Brazing and Soldering Process: Working, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications [PDF]

In all the non-fusion welding processes, when the liquid molten metal is poured at the joint, it gets wet and Solidifies. During the process of Solidification, the atoms present on the surface of the filler rod are sharing the energy with atoms present on the surface of parent material, and thereby it produces the joint.
When the surface atoms are sharing the energy-producing the joint it is called Surface Alloy Joining.
Now let's see the Detailed Explanation of Brazing and Soldering Process in detail along with Advantages, disadvantages and Applications.
Brazing Process:
Joining of two metals without preparing any joint is called as brazing operation.The mechanism of the joint is Wetting and Surface Alloying.
The temperature of the joint must be greater than the melting point of metals. So here in the case of brazing, the temperature of the joint must be greater than 450-degree centigrade.
It is a process of joining similar or dissimilar metals using filler material. The filler material is called Spelter and the filler material is made up of Copper alloy.
Out of the different metals, the molten metals copper, zinc alloy is having the highest capillary action. hence, it is used as a filler rod in the brazing operation.
A mixture of Spelter and Borax with Water is used as a paste and is applied to the metal parts at the joints.
Spelter+Borax+Water = Paste
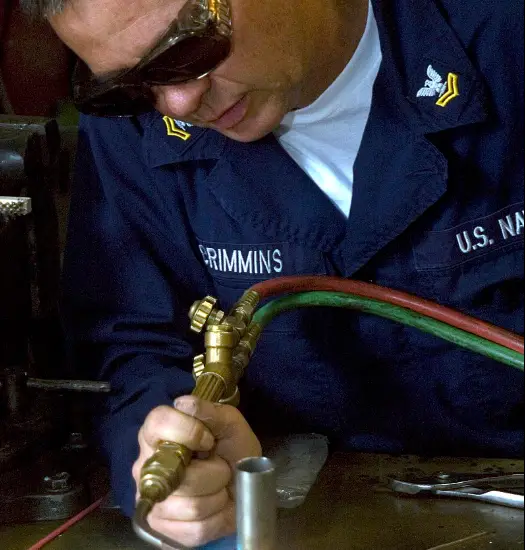

Working Principle of Brazing Process:
First, you need to take two workpieces to join them through the process of brazing. As in the case of soldering, we had used a soldering gun and filler material for the formation of joint whereas, in the Brazing process, a paste is used, which is the mixture of (Spelter+Borax+Water) and is to be applied on to the work region.
The type of joint formed is Permanent and the load bearing capability is also high.
Later, the applied material has to be heated so that it can melt and form as a layer in between two workpieces. Here, Oxy-Acetylene gas welding is used to heat the mixture for the formation of joints, and the Copper alloys are used as a filler rod.
- Most commonly used filler rod materials in the brazing and braze welding are copper alloys therefore for melting of the filler rod material, Joint must be heated at a temperature greater than 450-degree centigrade.
- As there is no joint prepared, the flow of molten metal into the joint is taking place due to capillary action.
The workpiece has to be cleaned after cooling so that the impurities cannot stick to the workpiece.
Advantages of Brazing Process:
The advantages of Brazing are as follows.
- Dissimilar metals can be joined by a brazing process
- The metals which cannot join by welding, in terms of thickness, can join by means of a Brazing process like Radiators, pipe fittings, containers, and heat exchangers.
- The leak-proof joints can be prepared by means of a brazing process.
Disadvantages of Brazing Process:
The disadvantages of Brazing are as follows.
- Skilled labor is required to do a brazing process.
- The joints produced due to brazing exhibit less strength than welding.
Applications of Brazing Process:
The applications of Brazing are as follows.
- Brazing is used for the fastening of pipe fittings, carbide tips on tools, heat exchangers, electrical parts, radiators, axles, etc.
- It can join cast metals to wrought metals, dissimilar metals, porous metal components, etc.
- It is used to join parts of the bicycle such as frame and rims.
Soldering Process:
It is a process of joining similar or dissimilar metals using filler material. The filler material is called as Solder and the filler material is made up of Lead-Tin alloy.
During soldering, there is a need for flux which is made up of Zinc Chloride, Ammonium Chloride, and resin is mixed with them.
The mechanism of the joint is Wetting and Surface Alloying.
Type of Joint: Temporary.
Load bearing capability: less than Brazing
The temperature of the joint must be less than the melting point of metals. So here in the case of soldering, the temperature of the joint must be less than 450-degree centigrade.
Filler Rod: (50% lead & 50% Tin Alloy)
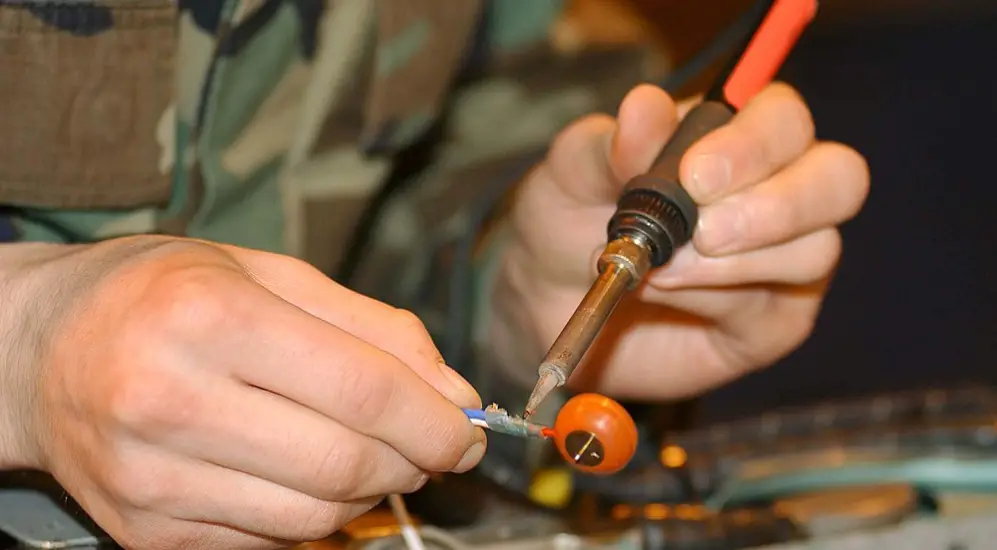

Working Principle of Soldering Process:
First, the Soldering gun is to be heated up to the desired temperature. Now, the filler metal has to be in contact with the soldering gun with which the filler metal melts and deposits on the work region.
When the (50% lead & 50% Tin Alloy) is to be heated to a temperature greater than 450-degree centigrade, the tin present in the lead & Tin alloy starts evaporating. Hence the temperature of the joint must be <450 Degree centigrade.
The melted filler metal enters into the work region by the action of capillarity and after cooling, the joint is formed.
Advantages of Soldering Process:
The advantages of Soldering process are as follows.
- Joints prepared using the soldering process will be dismantled easily.
- Soldering can be done at a low temperature of less than Brazing operation.
- The soldering cost is very less.
- It's simple in design and economical.
Disadvantages of Soldering Process:
The disadvantages of Soldering process are as follows.
- Skiller worker is required to make a perfect and stronger joint.
- Solders are costlier.
- Soldering can be applied only for small joints but it cannot be applied for heavy parts.
Applications of Soldering Process:
Mostly used to solder the wires on the Printed Circuit Boards(PCB).
Now lets discuss the differences between Soldering and Brazing.
Soldering V/S Brazing:
The comparison chart of Soldering vs Brazing was presented below.
| Soldering | Brazing |
|---|---|
| The boiling point of filler material is below 450°C. | The boiling point of filler material is above 450°C. |
| The filler material is called as Solder. | The filler material is called as Spelter. |
| The filler material is made up of Lead-Tin alloy. Filler Rod: (50% lead & 50% Tin Alloy) | The filler material is made up of Copper alloy. |
| It is a Temperory joint. | It is a Temperory joint. |
| The strength at the joint is very less compared to the Brazing. | The strength of the material after brazing is very high comapred to Soldering. |
| The preheating is not required for the base metal. | The preheating is required for the base metal. |
| The setup cost is very small compared to brazing. | The setup cost is very high compared to brazing. |
| It's simple in design and economical. | It is not economical. |
| Applications: It is mostly used in Printed Circuit boards (PCB's) | Applications: It is mostly used in all kinds of metals, pipe fittings etc. |
This is the complete explanation of Brazing and Soldering operations in a detailed way.