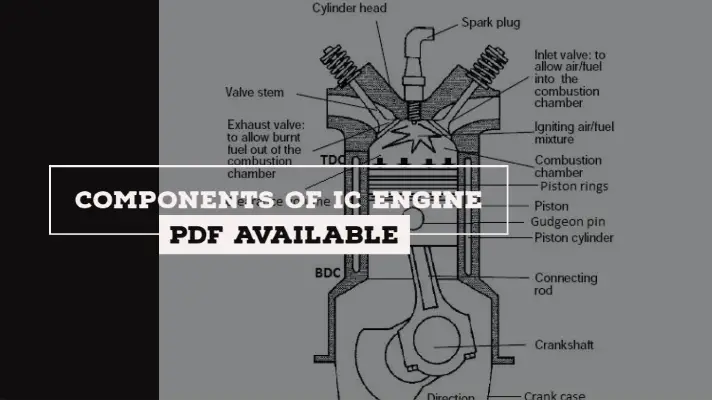
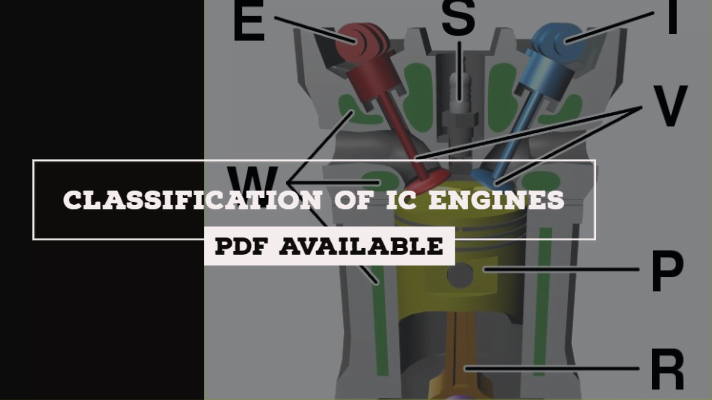
Classification of IC Engines [PDF]
In the previous session, we had discussed SI Engine & Otto Cycle, Diesel Cycle, Carnot cycle etc. Whereas In today's article, we will discuss about Classification of IC Engines in detailed.
But before that, we need to know about Heat Engines and its basic Classification.
Definition of Heat Engine:
Any type of engine or machine which derives heat energy from the combustion of fuel or any other sources and converts that energy into mechanical work is termed as a heat engine.
Classification of Heat Engines:
Heat engines are classified into two types.
- External Combustion Engine and
- Internal Combustion Engine
The detailed explanation of the above engines is as follows.
External Combustion Engine:
In this case, combustion of fuel takes place outside of the cylinder as in the case of steam engines, where the heat of combustion is employed to generate steam which is used to move a piston in a cylinder.
Ex: The steam turbine and closed-cycle gas turbine.
These engines are generally used for driving locomotives, ships, generation of electric power etc.
Internal Combustion Engine:
In this case, combustion of the fuel occurs within the cylinder of the engine. The IC Engines group includes engines employing mixture of combustible gases and air known as gas engines.
Those using lighter liquid fuel are known as Petrol Engines and those using heavier liquid fuels are known as oil compression ignition or diesel engines.
Combustion: Burning of the fuel (Air Fuel Mixture) is known as Combustion.
Now lets discuss about Classification of IC Engines...
Classification of IC Engines:
IC Engines stands for Internal Combustion Engines which can have :
- Higher Overall Efficiency
- Low Weight to Power Ratio
- Requires less space and
- has Greater Mechanical Simplicity.
The Classification of IC Engines was dependent upon its functional characteristics.
- Basic Engine Design
- A cycle of Operation(Working Cycle)
- Number of Strokes
- Type of Ignition
- Method of Cooling
- Method of Charging
- No. of Cylinders
- Cylinder Arrangement or Type of cylinder
- Fuel used
- Method of Fuel Supply
- Engine Speed
- Applications
The Detailed classification of IC Engines was presented below.
Basic Engine Design:
- Reciprocating Engines
- Rotary Engines (Wankel Engine)
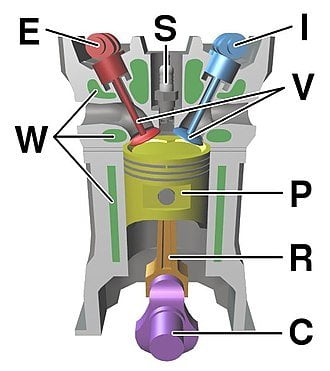

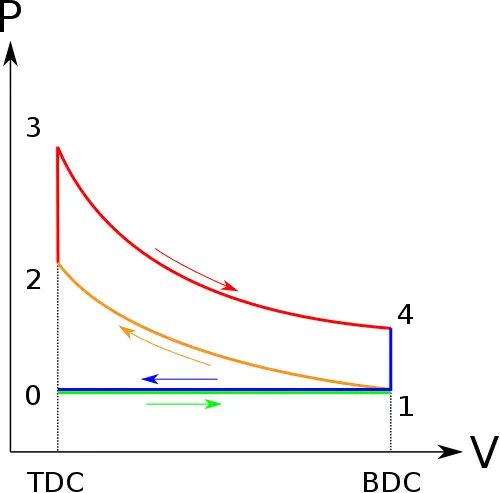
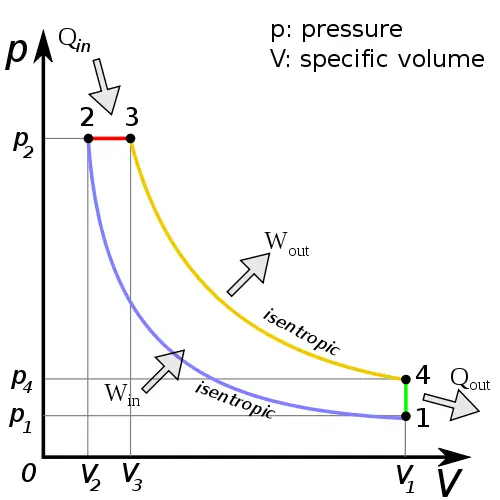
Cycle of Operation (Working Cycle):
- Engines working on OTTO Cycle (SI Engines)
- Engines working on DIESEL Cycle (CI Engines)
Number of Strokes:
- Four-Stroke Engines
- Two-Stroke Engines
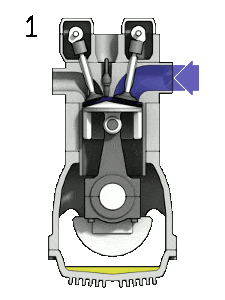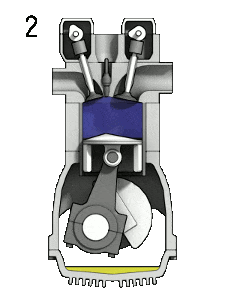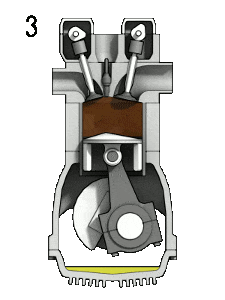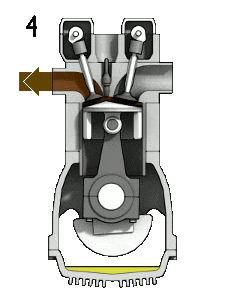
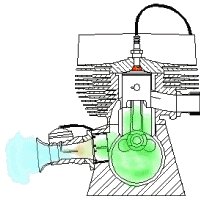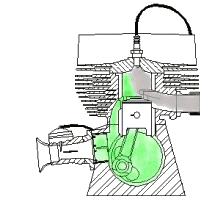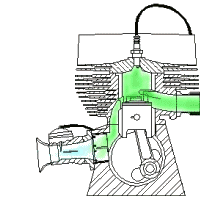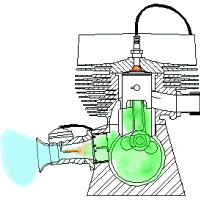
Based On Type of Ignition:
- Spark Ignition Engines: Spark Is Generated through an External Source
- Compression-Ignition Engines: Air Is Heated to a Sufficiently High Temperature Because of High Compression Ratio
Method of Cooling:
- Cooling Is Essential for the Satisfactory and Healthy Working Of the Engine (Otherwise Results In Engine Seizing)
Two Types of Engine Cooling In Practice i.e. Air-cooled Engine and Water Cooled Engine
Classification Based On Method of Charging
a. Naturally Aspirated Engines
Admission of Fuel-air Mixture at Near Atmospheric Pressure
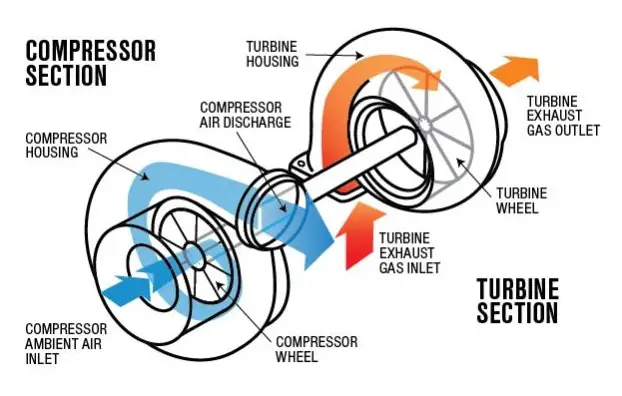
b. Super-charged Engines
Admission of Fuel- Air Mixture Under Pressure (Above Atmospheric)
No. of Cylinders:
- Single Cylinder
- Multi-Cylinder
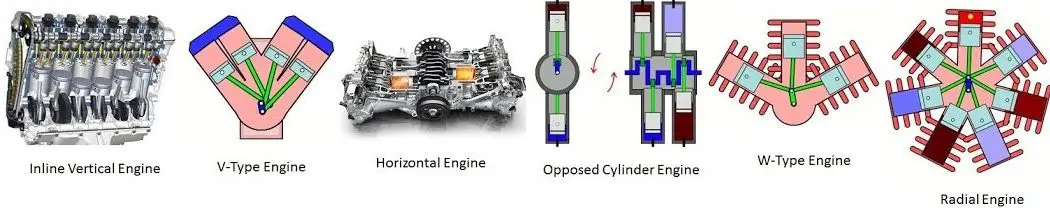
Type Of Cylinder Arrangements
- Inline Vertical Engine
- V- Type Engine
- Horizontal Engine
- Opposed Cylinder Engine
- W-type Engine
- Radial Engine
Fuel used :
- Gasoline or Petrol Engines
- Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) Engines
- Diesel Engines
Fuel Supply:
- Carbureted type- Fuel supplied through Carburetor
- Injection type-Fuel injected into the cylinder just before Ignition.
Classification Based On Engine Speed
- Low Speed - up to 500 rpm
- Medium Speed – 500 to 1000 rpm
- High Speed - above 1000 rpm
Classification Based On Applications:
- Motor cycle engine
- Automobiles
- Earth Movers
- Locomotive engine
- Marine engine
- Aero engine
- Prime movers for Electric Generators
This is the complete Classification of IC Engines in detailed. If you have any doubt feel free to ask from the comments section.
More Resources:
Cooling Systems in IC Engines
Lubrication Systems
Ignition System-Battery, Electronic and Magneto
Supercharger VS Turbocharger
References [External Links]:
- Internal Combustion Engine Basics | Department of Energy
- internal-combustion engine | Definition & Facts | Britannica
Media Credits:
- Image 1: By User:Wapcaplet - Own work, made with Blender, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=182044
- Image 2: CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=155625
- Image 3: By Luc1992 - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=41130463
- Image 4: By Tokino (original PNG file)MaxDZ8 (conversion to SVG) - Own work, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1924714
- Image 5: By Zephyris - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=10896588
- Image 6: By derivative work:Turbojet (talk)Arbeitsweise_Zweitakt.gif: Topory, A7N8X - Arbeitsweise_Zweitakt.gif, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=4410942