Lathe Machine: Definition, Parts, Accessories, Types, Working Principle, Operations, Specifications, Applications, Advantages, and Disadvantages [PDF]
Lathe Machine is used in all the engineering applications and also in the college Workshops. Lathe machine is used to perform all the basic operations such as drilling, cutting, tapping, turning, etc. with the help of different tools placed in the work environment.
Here in this article, I am going to discuss the Lathe Machine along with its Definition, Parts, Types, Working Principle, Operations, Specifications, Applications, Advantages, and Disadvantages.
Definition of Lathe Machine:
Lathe Machine is a machine tool that uses a cutting tool for removing the material from the surface of the workpiece which is held in the chuck for holding the workpiece and feed was provided by the tool on to the workpiece for the removal of material. It is the most versatile and widely used machine in industries, institutions, etc.
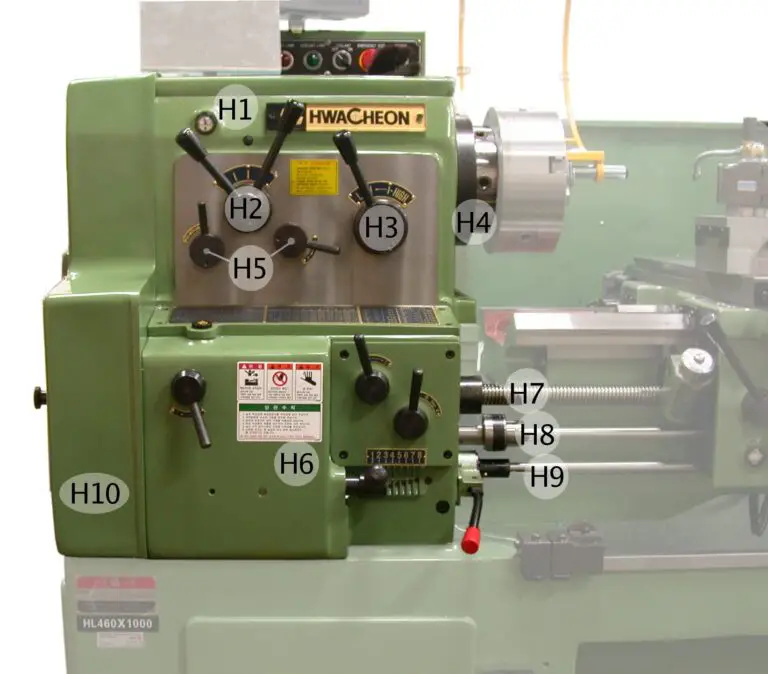
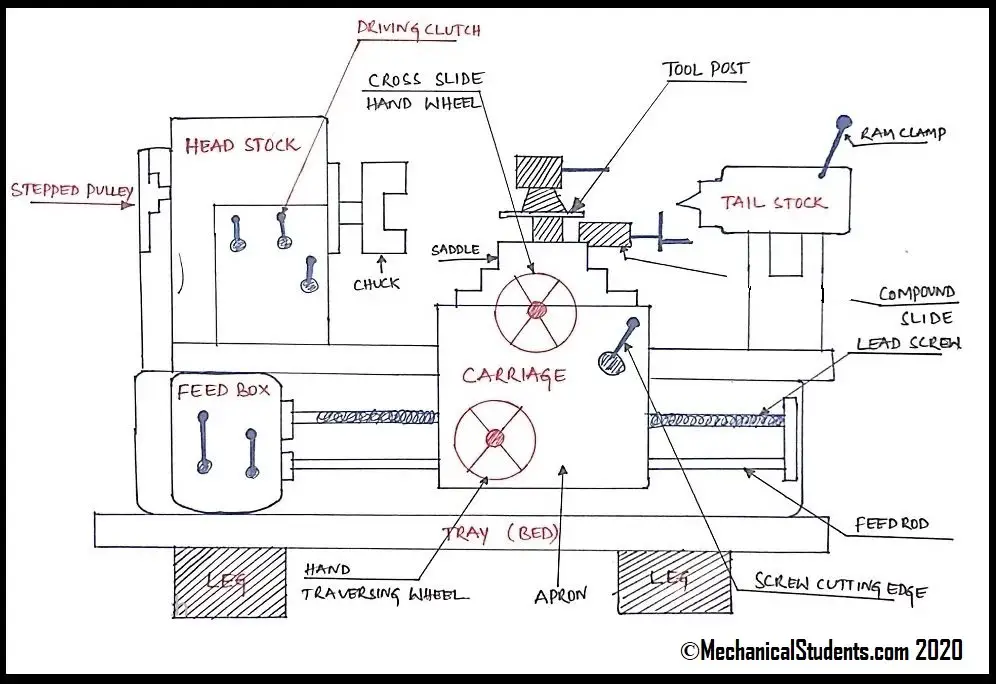
Now lets discuss the parts of lathe machine along with its accessories with the help of a Line diagram.
Line Diagram of Lathe Machine:
The Line Diagram of Lathe Machine is shown below.
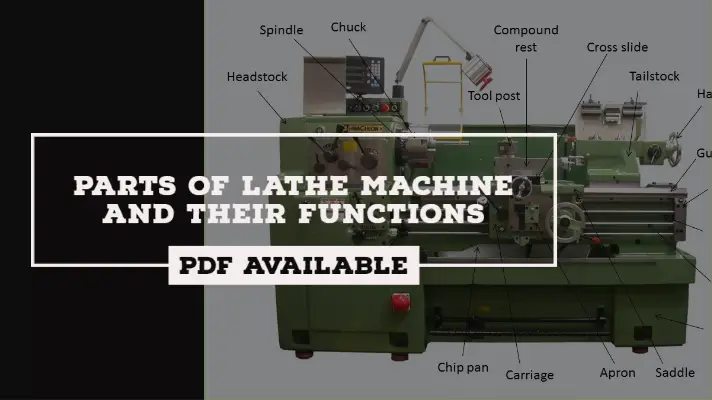
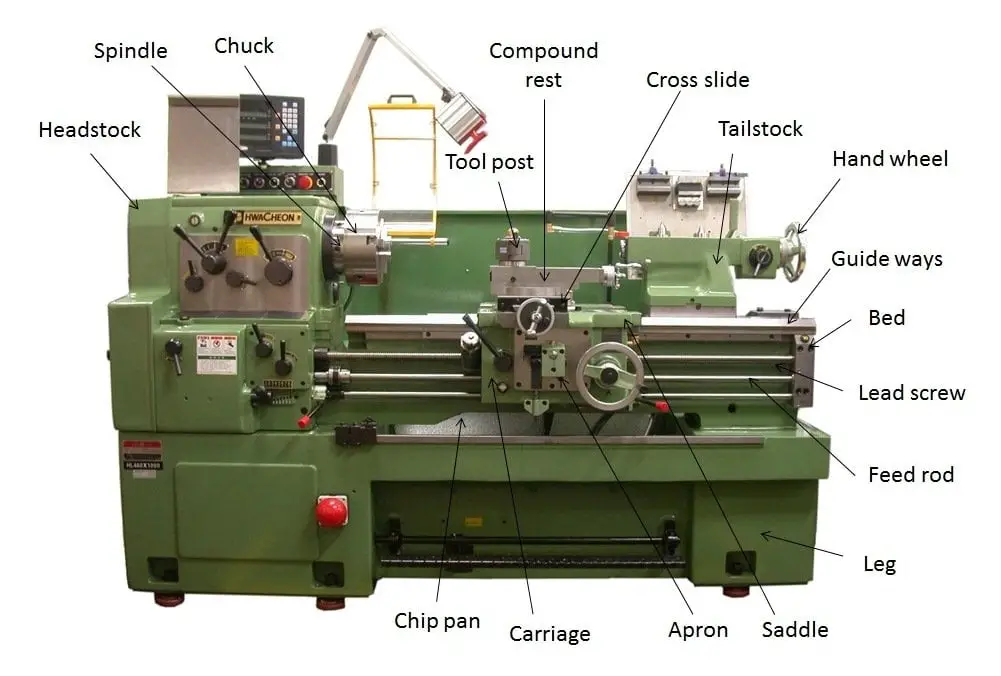
Parts of Lathe Machine:
The Parts of the lathe machine are as follows.
- Bed
- Lead Screw
- Guideways
- Prime mover
- Transmission system
- Headstock
- Spindle
- Chuck
- Feed Gearbox
- Thread Chasing Dial
- Split nut
- Carriage
- Slideways with saddle
- Compound rest
- Toolpost
- Tailstock
- Quill
The detailed explanation of all the parts is as follows.
Bed:
- It should be rigid enough to withstand for the forces acting during machining and self-weight of the workpiece.
Lead Screw:
- It is used for converting rotational movement into linear movement.
- The material of the lead screw must be selected such that it should have high wear resistance.
Guideways:
- They are guiding the moving parts in a machine tool. They act as a mediator for transmitting forces to the bed of a machine tool.
Prime Mover:
- Whatever the energy required for performing the machining operation is obtained from Prime mover.
Transmission System:
- Even though prime mover is rotating at only one particular RPM, to get the different RPM of the spindle on a job during machining of different sizes of the components at different velocities, it is required to use mechanical transmission system between the prime mover and the spindle.
Head Stock:
The headstock is acting as a house for keeping some of the parts like transmission system, Prime mover, etc. and it also acts as a support for supporting the components at one side.
Spindle:
- It is the hollow shaft used for transmitting power from the transmission system to the workpiece.
- It also supports the longer length of the workpiece during machining.
Chuck:
It is a work holding device used for holding the workpiece at one end.
Chuck Is classified into two types:
- 3-Jaw chuck: It is used for cylindrical and circular shape jobs
- 4-Jaw chuck: It is used for non-circular jobs.
Feed Gear Box:
It is used for transmitting power from spindle to the lead screw at different speeds.
Thread Chasing Dial (TCD):
It is used in thread cutting operation for reducing multiples start of the thread with multiple cuts.
Split nut:
Split nut with the lead screw will be used for converting rotational movement into linear movement.
Carriage:
The carriage is the device used for carrying a moving part in a lathe machine globally.
Slideways with Saddle:
It is used for moving the tool locally.
Compound Rest:
It is used for rotating the tool to perform the taper turning operation.
Tool Post:
It is the device which is used for holding the tool.
Tailstock:
It is used for supporting the workpiece at the other end.
Quill:
For localized movement of the Dead Centre, Quill will be used.
In general, the axis of the Dead Centre will be coinciding with the axis of the spindle or chuck but sometimes to perform the taper turning operation, the dead center can be absent by moving the tailstock in the transverse direction.
Accessories of Lathe Machine:
The Lathe Machine Accessories are as follows.
- Steady rest
- Catch plate or Dog plate
- Face Plate
- Mandrel
- Follower rest
Types of Lathe Machine:
The various types of lathe machines are as follows.
- Bench Lathe
- Speed Lathe
- Tool Room Lathe
- Capstan and Turret Lathe
- Center or Engine Lathe
- Automatic Lathe
- Special Purpose
- CNC Lathe Machine
Lets study all the types of lathe in a detailed way along with its figure.
Bench Lathe Machine:
It is a small lathe machine which is mounted on the workbench that has all the parts of speed lathe and engine lathe.
Speed Lathe Machines:

As the name speed indicates that the headstock spindle is rotating with high speed. This machine does not have any feed mechanism like engine lathe and the speed ranges from 1200 RPM to 3600 RPM.
It is used in polishing, spinning, centering and machining of wood.
Tool Room Lathe:

This machine works at a speed of 2500 rpm.
It is mainly used in die gauges, grindings, working on the tool where high accuracy is maintained.
Capstan and Turret Lathe:

It is an advanced version of Engien lathe machine and is used for mass production.
Instead of Tailstock, these machines are provided by hexagonal turret head in which multiple operations can be performed without changing the tool in a sequence.
The Capstan and Turret lathes are applicable only for larger components.
Less skilled operators also can do the job on this Capstan and Turret lathe.
Center or Engine Lathe:

This type of Center lathe machine was the basic machine and it will be used in many of the workshops too.
Various types of lathe operations can be performed on this machine like turning, taper turning, grooving, threading, knurling etc.
To do any operation on the lathe machine, the headstock is fixed and the tailstock can be movable depending upon the workpiece.
If the workpiece is small then there is no need of Tailstock and if the workpiece is large, then only there is a need of it to support the workpiece.
Automatic Lathe:

As the name indicates that it works its operations automatically, that is there is no need of operator during the performance of experiment.
Depending upon the operation, it can changes its tool automatically and there is no need to change the tool one operation after the other manually.
This type of lathes are applicable for heavy duty type and high speed.
The automatic lathe does various operations and can be applicable for mass productions.
Due to this automatic machines, a single operator can handles more than one machine effectievely.
Special Purpose Lathe:

As the name indicates that it is a Special Purpose lathe, which means that it can perform only special operations which are not performed by standard machines.
The Special prurpose lathe are applicable for heavy duty production.
Some of the special purpose lathes include Wheel lathes, Multi Spindle lathes, Vertical lathes, T-lathe, Tracer lathes, etc.
CNC Lathe Machine:
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control.

The components produced by the CNC lathe are having high dimensional accuracy. No manual operators are required. Just a program is written in the form of G-Codes and M-Codes to run various operations on the components.
High accuracy is obtained compared to conventional lathe machine.
These are the various types of Lathe machines. Now lets see the working principle of it in a detailed way.
Working Principle of Lathe Machine:
The basic function of the Lathe machine is to remove the material from the surface of the workpiece by the usage of cutting tools providing the necessary amount of feed and this can be done by placing the workpiece in the chuck which rotates with the help of a motor.
For Circular workpieces, Three Jaw Chuck will be used whereas for the Rectangular/Square workpieces, Four Jaw Chuck will be used for better stability.
The headstock consists of a Power transmission system where the action will be provided by engaging with suitable levers. It also consists of a chuck where it can hold the workpiece firmly.
For smaller workpieces, there is no need for Tailstock whereas, for larger workpieces/specimens, there is a need for it for supporting such that the workpiece can be fixed firmly without any vibrations during machining.
The tool is placed in the Toolpost and is perpendicular to the workpiece for removing the material from the circumference of the workpiece such that the diameter can be reduced.
When the power supply is given, the chuck starts rotating with the help of a power transmission system and the workpiece placed inside the chuck also rotates. With respect to the workpiece, the Tailstock is used. Now w.r.t. the type of operation, the tool is placed either perpendicular or angular to the workpiece.
For Turning operation, the workpiece and the tool are perpendicular to each other whereas, in the Taper turning operation, the tool and the workpiece are inclined to each other.
In this way, by giving the necessary amount of feed, material removal takes place. The speed can be increased by the levers in the Headstock by changing them w.r.t. the material removal.
The lathe machine can be performed Manually or Automatically. In small scale industries, we can go with manual operation whereas, in large scale industries, CNC machines are used where they can run automatically with the help of the program.
This is the detailed explanation on the Working of Lathe machine.
Lathe Machine Operations:
The operations which are performed on the lathe machine are called lathe operations and are as follows.
- Turning
- Facing
- Thread Cutting
- Drilling
- Boring
- Counterboring
- Countersinking
- Reaming
- Trepanning
- Spot Facing
- Honing
The detailed explanation of the above lathe operations was as follows.
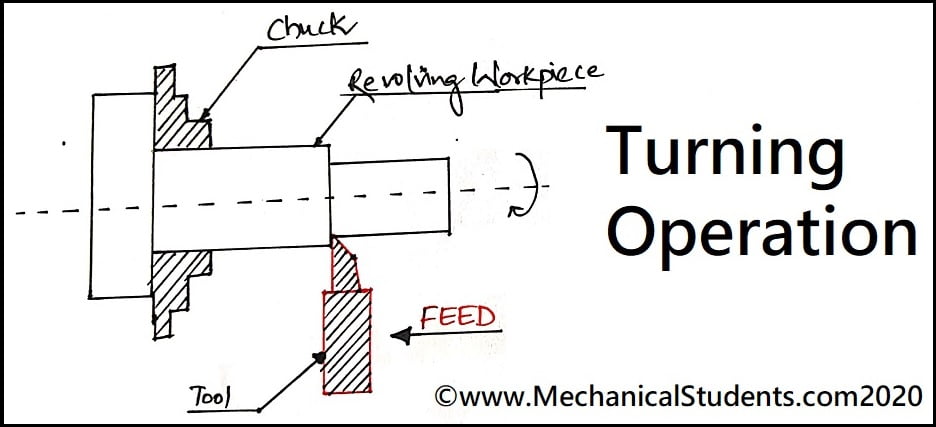
Turning:
The process of removing material from the circumference of the workpiece is called Turning Operation.
Step Turning Operation:
If the material is removed in terms of steps from the surface of the workpiece then it is called a Step turning operation.
Taper Turning Operation:
The turning operation used for producing tapered components is called a taper turning operation.
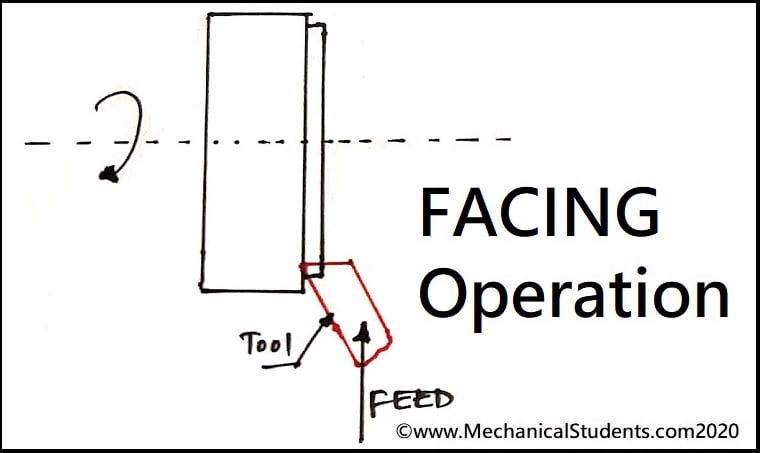
Facing or Face Turning Operation:
The turning operation used for reducing the length of the component by removing the material from the face of the workpiece called a face turning operation.
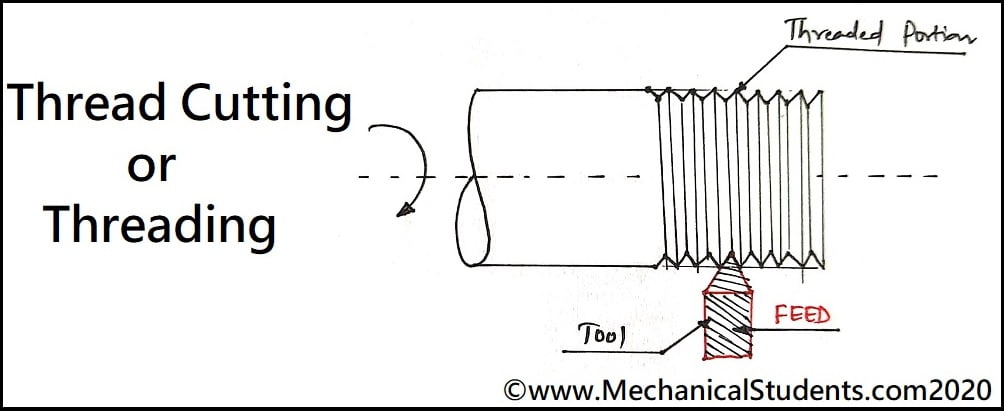
Thread Cutting:
The turning operation used for producing the threads on the surface of components is called as thread cutting operation.
Drilling Operation:
It is an operation used for producing holes in the components.
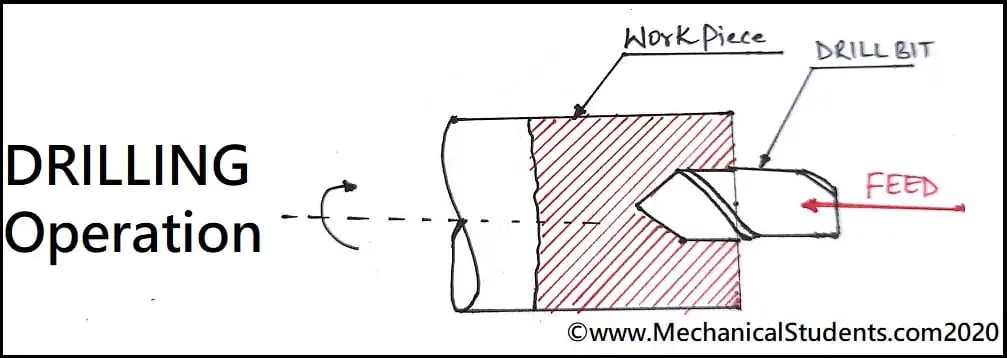
Boring Operation:
It is an inter turning operation used for enlarging the existing hole by some amount called boring operation.
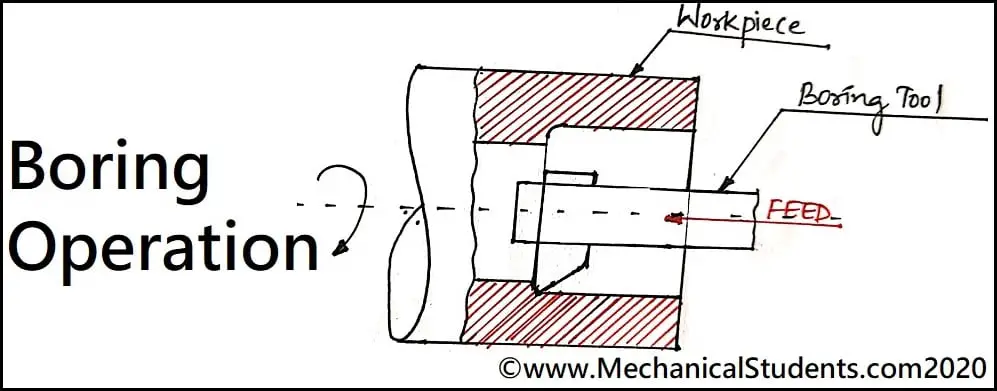
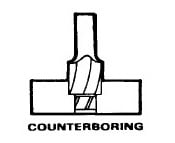
Counterboring Operation:
The Boring operation used for enlarging the end of the hole is called as counterboring.
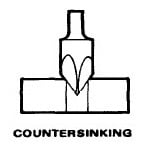
Counter Sinking Operation:
Conical enlargement of an end of the hole is called a countersinking Operation.
Reaming:
Reaming is similar to drilling operation used for removing a small amount of material for sizing and finishing of the hole to get exact dimensions.
The maximum size of the hole produced by using in stages method of drilling operation is up to 50 mm only.
Trepanning Operation:
It is the operation of producing large size holes without drilling operation called the Trepanning.
Spot Facing:
Making the surface of the hole flat and Square for the proper sitting of the bolt head or nut is called Spot facing Operation.
Spot facing is done by using an end mill cutter with a drilling machine.
Honing Operation:
Honing is the finishing operation used for producing an excellent surface finish on the holes.
Knurling Operation:
It is a pattern of straight, crossed or angled lines on the surface of the tool which is pressed against the workpiece such that it can forms an impression on the surface of workpiece. The holding of the workpiece will be better by this operation.
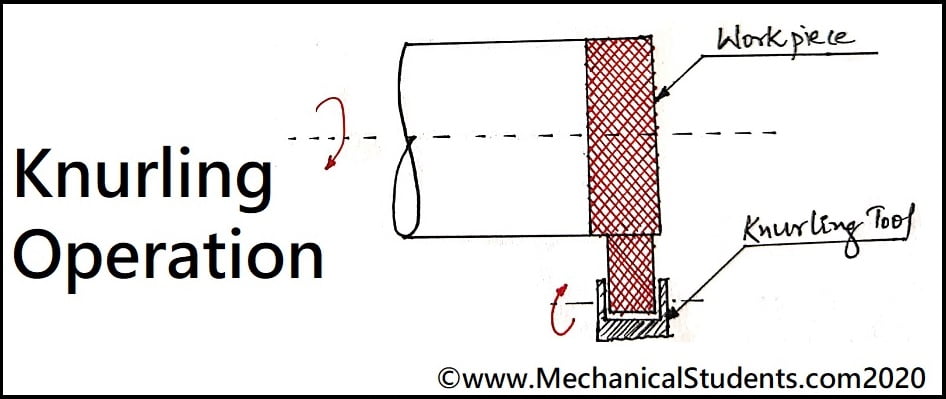
These are the different lathe Operations performed on the lathe machine with high dedication and accuracy.
Lathe Machine Specifications:
The specifications of Lathe Machine are as follows.
- The distance (L) between the two centers-750 to 800 mm.
- The diameter of Chuck is 160mm.
- The guide length of carriage is 350-365 mm.
- The width of lathe bed is 260mm
- The pitch of the lead screw is 6mm.
- The Length, width, and height of a lathe are 2000, 1000, and 1400 mm.
- The spindle bore is 35 mm.
Applications of Lathe Machine:
The Applications of Lathe Machine are as follows.
- It is mainly used in industries to shape change the metal components as well as wooden components by machining lathe and wood lathe.
- It is used in Thermal spraying and Metal spinning.
- A CNC lathe finds its applications in the fields of Aerospace, Automotive, Medical, Textile, industries of automobiles, etc.
- The lathe is also used in various institutions for doing lab experiments.
Advantages of Lathe Machine:
The Advantages of Lathe Machine are as follows.
- The accuracy is very high in the case of CNC lathes compared to Normal Machining lathes.
- The flow of production is more.
- It requires few operators in a manual lathe.
- The machining in the lathe and CNC lathe was very fast.
- Due to the CNC lathes, the time to carry out the experiment was very less than conventional machines.
- The lead time will be very less.
Disadvantages of Lathe Machine:
The limitations of lathe machine are as follows.
- If the maintenance was not good then it results in the damage of machine parts by not using lubrication.
- The tool also wears out fastly, if the operator is not good to handle the experiment.
- Due to the cutting speeds, the odor in the environment will be very high which impacts the health also.
- These machines were more expensive than other conventional machines because you can do almost all operations on the lathe.
Some FAQ's on this Topic:
What is the use of Lead Screw in Lathe machine?
How do lathe machines work?
How much does a lathe machine cost?
Medium Duty Cone Pulley Lathe Machine, Rs. 92,000/-
Heavy Duty Cone Pulley Lathe Machine, Rs. 178,000/-
What are types of lathe machine?
What are the parts of Lathe Machine?
Which tool is used in lathe machine?
More Resources:
Radial Drilling Machine
Milling Machine
Drilling Machine
Surface Grinding Machine
NC Machine
CNC Machine
References [External Links]:
- MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS
- Chapter 2: Lathe Machine – Manufacturing Processes 4-5