Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): Parts, Working Principle, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications [PDF]
Electrical Discharge Machining is also known as Spark Machining or Spark Eroding process.
As you know that there are various Non-traditional machining methods and EDM is one of them and the rest are presented below.
- Ultrasonic Machining Process
- Electrochemical Machining Process
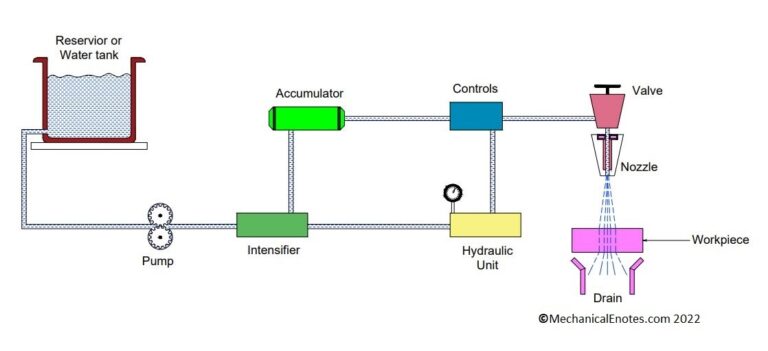
- Water Jet Machining
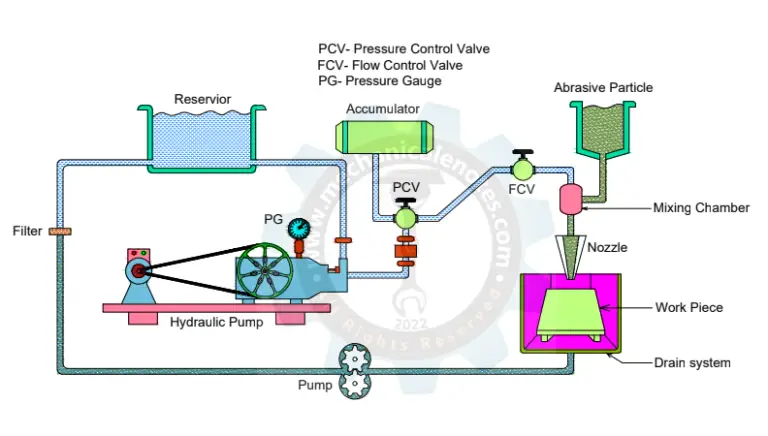
- Abrasive Water Jet Machining
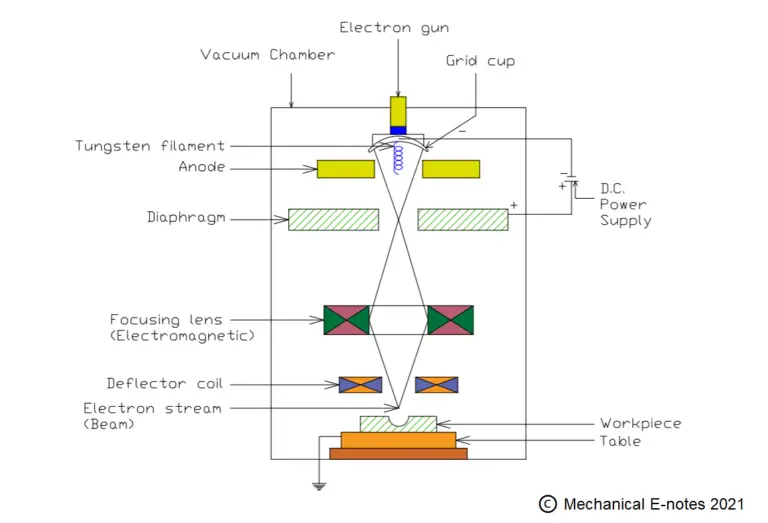
- Electron Beam Machining Process
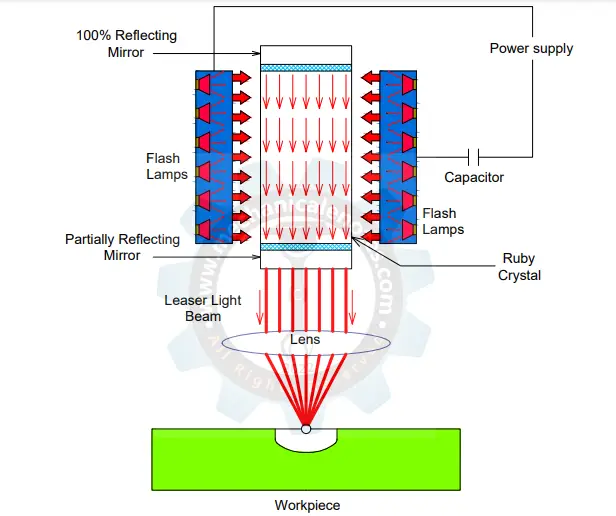
- Laser Beam Machining Process
- Electrical Discharge Machining Process
Lets dive into the Electrical Discharge Machining Process in detail...
Electrical Discharge Machining Definition:
It is a process in which electrical energy is used to generate the Spark between the tool and workpiece submerged under the dielectric medium so that material removal takes place from the surface of the workpiece by local melting or Vaporization called as Electric Discharge Machining.
Electrical Discharge Machining Diagram:
The diagram of Electrical Discharge Machining is shown below.
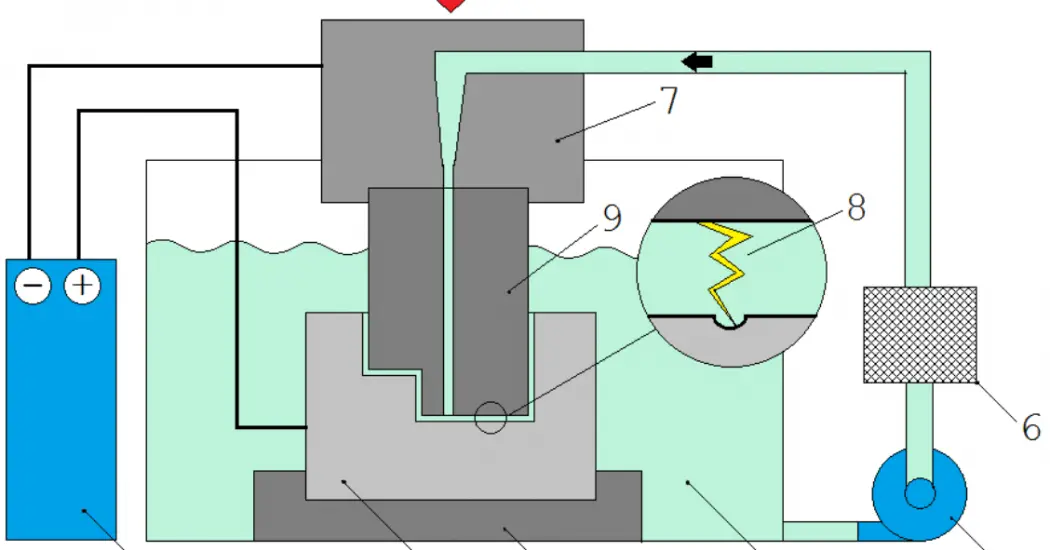
Parts of Electrical Discharge Machining:
The Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) setup consists of
- Pulse Generator (Power Supply)
- Workpiece
- Fixture
- Dielectric Fluid
- Pump
- Filter
- Tool Holder
- Spark generation
- Tool
An Explanation for the parts of Electrical Discharge Machining:
An Explanation for the parts of Electrical Discharge Machining is as follows.
1.Pulse Generator (Power Supply):
The power supply is given to the EDM process i.e. Negative terminal is given to the tool and a Positive terminal is given to the workpiece.
2.Workpiece
The workpiece is fixed in the dielectric container using a fixture and is given the positive terminal of the power supply.
3.Fixture:
The fixture is used to hold the workpiece properly in a dielectric container.
4.Dielectric Fluid:
The workpiece and the tool are separated using dielectric fluid and an optimum gap is maintained between them.
At normal conditions, the dielectric fluid acts as an insulator. In this sense, no electrical conductivity is taking place.
But, by an increase of high pressure, the dielectric fluid ionizes into Negative and Positive Ions and now it is ready to conduction.
Properties of the Dielectric Fluid/Medium:
- Low viscosity.
- Remain electrically non-conductive up to the desired voltage breakdown takes place.
- It can act as a good cooling medium.
- It can carry away all the metal particles produced during the spark erosion.
Electrolyte used:
Kerosene acts as a Dielectric Fluid in Electrical Discharge Machining process.
Optimum Gap:
The Optimum gap between the tool and the workpiece is 0.03 mm.
Voltage - 70V
5.Pump:
A pump is used to send the dieclectric fluid from the base of the container to the tool and workpiece such that more MRR takes place.
6.Filter:
A filter was situated just above the pump to remove any irregularities or dust particles present in the diectric medium.
7.Tool Holder:
It is used to hold the tool properly.
8.Spark generation:
A spark is geerated between the tool and workpiece in the presence of dielectric medium and thereby material removal takes place from the surface of workpiece.
9.Tool:
The tool used in the Electric Discharge Machining process is either Copper or Tungsten or Copper-Tungsten Alloy.
Properties Possessed by the Tool:
It must possess high
- Melting Point
- Electrical Conductivity.
MRR (Material Removal Rate):
Out of all the non-traditional machining methods, the Electric Discharge Machining will remove more material. In this sense, the MRR is higher for EDM.
This is the explanation for the parts of EDM. Let's dive into the working of it...
Working Principle of Electrical Discharge Machining Process:
The workpiece is fixed in the dielectric container using a fixture.
The tool is fed up by the Servo Feed Unit which can move downward in a vertical direction.
The power supply is given to the electrical discharge machining process i.e. Positive terminal is given to the workpiece and a Negative terminal is given to the tool.
The tool and workpiece are separated using dielectric fluid and an optimum gap is maintained between them.
As stated above, that at normal conditions, the dielectric fluid acts as an insulator. In this sense, no electrical conductivity is taking place.
But, by an increase of high pressure, the dielectric fluid ionizes into Negative and Positive Ions.
The positive ions are attracted to negative ions and negative ions are attracted to positive ions and thereby the heat is generated.
When positive and negative ions collide with each other then the spark is generated between the tool and workpiece which can remove the material from the surface of the workpiece.
When there is no spark in the container, then the dielectric fluid again turns as an insulator
The same procedure is repeated to remove the material from the surface of the workpiece.
This is a detailed explanation of the Electrical Discharge Machining process along with the basic terms and working.
Advantages of EDM:
These are some advantages of using Electrical Discharge Machining:
- The machining process does not depend on the mechanical properties of the workpiece.
- No residual stresses will be generated because no forces are acting.
- The deeper hole is possible to produce (L/D) up to 20.
- Out of all the non-traditional machining methods, EDM is the method with higher Material Removal Rate (MRR).
- The surface finish is better due to melting and vaporization.
Limitations of EDM:
However, EDM has some limitations too, here are those:
- Workpiece material must be electrically conductive.
- Perfect square corner holes are not possible to produce.
- Hardening of the workpiece is taking place near to the hole.
Applications of EDM:
Here are some applications of Electrical Discharge Machining:
- It is used for producing hole size less than 0.1 mm
- Used for die sinking or die manufacturing.
- holes in the air brakes or Pneumatic Brakes were done by an electrical discharge machining process.
So this is all about Electrical Discharge Machining, I hope you liked this paper, if so then don't forget to share your thoughts on the comment section, and do not forget to share this stuff with your friends.
Watch EDM: