Types of Axles: Front Axle, Rear Axle and Stub Axle [PDF]

An Axle is a shaft for rotating wheels of the vehicle. One end of the axle is connected to the differential via Sun gear and the other end is connected to the wheels. In the last article, we had discussed Synchromesh Gearbox and Epicyclic Gearbox which comes under manual and Automatic Transmissions. In today's class, we can discuss on Types of Axles in a detailed way.
In majority of the cases, the axles are fixed to the wheels and rotate around them.
In some of the cases, the axles might be fixed to the vehicles and only wheels can rotate on the axles and this can be possible by placing bearings on the axle, and the wheels are mounted on the bearings for the movement of the vehicle.
Let’s discuss the Types of Axles in detail.
Types of Axles:
There are 3 types of axles.
- Front Axle
- Rear Axle
- Stub Axle
Let’s discuss in detail about the Types of Axles mentioned.
Front Axle:
Front wheels of the automobile are mounted on front axles and the functions of the front axle are:
- Supporting the weight of the front part of the automobile.
- Absorbing shocks transmitted due to the uneven surface of the road.
- Facilitating Steering mechanism etc.

The front axle is made up of a circular or elliptical section at the ends and I-section in the middle portion.
This cross-section of the axle withstands bending loads due to the weight of the vehicle and torque applied due to braking.
Now let’s discuss types of front axles in detail.
Types of Front Axles:
There are two types of front axles:
- Dead front axle
- Line front axle.
Dead Front Axle:
- The Dead Front Axles are those axles, which do not rotate and these axles have sufficient strength and rigidity to take the weight of the vehicle.
- The ends of the front axle are designed to accommodate the stub axles.
Live Front Axle:
They are used to transmit the power from Gearbox to front wheels.
Rear Axle:
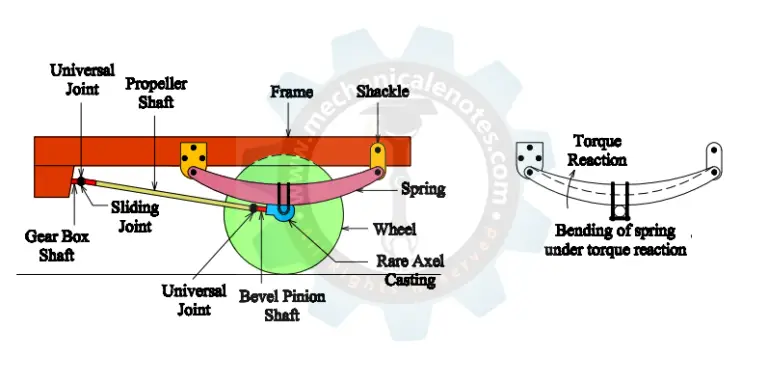
Rear-axle is the half shaft that is used to transmit the power from the differential to the rear wheels and in most of the automobiles, Rear Axles are the drive shafts.
Two rear axles are placed in between the differential and the wheels. The differential and the rear axles are enclosed in a housing that is protected from dust, rain, etc.
Types of Rear Axles:
Rear Axles are classified based on:
- Rear axle casing and
- Method of supporting
Rear Axle Casing:
According to the casing of Rear axle, it is classified as
- Split Type casing
- Banjo Type or Separate Carrier type
- Integral Carrier type
Split Type casing:
In Split type casing, the axle casing is made into two halves and they are bolted together employing nuts as an assembly.
The Disadvantage of Split Type Casing:
The disadvantage of this case is if any fault arises, the whole axle casing has to disassemble and due to this reason it is obsolete now.
Banjo Type Casing:
Banjo type casing is of one-piece type i.e. the whole casing acts as a single unit whose shape looks like a banjo.
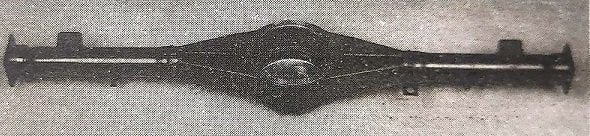
The whole differential unit is to be placed in this banjo casing at the center and the two axles are placed at either end so that the power can be transmitted to the wheels via rear axles.
Advantage of Banjo Type Casing:
The advantage of this case is, if any fault arises, just remove the rear axles from the sides and if the problem is not solved then remove the differential unit by opening the bolts.
Integral Carrier Type:
Its construction is similar to that of banjo type except that it has a permanent housing tube pressed and welded in the sides. It is also called as Unitized carrier housing according to S.A.E. Nomenclature.
Advantage of Integral Carrier Type:
This type of housing is most widely used these days in rear-wheel-drive cars.
Method of Supporting:
Based on the method of supporting, it is classified as
- Semi-Floating Axle
- Full-Floating Axle
- Three quarter Floating Axle
The explanation for the above types of axles is as follows.
Note: In all these cases, the placement of bearings places a vital role.
Semi-Floating Axle:
The axle casing is around the axle shaft and the wheel hub is directly connected to the axle shaft as shown in the figure.
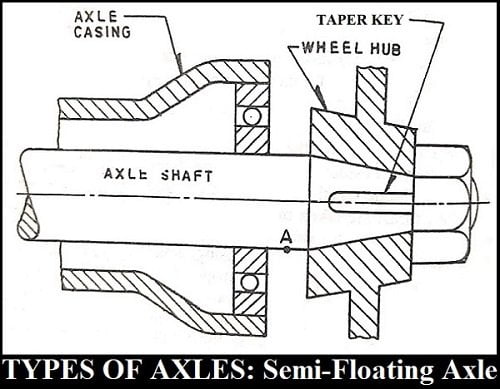
In the semi-floating axle, the bearing which supports the axle was placed inside the casing. The axle of the wheel is located at the center of the axle casing.
The whole weight of the vehicle is transmitted to the half shafts through the casing and the bearings.
This load causes bending and a tendency to shear at the point marked ‘A’ as shown in the fig. Besides, side forces also cause end thrust and bending moment in the axle shafts.
However, the axle shafts have to support all the loads, the diameter of the axle shaft has to be larger.
Advantage of Semi-Floating Axle:
This axle is the cheapest and simplest of all types of axles.
Application of Semi-Floating Axle:
This type of semi-floating axle is mostly used in cars because the loads acting are less compared to heavier vehicles.
Full-Floating Axle:
As shown in the figure, the axle shafts have flanges at the outer ends and are connected to the flanged sleeve through bolts.
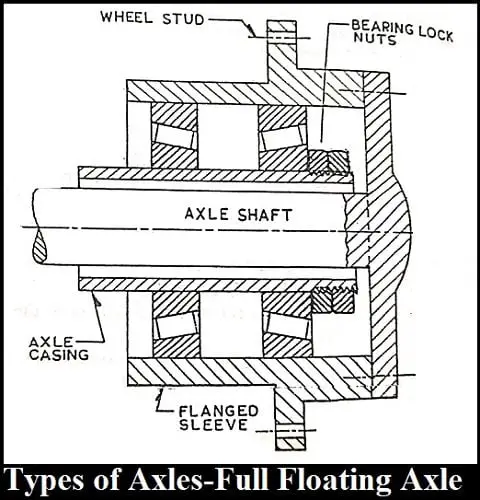
The axle shafts carry only the driving torque whereas the sideload is carried by the two taper roller bearings supporting the axle casing.
The weight of the vehicle is completely supported by the axle casing and the wheels. As the axle shafts carry only the driving torque, their failure does not affect the wheels. i.e. the vehicle can travel even with a broken half shaft.
The disadvantage of Full-Floating Axles:
It is costliest then other types of axles.
Advantage of Full-Floating Axle:
This type of full-floating axle is mostly used in heavier vehicles.
Three Quarter Floating Axle:
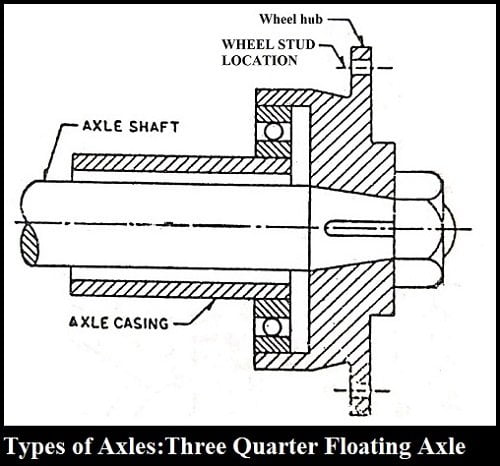
This axle is a compromise in between the simplest semi-floating axle and the robust Full-floating axle.
In this axle, bearings are placed between the wheel and the axle casing and on the outer side of the casing. At the end of the axle, the wheels are fitted through a key, bolt, or nut.
Advantage of Three Quarter Floating Axle:
The main advantage of this axle over the half floating axle is that the major part of the load is taken by the axle casing and not by an axle.
Stub Axle:
An axle which supports only one wheel of a pair on the opposite sides of a vehicle is called stub axle.
Types of Stub Axle:
The 4 types of Stub axles are as follows.
- Lamoine
- Reverse Lamoine
- Elliot
- Reverse Elliot
Lamoine:
This Lamoine stub axle type has an L-shaped spindle instead of a yoke-type hinge.
Reverse Lamoine:
Its layout is opposite to the layout of a standard Lamoine stub axle.
Elliot:
This type of stub axle uses a kingpin, a cotter and a yoke to connect to the front axle.
Reverse Elliot:
This type has the layout opposite to that of a standard Elliot stub axle.
This is the explanation for the Types of Axles in a detailed way. Feel free to share your doubts or thoughts regarding this, and also don't forget to
More Resources:
Constant Mesh Gearbox
Sliding Mesh Gearbox
Synchromesh Gearbox
Epicyclic Gearbox Gearbox
References [External Links]:
- Unit 7:Front axle and steering - IGNOU