Laser Beam Machining [with PDF Notes]: Definition, Construction, Working Principle, Types, Process Parameters, MRR, Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages
In the last article, we had discussed what is machining process? and the types of machining processes like EDM, EBM, ECM, USM, etc. whereas in today's article, we will discuss in detail about Laser Beam Machining process along with its Definition, Construction, Working Principle, Types, Process Parameters, MRR, Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages in a detailed way.
History of Laser Beam Machining
The laser cutting machine is used to drill holes in the diamond dies in the year 1965 and later on, the laser-assisted oxygen jet cutting for metals was started in the year 1967. In the early 1970s, this technology is used to cut titanium for aerospace applications.
What is Laser Beam Machining
A laser beam machining is a non-conventional machining process in which the operation is performed by the application of laser light which exhibits the maximum temperature strikes onto the workpiece to remove the material from the surface of the workpiece.
The Abbreviation of LASER is Light Amplification Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
Laser Beam Machining Diagram
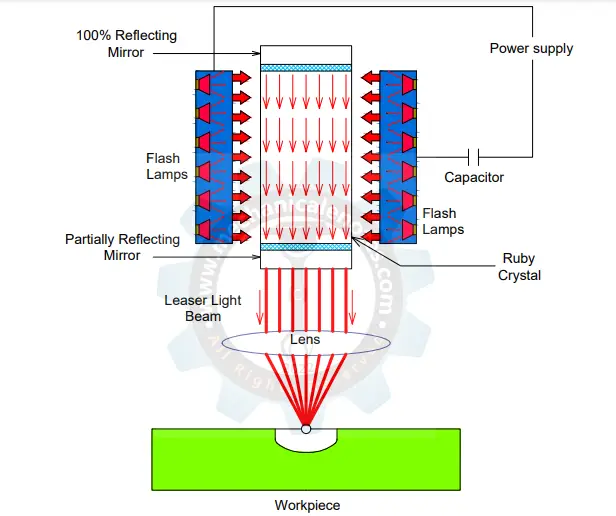
The diagram of Laser Beam Machining is shown below.

Construction or the Main Parts of Laser Beam Machining
The main parts of the Laser Beam Machining process are as follows.
- Power Supply
- Capacitor
- Reflecting Mirror
- Flash Lamps
- Laser Light Beam
- Lens
- Ruby Crystal
- Workpiece
Power Supply:
A high voltage electric current is supplied to the system which is used to produce light in flashlight tubes.
Capacitor:
The main aim of a capacitor is to store and release the energy present in it. The capacitor is used to operate the laser beam machine at pulse mode.
Reflecting Mirror:
100% reflecting mirror and the partially reflecting mirror are used in this laser beam machining process. These two mirrors are placed opposite to each other. The laser beam reflects from the 100% reflecting mirror and will pass partially from the partially reflecting mirror.
Flash Lamps:
The flash lamps are filled with gases that ionize to form a large amount of thermal energy that will melt and vaporize the material from the surface of the workpiece.
Laser Light Beam:
It is the beam of radiation produced by the laser.
Lens:
The lens is used to focus the laser beam onto the workpiece to remove the material into the desired format.
Ruby Crystal:
Ruby laser produces a series of coherent pulses which are deep red in color passes through the partially reflecting mirror.
Workpiece:
A metallic or Non-Metallic workpiece is used in this machining process.
These are the various parts of the Laser beam machining process. Let's discuss the Working of it.
Laser Beam Machining Working Principle:
The working principle of the Laser Beam Machining process is as follows.
The high voltage power supply is applied on both sides of the flash tubes which emits light photons that contain energy. A capacitor is used to operate the flash tube at pulse mode.
When the power supply is given to the laser gun, it is producing very high-intensity electromagnetic waves in the form of a beam called a laser beam with a wavelength ranging from 0.1 to 70 micrometers.
These light photons emitted by the flash tube are absorbed by the ruby crystal. As this system has two reflecting mirrors opposite to each other can prevent and partially reflect the laser beam through the reflecting mirror.
After that, the laser beam can pass through the lens where the intensity or concentration of the laser light will be increased and it can remove the material from the surface of the workpiece.
Laser Beam Machining Process Parameters
- No tool, but a laser gun is made by using Ruby Rod as a material.
- Medium: atmospheric air
- Wear Ratio: infinity.
Material Removal Rate of LBM
If a lower amount of power supply is given to the Ruby rod, the intensity of the electromagnetic waves is reduced. Therefore the heat generated in the workpiece is sufficient to melt and join the blades called a laser beam welding operation.
In practical conditions, the wavelength of the laser beam is about 0.4 to 0.6 micrometers only.
It's Applications
- No vacuum is required.
- Mainly used for producing holes in the diesel injection nozzle.
- Also used for producing blind holes, Narrow slots in the workpieces.
Advantages
- No vacuum is required.
- No electrical conductivity of the workpiece is required.
- The machining zone will be seen by a machine operator.
- Because of the high flexibility of the Ruby rod, the zigzag holes can be produced easily with Laser Beam Machining.
Disadvantages
- The power requirement for Laser Beam Machining is very high.
- Highly reactive metals can't be machined
This is a detailed explanation of the Laser Beam Machining Process. If you have any doubts, you can ask us and we can reply in 24 hrs.
More Resources
Electrical Discharge Machining
Electrochemical Machining Process
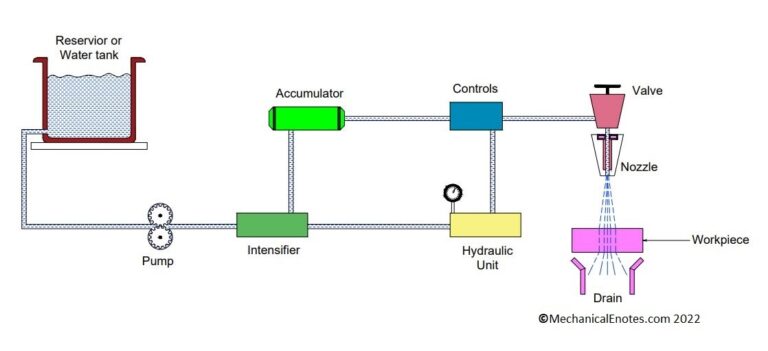
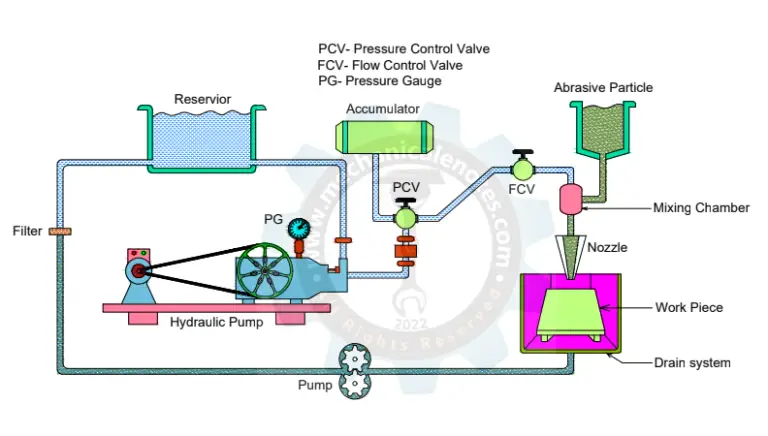
Abrasive waterjet machining Process
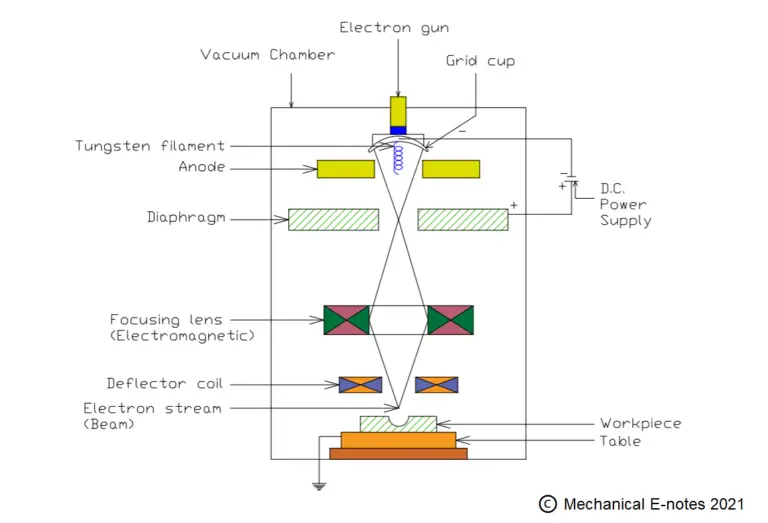
Electron beam machining Process
Machining Process