Electric Arc Welding: Equipment, Working Principle, Advantages, and More [PDF]
It is a process of joining two or more similar or dissimilar metals with or without the application of heat, with or without the application of pressure, with or without the application of filler material.
This welding process is widely used as a fabrication of joining two or more parts and repairing process in industries.
Some of the applications of welding include the fabrication of automobile bodies, ships, pressure vessels, welded pipes, bridges, sealing of explosives, etc.
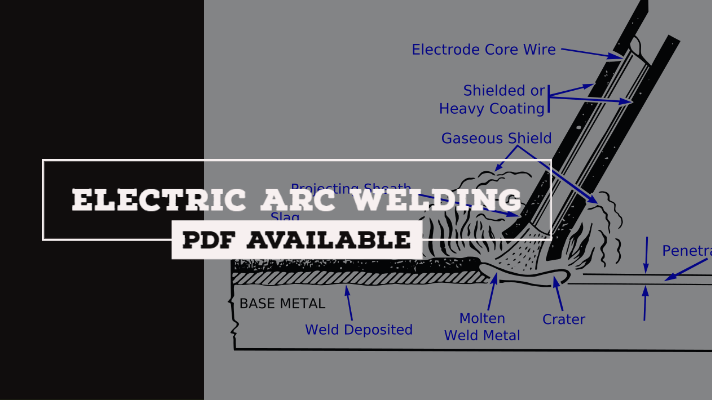
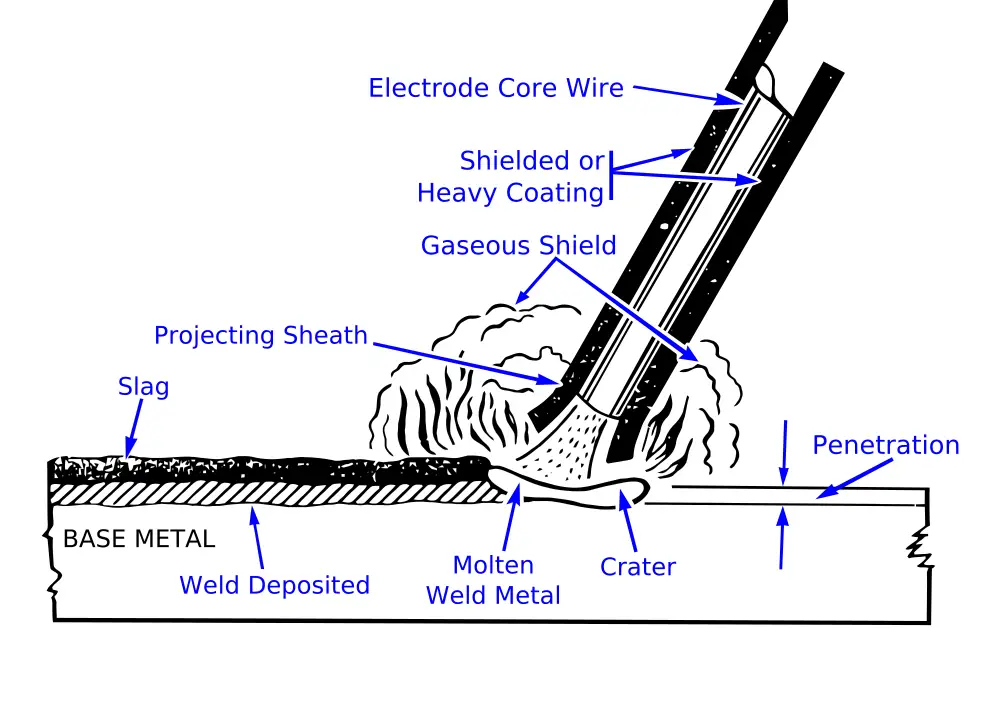
By using Electric Arc, If the heat required for melting of plates is obtained, called as Electric Arc Welding Process.
The fusion of metals by an electric arc is one of the most important processes in the industry. This is commonly called arc welding or SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding).

Parts of Electric Arc Welding:
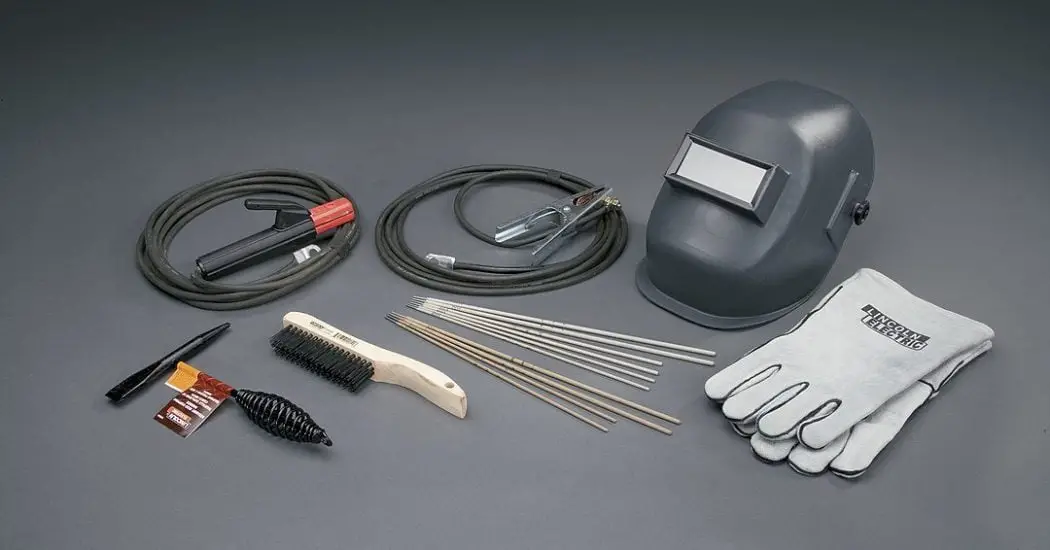
The Electric Arc Welding Process Equipment generally consists of the following parts:
- Arc welding power source
- Welding Electrodes
- Welding cables
- Electrode holder
- Hand Screen
- Chipping Hammer
- Wire brush
- Protective clothing
1. Arc welding power source:
- Both direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) are used for electric arc welding, each having its particular applications.
- For AC welding supply, transformers are predominantly used for almost all Arc welding processes
- DC welding supply is usually obtained from generators driven by the electric motors
- They have to step down the usual supply voltage (200-400 volts) to the normally open circuit welding voltage (50-90 volts) by means of Step-down Transformer.
2. Electrode holder:
- Electrode holder is used for holding the electrode manually.
3. Welding Electrodes
- An electrode is a piece of wire or a rod of a metal or alloy, with or without coatings.
- An Electrode can generate the arc at the desired welded location between electrode and workpiece.
4. Welding cables
- Welding cables are required for conduction of current from the power source to various parts of Arc welding process equipment i.e.electrode, the arc, the workpiece and back to the welding power source.
- These are insulated copper or aluminum cables.
5. Hand Screen
- Hand screen is used for the protection of eyes during Arc welding process.
6. Chipping hammer
- It is used for striking the slag from the weld bead region.
7. Wire brush
- A wire brush is generally used to clean the surface before and after the welding process.
8. Protective clothing
- The operator wears protective clothing such as apron to keep away from the exposure of direct heat to the body.
- Always wear gloves before touching any item in the workshop.

Working Principle of Electric Arc Welding:
- The work to be welded is connected to one side of an electric circuit(Anode), and a metal electrode is connected to the other side(Cathode).
- When the power supply is given and the optimum gap is maintained between Cathode and Anode, the very high velocity negatively charged electrons will be generated at the cathode.
- These will be attracted by the anode and moving towards the anode. When these very high velocity negatively charged electrons are impinging on to the anode, the Kinetic Energy of electrons is converted into Heat energy. Therefore, the heat generation is taking place at the anode.
- Simultaneously, the Positively charged ions also will be generated at the anode which is attracted by the cathode and moving towards the cathode.
- When these high-velocity ions impinging on to the cathode, the Kinetic Energy of ions is converted into Heat energy.
- Therefore, heat generation is taking place at cathode also.
- The ratio of Heat generation between the cathode and anode is given as follows.
- Heat Generation of Cathode:Anode=2:1
Spark Zone in Electric Arc Welding process:
- During the flow of electrons and ions, some of them may get collided in between the path so that the Kinetic Energy possessed by both the elements is converted into heat energy.
- This spontaneous release of heat energy will induce the sparkling and in the spark zone, the temperatures induced are very high which is about 5000°C-6000°C.
- This high-temperature zone will produce UV rays. Hence the Electric Arc Welding process Zone must be seen only through safety goggles to safeguard the human eye.
Features of Electric Arc Welding Process:
- In DCSP, because of higher heat generated at the workpiece, high Melting Point metals and higher thickness plates can be welded very easily and depth of penetration is also higher.
- Because of lower heat generated at the electrode, the melting rate of the electrode is low, deposition is low hence welding speeds are possible.
- In DCRP, because of lower heat generated at the workpiece, only low Melting Point metals and lower thickness plates can be joined and depth of penetration is also low.
- Whereas in the case of the electrode, because of the higher heat generated at the electrode, the melting rate of the electrode is high, the deposition rate is high. Hence higher welding speeds are possible.
- In ACHF, heat generation is 1:1 ratio. Hence, this can be used for medium conditions and depth of penetration is also medium.
Arc Recovery Time and Arc Characteristics in Electric Arc Welding Process:
The time taken for establishing the arc between electrode and workpiece is called Arc Recovery Time. This article focus on Arc Recovery Time and Arc Characteristics in Electric Arc Welding Process in a detailed way which is mentioned below.
Explanation of Arc Recovery Time:
- Establishing the arc means establishing the flow of electrons and ions in their respective directions.
- In DC Arc welding, because the terminals are fixed, whatever may be the arc recovery time, it doesn't have any influence on the welding operation.
- Whereas in AC Arc welding, because the terminals are continuously changing, the arc recovery time should be less than the cycle time(C.T).
But, for effective Arc Welding operation, the Arc Recovery Time (ART) must be less than half of the cycle time i.e. ART < (C.T/2)
- The Arc Recovery Time can be reduced by increasing the voltage of power supply i.e. by increasing the voltage of power supply, the reaction time for producing electrons and ions will be reduced.
If V≅ 30V Then,
ART≅ (C.T/2)
It means that as Voltage(V) increases, it reduces the ART.
Max. Voltage ≤70V i.e. Voltage is {30V,70V}
- The range of Voltage used in the AC Arc welding is (30V-70V)
Stable Equilibrium Conditions of Electric Arc Welding Process:
- To ensure the stable Equilibrium conditions of Arc welding process and Arc welding Equipment, whatever the energy supplied by using the power supply unit is only has to be utilized at the Arc point.
- To ensure the above conditions, the energy supplied by using power supply unit is controlled by using the voltage and current settings of power source whereas energy utilization at the Arc point is controlled by using ARC LENGTH.
- Therefore, for stable Equilibrium conditions, it is required to determine the optimum arc length and optimum settings of a power source
Vo- Open Circuit Voltage (or) Actual EMF generated in 2°windings of a transformer(or)Max Voltage in 2°
Is- Short Circuited Current (or) Max. the current which is possible to pass through the 2° windings.
Rs- Resistance of 2° windings
The Resistance of 2° windings = Vo/Is
where
V = Vo-Vdrop
=Vo-(Rs*I)
V =Vo-({Vo/Is}*I)
Explanation of Arc Characteristics:
As mentioned above,
- L - Arc Length
- I - Current
- Is- Short Circuited Current.
If L =0, I=Is, Rair =0
L=large,I=0,Rair=∞
then,
Vair = I*Rair
i.e. Va =a+bL ;where a,b are constants.
At stable Equilibrium condition, the voltage in power source = Voltage in Arc point
i.e. Vp =Va⇒Va = Vp
a+bL =Vo-[{Vo/Is}*I]
[{Vo/Is}*I] =Vo-a-bL
I = {Is/Vo}*(Vo-a-bL)
Since Power P = V*I
=(a+bL)*{Is/Vo}*(Vo-a-bL)
For a minimum power supply, Derivate the above equation w.r.t Length(L) and equate to zero. Then you can get an equation in terms of ARC LENGTH(L)
This is the detailed explanation of Arc Recovery Time and Arc Characteristics of the welding process in a detailed manner. If you like this post share this with the whole world so that it can reach to many.
Electrode Specification E-7018X:
Electrode plays a vital role in the welding process. Without electrodes also, many welding processes are present which are used in high-end applications. In this article, I will explain about the specification of Electrode E-7018X in a detailed manner. Electrode specification is must in any welding process and the specification of Electrode E-7018X is as follows.
- The electrode E-7018X stands for E-Electrode
- 70-How strong the electrode is when welded
- 1-in what welding positions it can be used
- 8-indicates coating,current types,penetration
- X-indicates that there are more requirements.
Features of Electrode E-7018X:
- They(E-7018X) are low hydrogen flux coated steel rods with a high yield tensile strength of 70000 PSI.
- They are often used in assembling structural steel used in the construction industry.
- These electrodes are called low hydrogen electrodes due to every attempt to lower the hydrogen content, these electrodes must be stored in an oven with a temperature between (250-300) Degree Fahrenheit.
This is the complete explanation of Electric Arc Welding. If you have any doubts, feel free to ask from the comments section. Please Share and Like this blog with the whole world so that it can reach to many.
References [External Links]:
- What is Welding?
- handbook on welding techniques - rdso
- Welding - UF MAE
- FUNDAMENTALS OF WELDING