Gas Welding Process: Definition, Equipment, Working Principle, Types of Flames, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications [PDF]
To speak simple, Gas welding is a process of joining two metals with the application of heat from the flames so that they will melt and join together. In the last session, we had discussed Electric Arc Welding process along with Arc Recovery Time and Arc Characteristics whereas, in today's session, we can discuss Gas Welding Process with its Definition, Equipment, Working Principle, Types of Flames, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications in a detailed way.
Definition of Gas Welding:
Gas Welding is a welding process that melts and joins the metals by heating them with a flame caused by a reaction of fuel gas and oxygen. The flux may be used to deoxidize and cleanse the weld metal. The flux melts, solidify and forms a slag on the resultant weld bead.
Types of Gas Welding Process:
There are 3 types of Gas welding process which are presented below.
- Oxy-Acetylene (C2H2) Gas Welding
- Oxy-Gasoline welding
- Oxy-Hydrogen Gas Welding
From the above types, Oxy-Acetylene Gas Welding was presented below in a detailed way.
Oxy-Acetylene Gas Welding:
The most commonly used Gas Welding is Oxyacetylene gas welding because of its high flame temperature.
Properties of Oxygen and Acetylene:
Oxygen:
- Colorless, odorless and tasteless gas
- Supports combustions & increase heat
Acetylene:
- Colorless and has a very distinctive odor
- Highly flammable
Equipment of Gas Welding Process:
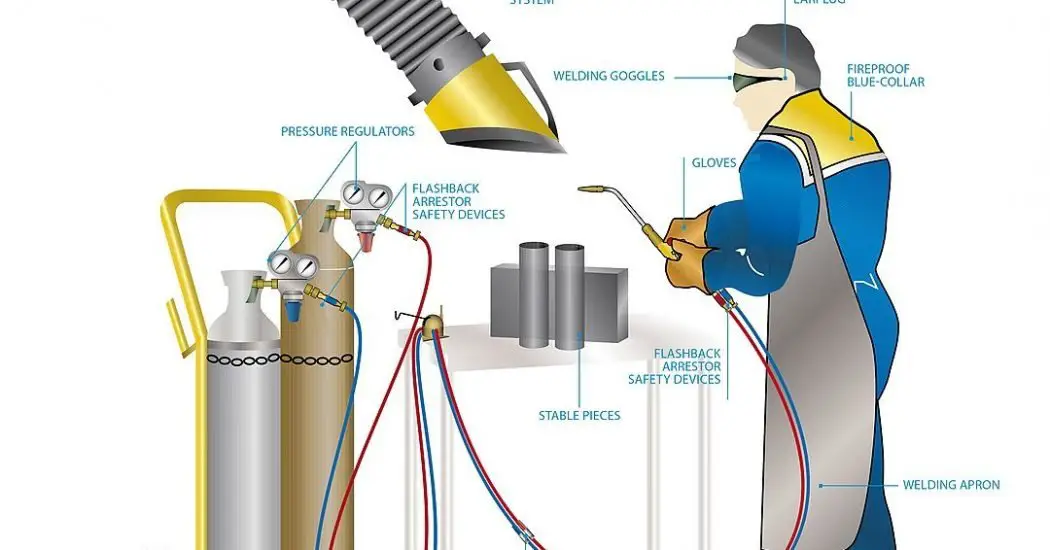
The Gas Welding Equipment consists of the following parts which are mentioned below.
- Oxygen pressure regulator
- Acetylene pressure regulator
- Oxygen gas cylinder (Black)
- Acetylene gas cylinder (maroon/red)
- Oxygen gas hose(Blue)
- Acetylene gas hose(Red)
- Welding torch or blowpipe with a set of nozzles and gas lighter
- Filler rods and fluxes
- Protective clothing for the welder (e.g., asbestos apron, gloves, goggles, etc.)
Working Principle of the Oxy-C2H2 Gas Welding Process:
The working principle of the Gas Welding process is as follows.
Oxygen and acetylene gases will be drawn from their respective cylinders mixed in the torch body so that the mixture is processing certain high pressure.
When these high-pressure mixture is passing through the convergent nozzle, the pressure energy is converted into velocity energy and coming out from the nozzle at high velocity.
When the initiation for the burning of this mixture is given, the continuous flame is produced and the heat available in the flame will be used for melting and joining of the plates.
Chemical Reactions Involved in Gas Welding:
C2H2 + O2 → 2CO + H2 + heat
2CO + O2→ 2CO2 + heat
H2 + 1/2 O2 → H2O + heat
For complete combustion of one unit Volume of acetylene, 2.5 units of volumes of oxygen are required.
Note:
Out of 2.5 units,1 unit volume of oxygen is obtained from the Oxygen cylinder and 1.5 units of volume of oxygen are obtained from the atmosphere.
Based on the amount of oxygen taken from the oxygen cylinder, the flame produced in oxyacetylene gas welding is divided into three types.
Types of Flames in Oxy-Acetylene Gas Welding:
The types of Flames in Oxy-Acetylene Gas Welding are as follows.
- Neutral Flame
- Oxidizing Flame
- Carburizing Flame
The detailed explanation of three types of flames is as follows.
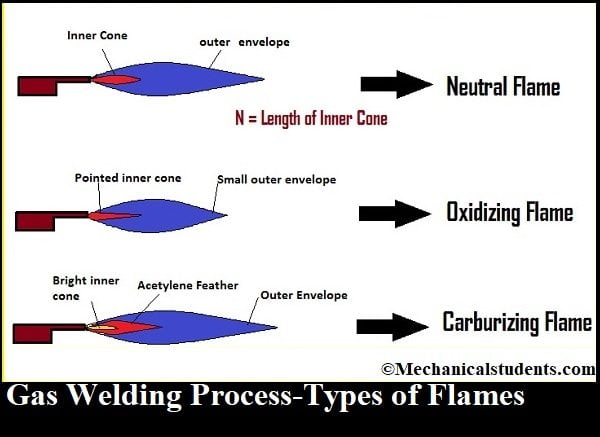
1. Neutral Flame:
O2/C2H2 = 1
The inner and Outer cone will be distinguished based on the color I.e. the inner cone is red or yellowish whereas the outer cone is a light blue color.
Red Colour Flame → Incomplete Combustion.
Light Blue Colour Flame → Complete Combustion.
Where N = 10 to 15 mm.
Temperature:
T max = 3260°C
Applications:
This flame is used for joining and cutting of all Ferrous and Non Ferrous metals except brass.
During the joining of brass workpieces, the zinc present in the weld bead will be getting evaporating and only copper is leftover in weld bead which is not giving required Mechanical properties of the weld bead.
2. Oxidizing Flame:
O2/C2H2 = 1.15 to 1.5
Inner Cone is in between N/3 to N/2.
Temperature:
T max = 3380°C
Because of an excess amount of oxygen supplied from the oxygen cylinder, the amount of oxygen to be taken from the atmosphere is reducing. Therefore, the mixture is burning within a short duration from the tip of the nozzle.
Due to the high average temperature of the flame, high melting point metals can be welded easily.
Advantages of Oxidizing Flame:
- The slightly lean mixtures will always give the highest efficiency of combustion hence the maximum temperature of the flame is higher.
- This method can be used for the joining of brass pieces.
Disadvantages of Oxidizing Flame:
- It should not be used for the joining of highly reactive metals like aluminum, magnesium, etc because the excess supply of oxygen from the oxygen cylinder may cause to leave the same amount of free oxygen in the flame which will be observed by the reactive metal and produces oxides.
- During the joining of brass workpieces, the free oxygen present in the flame will be combining with the same quantity of zinc present in the weld pool and produces zinc oxide also called tenuous oxide.
- This tenuous oxide is floating on the weld pool and it is not allowing the remaining zinc to evaporate.
3. Carburizing flame:
O2/C2H2 = 0.85 to 0.95
Inner Cone is in between 2N to 3N.
Tmax = 3040°C
The oxygen to acetylene ratio is 0.85 to 0.95 and the inner cone is in the range of 2N to 3N and the maximum temperature is 3040-degree centigrade.
because of the short supply of oxygen, the flame has to travel for larger distances to completely burn.
Hence, the heat lost by convection and radiation will become considerable.
Due to this, the maximum temperature is only about 3040-degree centigrade.
Advantages of Gas Welding:
The Advantages of the Gas Welding Process are as follows.
- Most commonly used for the joining of high Carbon Steel.
- It can adopt different jobs at a time because of the presence of strong flame.
- In the case of Steels, as the carbon content is increasing, the melting point of steel is reducing I .e.high carbon Steel will have a low melting point.
- Also, high carbon steel is already saturated with carbon. Even though, free carbon is available in the flame. It cannot be absorbed by the high carbon Steel.
- To withstand high pressures, the material used for the manufacturing of a hosepipe connected to the oxygen cylinder is made by copper as a material.
- It can be portable.
Disadvantages of Gas Welding:
The disadvantages of the Gas Welding process are as follows.
- Because of the lower average temperature of the flame, high melting point metals cannot be joined.
- This flame cannot be used for ferrous materials because when a short supply of oxygen is given, there is a possibility of free or unburned Carbon present in the flame which is absorbed by the iron and increase in brittleness of the weld bead.
- If copper hose pipe is connected to the Acetylene cylinder, the copper is chemically reacting with acetylene and produces Paste like material. Therefore, it will fail at lower pressures also.
- Because of lower pressure, the hosepipe connected to the Acetylene cylinder is made by using rubber or plastic and by mistake, if the hose pipes are interchanged, both the hose pipes will get failed.
- To avoid this, the distinguishing between cylinders will be done by looking at the size, color, type of threads, etc.
Applications of Gas Welding:
- It is used for most ferrous and non-ferrous metal
- It is used in aircraft industries.
- It is used in automotive industries
- Most commonly used for the joining of high Carbon Steel.
- It is used for joining thin materials.
This is the complete Explanation of Oxy-Acetylene gas welding process which was explained in a detailed manner.
More Resources:
Resistance Spot Welding
Electric Arc Welding Process
Types of Welding Process
References [External Links]:
- Welding - UF MAE [PDF]
- basic welding - Technical Learning College [PDF]