Types of Plastics-Properties of Thermosetting Plastics & Thermoplastics [PDF]

In this article, I will be explaining the different types of Plastics used in our household applications as well as industrial applications in the form of Thermoplastics and Thermosetting Plastics with there Properties.
but before that let we know what is a Plastic?
Plastics:
Plastics are also called as Polymers. They are made up of carbon, hydrogen and sometimes oxygen, chlorine, nitrogen, fluorine, sulfur, phosphorus or silicon.
Majority of the times, polymers are made up of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen only.
- It is a low-density polymer and thereby it possesses lightweight.
- It is Anti-Corrosive in nature.
- It has low strength.
- These chains are called polymers and that is why many plastics begin with “poly,” such as polypropylene, polyethylene, and polystyrene.
Properties of Plastics or Polymers:
Properties of plastics or polymers play a vital role in the field of Mechanical Engineering.
When you want to apply any type of load on a particular member, you need to know its material properties, density, etc. For that, in this article, I am exploring the necessary properties of polymers in a detailed manner.
The Properties of Polymers or plastics which are essential to know for any mechanical engineer are as follows:
Bond:
It possesses a Covalent bond.
Strength:
The strength of the polymer is low when compared with Metals.
Binding Energy:
The formation of C, H&O atoms forms a polymer. The distance between the atoms is more when compared with metals and thereby the Binding energy is low.
Ductility:
It possesses good ductility also.
Conductivity:
The polymers possess bad electrical conductivity because of the absence of free electrons.
Thermal Conductivity:
The polymers possess bad thermal conductivity.
Density:
The polymers possess low density which means that the weight of the polymer is less and this is one of the advantages of polymers.
Corrosiveness:
The polymers are Anti-Corrosive to the environment.
Servicing Temperature:
The servicing temperature of the polymer is 300̊ C.
Hazardous:
It is hazardous and is not environmental friendly.
Recyclability:
The polymers are recyclable in nature.
These are the 11 properties of polymers or plastics which are discussed in a detailed manner. Hope you had got an idea of what plastic is? Now, let's discuss the Classification or Types of Plastics.
Types of Plastics:
They are two types of Plastics:
- Thermoplastics
- Thermoset Plastics or Thermosetting Plastics
Thermoplastics:
By heating the polymer, if it turns soft, then it is called as Thermoplastic material. At room temperature, they are available in the form as Solids.
A thermoplastic is a plastic material that becomes moldable above a specific temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
In this article, I will be explaining the top 10 properties of thermoplastic materials in a detailed manner.

Properties of Thermoplastic Material:
The Properties of Thermoplastic material are as follows.
- By heating the polymer, it turns as soft material.
- It is available in the form of solids at Room temperature.
- It is a recyclable process.
- Thermoplastic material in the form of solid is converted into Thermoplastic material in the form of liquid which is done by the action of heating and the Vice-versa also takes place in another direction.
- Loses Strength: By heating the thermoplastic material it loses its strength.
- Gains strength: By the action of cooling, the thermoplastic material gains strength.
- Shape change: During cooling only, the thermoplastic material changes its shape.
- Temperature: The servicing temperature of thermoplastic material is 150°C.
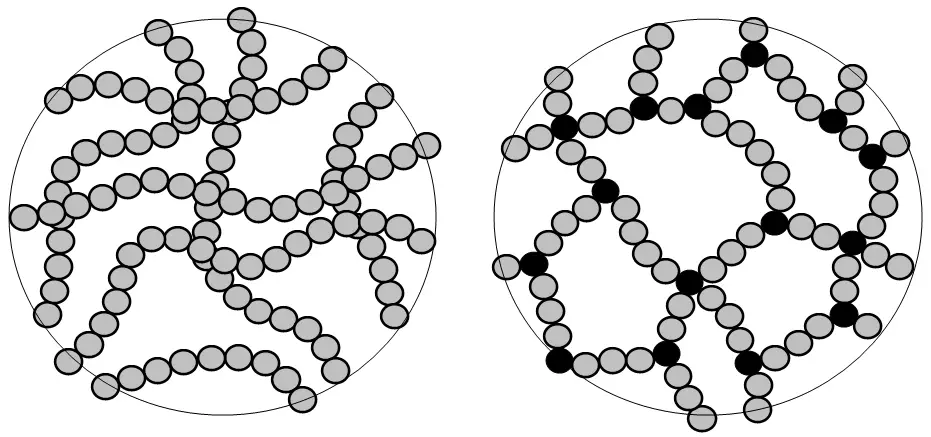
- Structure: The thermoplastic material exhibits Linear structure i.e. -CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-
- The thermoplastic material is hazardous to the environment which is less when compared to the thermoset and rubber.
Thermoplastic Examples:
The examples of Thermoplastics are as follows.
- Polyethylene
- Poly Vinyl Chloride(PVC)
- Teflon
Thermosetting Plastics or Thermoset Plastics:
By heating the polymer, if it turns hard, then it is called as Thermosetting plastic material. At room temperature, they are available in the form as liquids.
Thermosetting plastics or Thermoset plastic are synthetic materials that strengthen during being heated but cannot be successfully remolded or reheated after their initial heat-forming called as Thermoset material.
Properties of a Thermosetting Plastic material:
The Properties of Thermosetting Plastic material are as follows.
- By heating the polymer, it turns as hard material.
- It is available in the form of liquid at Room temperature.
- It is a Non-Recyclable process.
- Thermoset in the form of liquid is converted into Thermoset material in the form of solid which is done by the action of heating and its Vice-versa is not possible.
- Gains strength: By the action of heating, the thermoset plastic material gains strength.
- No change in the strength of the thermosetting plastic is done by the action of cooling.
- Shape change: During heating only, the thermoset material changes its shape.
- Temperature: The servicing temperature of a thermoset plastic material is 300°C.
- Structure: It exhibits a Cyclic structure.
- It is hazardous to the environment which is more when compared to the thermoplastic and less than the rubber.
Thermosetting Plastic Examples:
The examples of Thermosetting plastics are as follows.
- Epoxy
- Silicone
- Polyurethane
- Phenolic
So this is all about types of plastics with their corresponding properties. I hope you liked this paper if so don't forget to share this stuff with your friends, and if you have any doubt do not hesitate to comment down below.
Some FAQ's on Types of Plastics:
What are the two main types of plastics?
What are the 7 types of plastics?
What is a good example of a thermoplastic?
What is a good example of a thermosetting plastics?
and Phenolic.
What are the properties of Thermoplastic polymers?
What are the properties of plastics?
More Resources:
Injection Moulding Process
Blow Moulding Process
Compression Moulding Process
Properties of Metals
References:
- Thermosetting Plastic Definition (Thermoset) - ThoughtCo
- Thermoset vs. Thermoplastics - A Comparison of Materials