
- Asymmetrical Spot Weld Marks
- The explosion of metal near weld site
- Cracks in the Weld Area
- Indented Surfaces
- Spattering
Advantages of Resistance Spot Welding:
The advantages of Resistance Spot Welding are as follows.
- Easy automation
- Low fumes
- Cost-effectiveness
- No filler materials are required.
Disadvantages of Resistance Spot Welding:
The disadvantages of Resistance Spot Welding are as follows.
- Low strength in the case of discontinuous welds.
- High equipment cost.
- The thickness of welded sheets is limited - 6 mm only.
More Resources:
References [External Links]:
- Guidelines For Resistance Spot Welding - Miller Welding
- FUNDAMENTALS OF RESISTANCE SPOT WELDING
- Video Credits: Animech YT channel