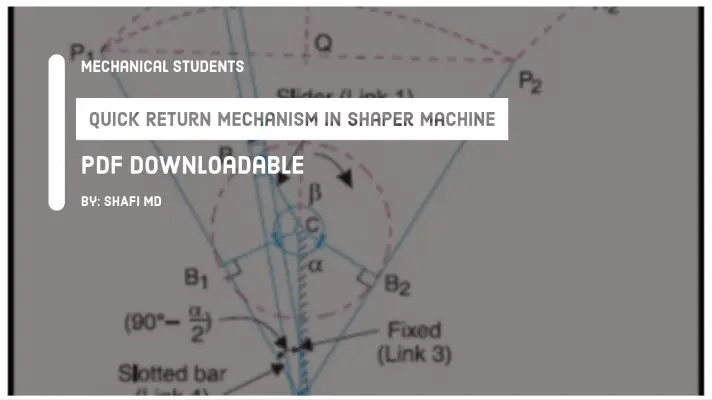
Shaper Machine: Definition, Parts, Working Principle, Types, Operations, Specifications, Applications, Advantages, and Disadvantages [PDF]

Hello Readers, In today's article we will discuss the Shaper Machine in brief along with its Definition, Parts, Types, Working Principle, Operations, Specifications, Applications, Advantages, and Disadvantages. So let's get started.
Definition of Shaper Machine:
Shaper Machine is used to remove the material from the surface of the workpiece by the usage of reciprocating single-point cutting tools basically on horizontal, vertical, and Inclined surfaces. The workpiece is fixed in the machine vice whereas the tool reciprocates on the workpiece by means of ram.
Parts of Shaper Machine with their functions:
The parts of Shaper Machine with their functions are as follows.
- The base of the shaper
- Ram
- Worktable
- Column
- Cross-rail
- Clapper box
- Saddle
- Tool head
The explanation for each part of shaper is as follows.
Base of the Shaper:
This is the strongest part of any type of machine that has the ability to absorb the vibrations produced during machining. So Cast Iron is a suitable material to absorb all the vibrations induced during various types of operations.
Ram:
- Ram carries the Single point cutting tool head and reciprocates on the column guideways.
- The tool head is in the clapper box and the forward stroke is the cutting stroke and the backward stroke is the idle stroke.
Worktable:
This is generally used to hold the machine vice where the workpiece will be held properly for various types of machining operations.
Column:
- It is a box like structure which is mounted on the base.
- Guideways are provided on the top of the column surface for smooth movement of Ram for foraward and return strokes.
- Inside the column, a driving mechanism was present which is used for the running of a machine.
Cross-rail:
It is mounted on the vertical.
Clapperbox:
Clapperbox holds the tool firmly during its cutting stroke and idle stroke.
Saddle:
Saddle is mounted on the cross rail and its cross wise movement can be controlled by the crossfeed screw.
Tool Head:
- A tool head holds the cutting tool and make its movement in vertical and Angular directions.
- A tool head consists of apron and clapper box.
- The Apron consists of a clapper box and it houses the clapper block through a hinge pin.
Working Principle of Shaper Machine:
The working principle of shaper machine is as follows:
Shaping is the operation of removing a layer of material from the flat surface of the workpiece using a reciprocating single-point cutting tool.
In shaping machine, the forward stroke of the tool will be considered as the cutting Stroke in which material removal is taking place from the workpiece and return stroke will be taking as an Idle stroke so that tool is simply moving in backward direction to take the position of the tool.

In the forward stroke/cutting stroke, the tool has to travel at optimum cutting velocity for removing the material from the workpiece whereas in return stroke because it is idle stroke, the tool has to travel at maximum possible velocity to minimize the production time.
The mechanism used in Shaper Machine is Whitworth Quick Return Mechanism. The explanation for this concept was presented under types of Shaper machines.
Types of Shaper Machine:
Let's discuss in detail the types of shaper machine based on various parameters.
1. Based on the type of Driving Mechanism
Based on above type, we have 3 mechanisms which are presented below.
- Crank Type (Mechanism involved is Whitworth Quick Return Mechanism)
- Clapperbox with Rocker Arm
- Ratchet and Pawl mechanism.
Crank Type or Whitworth Quick Return Mechanism:
In shaping machine, the half revolution of crank produces forward stroke and another half revolution of the crank produces return stroke. As per the requirement of a shaper machine, the velocity of forward and return strokes must be different.
To get the different velocities of Ram, it is not possible to have different velocities of the crank in two different half revolutions of the crank.
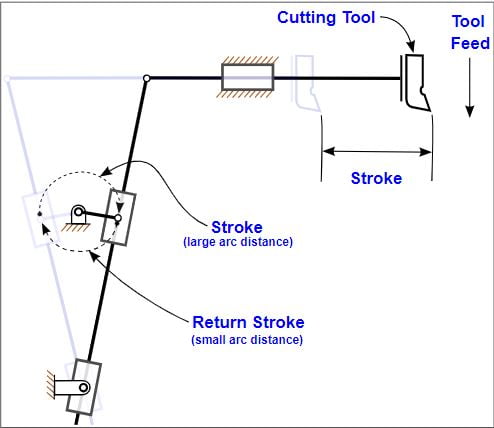
To get the variable velocity of Ram even though the crank is rotating at uniform velocity, a mechanism is used between the Ram and the crank called Whitworth’s quick return mechanism which is one of the inversions of single slider-crank mechanism.
In the total movement of Ram, the maximum velocity occurs at the middle of the Return stroke, the next maximum possible velocity occurs at the end of the Return stroke and the lowest velocity occurs at the beginning of the forward stroke.
During the metal removal process in shaping operation, physician the tool should be in position for removing the material from the workpiece during the cutting stroke. But during the return stroke of the tool, the tool has to be lifted upwards bringing it back without having contact with the workpiece, and again at the beginning of Forwarding stroke/cutting stroke, the tool should take a position for removing the material from the workpiece.
Clapper box with Rocker Arm:
To do this job, a mechanism called a clapper box with the Rocker ARM will be used to minimize the tool wear.
Ratchet and Pawl Mechanism:
The automatic feed required for shaping operation will be given to the workpiece only as an intermittent feed.

The ratchet and pawl mechanism will be used for obtaining the intermittent-feed in shaping operation.
2. Based on the Table Design
- Universal Shaper
- Standard Shaper
Universal Shaper:
Here in this shaper, you can give the feed in all directions like horizontally, vertically, or an inclined plane. The table can also swivel in its own axis.
The universal feature of the machine enables various operations to be performed on it.
Standard Shaper:
It is the most commonly used shaper in the industries as well as educational institutions in which the forward stroke is the cutting stroke and the backward stroke is the idle stroke.
The return stroke is guided by the Whitworth Quick return motion mechanism.
3. Based on the Ram Travel:
- Vertical Shaper
- Horizontal Shaper
Vertical Shaper:
The workpiece is placed on the machine vice which is fixed on the work table.
The workpiece can be movable in longitudinal, cross, and rotational movement.
It is essentially the same thing as of slotting machine. It is widely used for key holes, grooves, and cutting slots.
Horizontal Shaper:
The horizontal shaper is generally used for the production of key-ways, flat surfaces, external grooves, etc.
This is the detailed explanation the Types of Shaper Machine. Let's discuss the operations performed on it.
Operations Performed in Shaper Machine:
The shaper machine operations are as follows.
- Horizontal Cutting
- Vertical Cutting
- Angular Cutting
- Irregular Cutting
Horizontal Cutting Shaper Operation:
Horizontal surfaces are machined by the use of horizontal cutting operation. This can be possible by setting the clapper box slightly inclined or vertical towards the uncut surface.
The tool doesnot drag on the surface of the workpiece rather it can enables the toll to lift automatically.
Vertical Cutting Shaper Operation:
It is used for squaring a block or machining a shoulder. The table is not moved vertically but the feed is given to the tool by rotating the feed screw of the verticla slide.
Angular Cutting Shaper Operation:
An inclined cut is made on the workpiece other than a right angle to the vertical or horizontal planar surface.
Irregular Cutting Shaper Operation:
For irregular cutting, a round nose tool is used for this operation to be carried out.
Specifications of Shaper Machine:
The various specifications of Shaper Machine depends upon the following
- Feed to be given to the workpiece
- Weight of the machine
- The ratio of forward stroke to return stroke
- Angular movement of the work table.
- Power inpit given to the machine.
- Floor space required to setup the machine.
- Types of driving mechanisms involved.
Applications of Shaper Machine:
The applications of Shaper machine are as follows.
- Mostly it will be used to remove the material from the wood or metal workpieces.
- This machine is used for the manufacturing of gear.
- It is used to make keyways in gears or pulleys.
- It is used for machining of dies, punches, etc.
Advantages of Shaper Machine:
The advantages of Shaper Machine are as follows.
- The shaper machine can be very easy to operate.
- The tooling cost will be low.
- The lead time between the components is low.
- The workpiece and the tool can be held in the machine very easily.
Disadvantages of Shaper Machine:
The Disadvantages of Shaper Machine are as follows.
- The cutting speed is low in the case of shaper.
- Only one cutting tool is used in this machine and there is no space for the installation of another tool.
- It can shape change only one workpiece at a time.
- Applicable only for those workpieces(stock) whose length is more than 25cms.
FAQ's:
What is a shaper machine used for?
How many types of shaper machines are there?
What is the function of RAM in shaper machine?
On which principle a Shaper works?
So this is the detailed explanation of Shaper Machine. If you have any doubts, you can feel free to ask and we will reply you as soon as possible.
More Resources:
Difference between Shaper and Planer Machine
Drilling machine
Milling Machine
Lathe Machine
Grinding Machine
Planer Machine
References [External Links]:
- Shaper Machine working principle, mechanism, Surface machining operation- Youtube
- Shaping, Planing and Slotting Operations- JNKVV [PDF]