Injection Moulding Process: Definition, Parts, Working Principle, Defects, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications [PDF]
The Injection Moulding Process is a manufacturing process used for producing parts or components by injecting molten material into the mold cavity. Injection molding can be performed with only one of these materials like glass, plastics, etc. and most commonly, thermoplastic polymers are used.
Note: It is applicable to thermoplastic materials only.
The Injection Moulding Machine was invented by John Wesley Hyatt, patented in 1872.
In the last articles, we had discussed Blow Moulding process whereas in Todays article, we will discuss on the Injection Moulding Process along with its diagram, Parts, Working principle, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications.
Parts of Injection Moulding Machine:
The parts of the Injection Moulding Machine are as follows.
- Reciprocating Screw
- Granules
- hopper
- heater
- Nozzle
- Fixed Pattern
- Mould cavity
- Moving Pattern
- Final Product
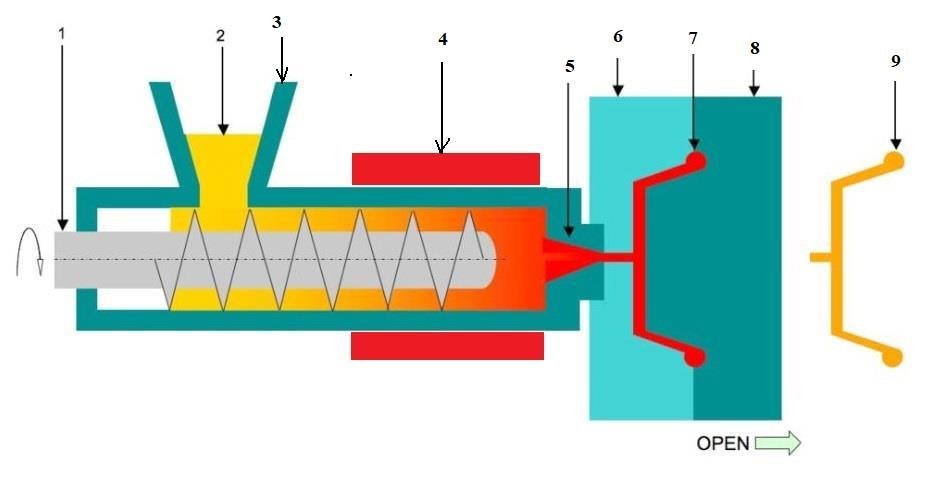
Explanations of the parts of the Injection Moulding Machine are as follows.
1. Reciprocating Screw:
The reciprocating screw rotates by means of a motor and the reciprocating motion is provided by a hydraulic system.
2. Granules:
The thermoplastic granules are to be used in the Injection moulding Machine to create solid components.
3. Hopper:
By the use of a hopper, the plastic granules are to be poured into the molding machine.
4. Heater:
It acts as a source of heat for heating the plastic granules to the molten state.
5. Nozzle:
A nozzle of the required size is to be placed at the end of the heating zone so that, molten material enters from it and acquires the required shape.
6 and 8. Fixed Pattern and Moving Pattern:
These are the two patterns that are placed side by side so as to form a mold. Among the two patterns, one is the fixed pattern and the other is the movable pattern.
During Solidification, the molten metal present in between these patterns can stay for some time and after that, the moving pattern moves aside, and thereby final product is obtained.
7. Mould Cavity:
It is the place where solidification takes place between the fixed pattern and moving pattern and the formation of the component takes place.
9. Final Product:
Thus the final product will be obtained after cooling.
Working Principle of Injection Moulding Machine:
- The reciprocating screw rotates by means of a motor and its reciprocating motion is provided by the hydraulic system.
- The Plastic granules are to be poured into the hopper and they will be passed through the chamber due to the rotation of the screw.
- The Heater heats the granules to their critical temperature.
- The thermoplastic molten liquid is pressurized (by the hydraulic system) outside the Assembly and allowed to travel through a nozzle of small diameter(Dn)[injector] with high velocity and low pressure into the space between the molds.
- The liquid will fill the mold with uniform compaction among the atoms and thereby density is uniform.
- After filling the liquid in the mold, by the cooling process, it will be solidified.
- Any shape and any size of the component can be produced with uniform density.
- Density can be controlled by varying the pressure in the pressure line and thereby production rate is high and wastage is recyclable.
- The component can be produced any number of times till it achieves the required shape.
Note:
- The thermoplastic molten liquid has low viscosity and thereby it can flow easily.
- In the case of thermoset liquids, the viscosity is high and thereby it is difficult to flow from the nozzle and that's the reason, thermoplastics will be used in Injection Moulding Machine.
Injection Molding Defects:
The defects of Injection Molding are as follows.
- Flash
- Short Shots
- Vacuum Voids
- Sink Marks
- Burn Marks
- Weld Lines
- Surface Delamination
- Warping
- Jetting
- Flow Lines
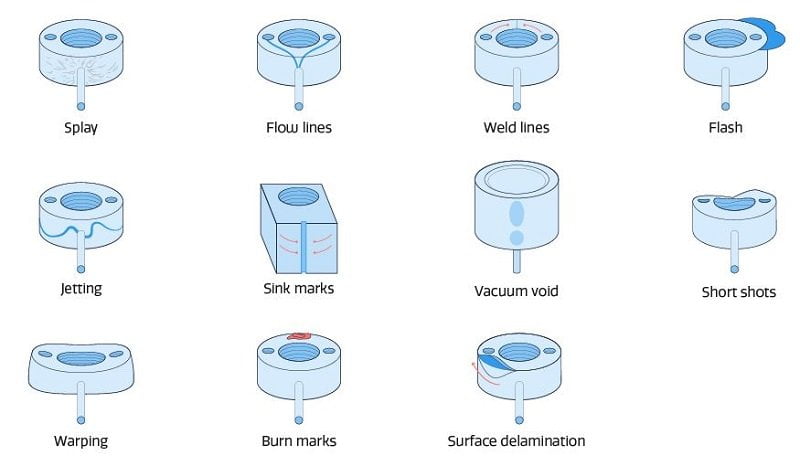
Flash:
When some of the molten plastic escapes from the mold cavity then the defect arises called Flash.
Short Shot:
When the molten plastic does not completely fill the mold cavity due to any of the reasons, then there will be a shortage of molding called a Short shot.
Vacuum Voids:
Vacuum voids are caused due to the uneven solidification between the inner section and surface of the prototype.
Sink Marks:
In Injection molded products, when the shrinkage occurs in the inner portions then small depressions develop in thicker regions called Sink marks.
Burn Marks:
Burn marks are rust-colored and can appear on the surface of Injection molded components.
Weld Lines:
Weld lines can appear on the components when the molten plastics meet each other as they are flowing from two different parts of the mold.
Surface Delamination:
Delamination is nothing but peeled off. It is a condition where thin surface layers appear on the component due to contaminant material. These thin surface layers appear like coatings and can be delaminated i.e. peeled off.
Warping:
In different parts of the mold component, when the shrinkage is uneven then it is called warping.
Jetting:
Due to the difference in speed of the injection of molten metal, the molten plastic sticks to the mold surface only, and this is a failure of not completely solidifying in the mold cavity.
This is the explanation for the defects of the Injection Molding Process.
Injection Moulding Process Advantages:
The advantages of Injection Moulding Process are as follows.
- The design flexibility of plastics is very high and it acts as an advantage to the manufacturers to create various products irrespective of design.
- The scrap is almost zero in this type of machine.
- The color of the products can be managed during the creation of components.
- high production rate.
- Different products can be manufactured by changing the dies of mold.
Injection Moulding Process Disadvantages:
The disadvantages of Injection Molding Process are as follows.
- The machine cost and the tool cost are high.
- The cost for the creation of molds is also higher.
- Larger and complex shapes of the components are difficult to produce with uniform density.
- Difficult to insert metal pieces in the plastic part during the production of the component.
Injection Moulding Process Applications:
The applications of the Injection Moulding Process are as follows.
- Kitchen Products
- Agriculture Products
- Plastic plates
- Industrial Pump Impeller
- Water Cooler Parts
- Medical Products
Watch a Youtube video on the Injection Moulding Process.
This is a detailed explanation of the Injection Moulding Process. If you have any doubts, let us know, we can solve them soon.
Internal Links:
References [External Links]:
- Complete Injection Moulding Process PDF
- Introduction to molding processes | Make