Electron Beam Machining: Definition, Parts, Working Principle, Process Parameters, Characteristics, Applications, Advantages, and Disadvantages [Notes & PDF]
The electron beam machining Process also comes under one of those Non-traditional machining methods where highly dedicated accuracy is maintained. It is also called EBM.
In the last article, we had discussed Ultrasonic Machining, Electrical Discharge Machining, Electrochemical Machining, etc. whereas, in today's article, we will discuss EBM along with Definition, Parts, Working Principle, Process Parameters, Characteristics, Applications, Advantages, and Disadvantages in a detailed way.
So, lets start with the definition of Electron Beam Machining.
Electron Beam Machining Definition:
Electron beam Machining is a process in which a high velocity of electrons are concentrated through a narrow beam and is then directed towards the workpiece such that the material removal takes place by melting and vaporizing from the surface of the workpiece.
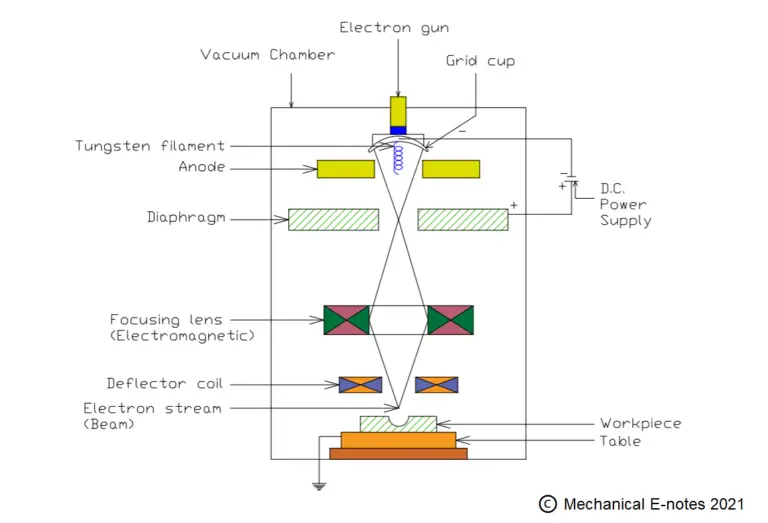
Electron Beam Machining Parts:
The parts of Electron Beam Machining are as follows.
Electron gun:
The major part of the electron beam machining process is the Electron gun which acts as a cathode and contains tungsten or tantalum filament that generates the beam of electrons to remove the material from the surface of a workpiece.
Vacuum chamber:
It is used such that there is no possibility of air in the setup.
Grid cup:
The electrons which were generated by the electron gun was been controlled by the grid cup.
Anode:
To accelerate the electrons to a much high velocity, anode is used in the experimental setup.
Focusing lens:
Their main aim is to allow the beam of convergent electrons to pass through it and they are used to focus the beam of light on a particular spot.
Deflector Coils:
Deflector coil guides the high-velocity electron beam onto the desired location of the workpiece maintaining efficiency for the formation of holes.
Workpiece and Table:
The workpiece is the region where we need to focus the beam of light to pass which removes the material from the surface of the workpiece. The table is used to hold the workpiece properly.
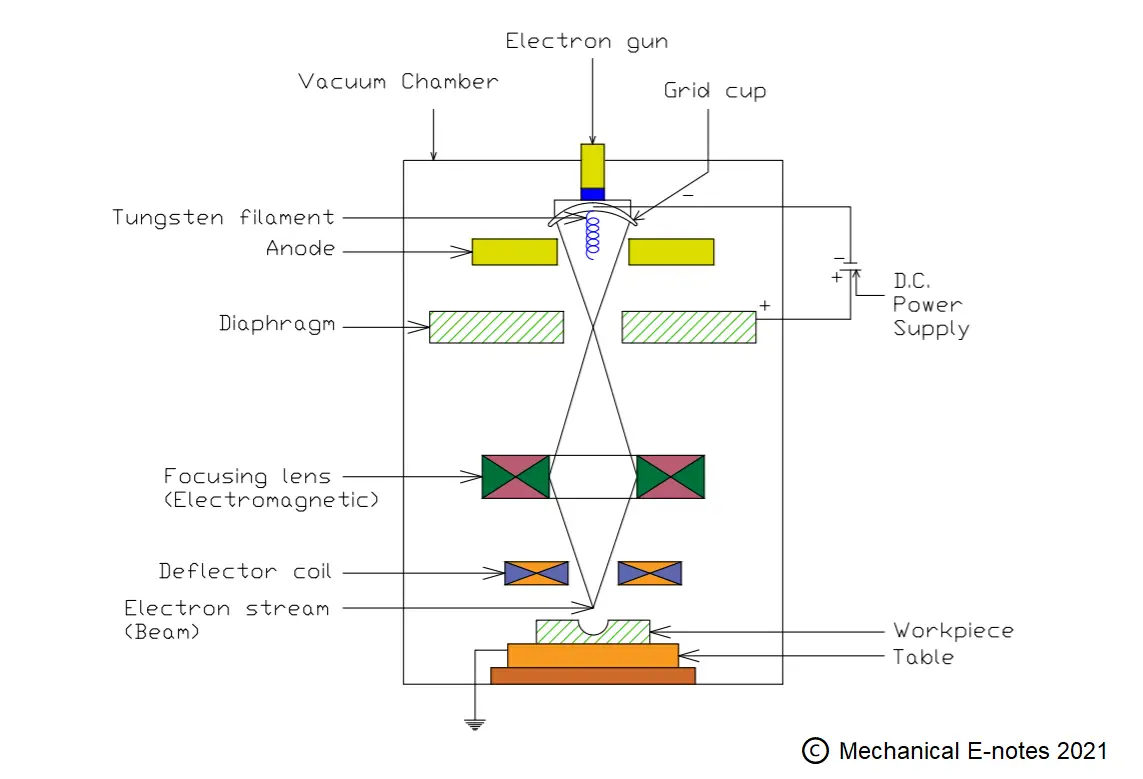
These are the parts of EBM. Lets discuss the working principle of it...
Electron Beam Machining Working Principle:
The working principle of Electron Beam machining is as follows.
When a very high voltage power supply is given to the electron gun, it is producing very high-velocity electrons in all the directions.
By using a magnetic lens or the deflector, all these high-velocity electrons are collected and formed like a beam of electrons having the cross-section area less than 0.05-millimeter square.
When this high-velocity electron beam is impinging onto the workpiece, the kinetic energy of electrons is converted into heat energy.
Therefore heat is getting generated at the workpiece and by using this heat, the workpiece is getting melting and evaporating i.e. the mechanism is melting and evaporation.
To avoid the Dispersion of electrons after the magnetic lens, the total setup is kept in a container which is maintained with a perfect vacuum.
There is no tool used and only an electron gun is used which is made by using a Germanium crystal type of material.
Medium: Perfect Vaccum
Wear Ratio: infinity.
This is the explanation behind the working of the Electron Beam Machining process.
Process Parameters of Electron Beam Machining:
The process parameters of EBM are as follows.
- Beam current: It is related to the emission of electrons by the cathode in the beam whose value is as low as 1µA.
- Duration of Pulse: It can be varied from 50 µs to 15 ms.
- Accelerating voltage (Va) is 100 Kv.
- Energy per pulse is 100 J/Pulse.
Characteristics of EBM:
The machining characteristics which are directly effected by the process parameters in EBM are:
- The velocity of the electron is 1.6 x 10^8 m/s.
- Specific power consumption is 0.5 to 50 kW.
- The MRR(Material Removal Rate) is up to 40 mm^3/s.
- The depth of cut is up to 6.5mm.
- Medium is Vaccum.
- The power density is 6500 billion W/mm^2.
Applications of Electron Beam Machining Process:
The applications of Electron Beam Machining Process are as follows.
- Mainly used for producing holes in the diesel injection nozzles.
- Also used for producing blind holes, narrow slots, etc. in the workpieces.
- In electron beam machining, if the voltage given to the electron gun is about 60 to 70000 volts, the velocity of electrons produced is reducing, heat generation at the workpiece is reducing.
- Therefore, the heat generated is sufficient to melt and join the workpiece called an electron beam welding operation.
Advantages of Electron Beam Machining Process:
The advantages of Electron Beam Machining Process are as follows.
- Very very small size holes can be produced.
- Highly reactive metals can be machined easily because of perfect vacuum is maintained.
- Heat affected zone will be minimum.
Disadvantages of Electron Beam Machining Process:
The disadvantages of Electron Beam Machining Process are as follows.
- Workpiece material must be electrically conductive.
- Maintaining a perfect vacuum is difficult.
- Out of all the non-traditional machining methods, the electron beam method has the lowest material removal rate.
- Because the total setup is kept in an enclosure, the machining zone can't be seen by a machine operator.
This is the complete explanation about the Electron Beam Machining process in a detailed manner. If you have any doubts, feel free to ask from the comments section.
More Resources:
Lathe Machine
Drilling Machine
Shaper Machine
Electrical Discharge Machining
References [External Links]:
- Manufacturing Processes – II - NPTEL
- (PDF) ELECTRON BEAM MACHINING (EBM) - ResearchGate