Electronic Ignition System: Parts, Working Principle, Advantages, and Disadvantages [PDF]
In this system, the contact breaker points assembly(in the Battery ignition system) is replaced by the armature. This armature is a pulse or signal generator that triggers the ignition module, also called the Electronic Ignition Control Unit or Electronic Ignition Module.
This control unit primarily contains a transistor circuit whose base current is triggered OFF and ON by the armature which results in the starting and stopping of the Primary current.
As we know that there are 3 types of ignition systems. They are Battery Ignition System, Electronic Ignition System, Magneto Ignition System, So, in this article, I will be explaining about the Electronic Ignition System in detail.
Parts of Electronic Ignition System:
The parts of the Electronic ignition system are:
- Battery
- Ignition Switch
- Electronic Ignition Module
- Ignition Coil
- Armature
- Distributor
- Spark Plug
The explanation of the Electronic ignition system is as follows.
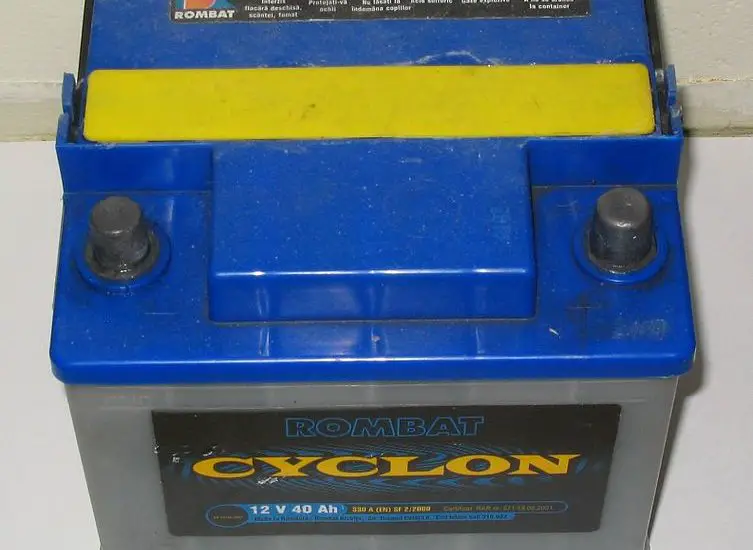
Battery:
A rechargeable Lead-Acid battery is used to provide electrical energy for ignition in the cylinder.
This battery is recharged by Dynamo which is driven by the Engine.

Ignition Switch:
One end of the battery is grounded and the other end(Positive Terminal) is connected to the primary winding of the Ignition coil using the ignition switch.
This switch(Key) is used to turn the Ignition system ON/OFF.
Electronic Ignition Module:
The electronic module senses the signal produced by the pickup coil and stops the current flow from the primary circuit. The timing circuit inside the ignition module turns ON and thereby the current will flow again into the circuit when the voltage is not produced.
Ignition Coil:
The ignition coil is the source of ignition energy. Its function is to step up the Low voltage to high voltage to induce an electric spark in the spark plug.
An ignition coil consists of a magnetic Soft iron core and two insulated conducting coils known as Primary and Secondary winding. The Primary winding consists of 200-300 turns with it’s both ends connected to exterior terminals.
The Secondary winding consists of 21000 turns with its one end connected to the high tension wire that goes to the Distributor and the other end is connected to the Primary coil.

Armature:
Contact breaker points of the battery ignition system are replaced by an armature. When the Armature tooth comes in front of the pickup coil, a voltage signal is generated. The electronic module senses the signal produced by the pickup coil and stops the current flow from the primary circuit.

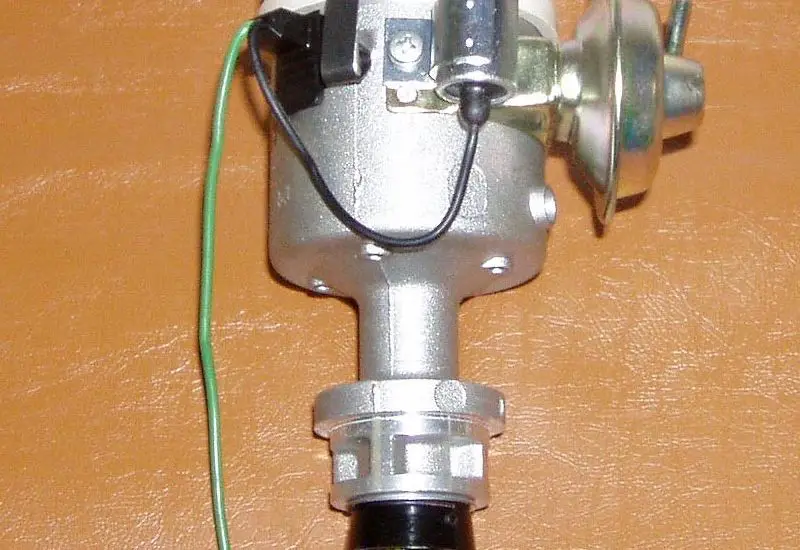
Distributor:
A distributor is provided for distributing the ignition surges to individual spark plugs in the correct sequence with respect to the firing order.
It consists of the rotor in the middle and the metallic electrode on the periphery. These metallic electrodes are directly connected to the spark plugs and are also known as Ignition harness
The Secondary winding of the ignition coil is connected to the rotor of this distributor which is driven by the camshaft. As the rotor rotates, it passes the high tension current to the ignition harness which then carried these high tension currents to the spark plugs.

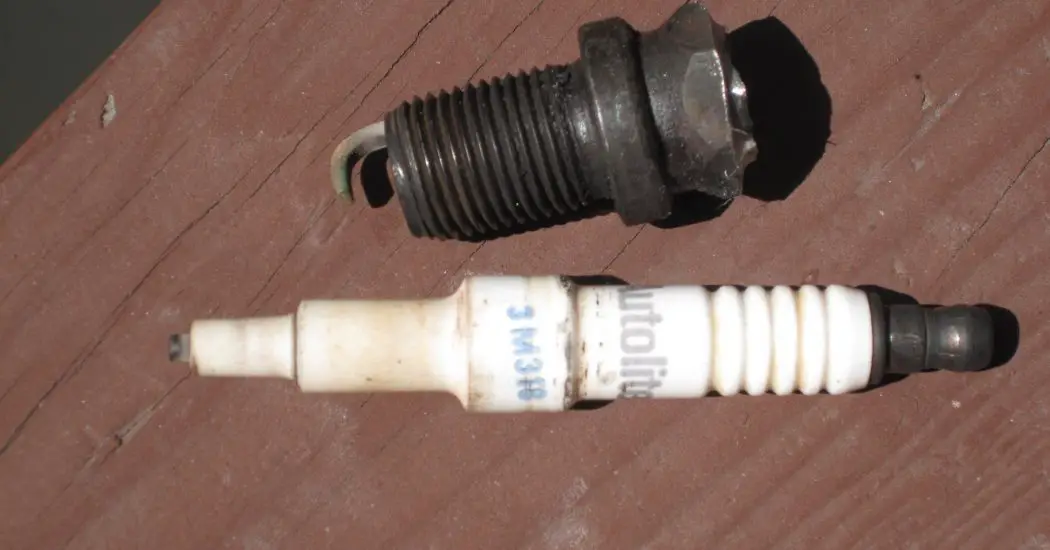
Spark Plug:
It is the output part of the whole ignition system which is responsible for the generation of spark in the engine cylinder.
It consists of 2 electrodes, one attached to the high tension current-carrying wires and the other is grounded. The potential difference between these electrodes ionizes the gap present between them and thus a Spark is generated which ignites the combustible mixture.

Working of Electronic Ignition System:
When the ignition switch is turned ON, current flows from the battery through the ignition switch to the coil primary windings.
When the reflector or armature tooth comes in front of the pickup coil, a voltage signal is generated. The electronic module senses the signal produced by the pickup coil and stops the current flow from the primary circuit.
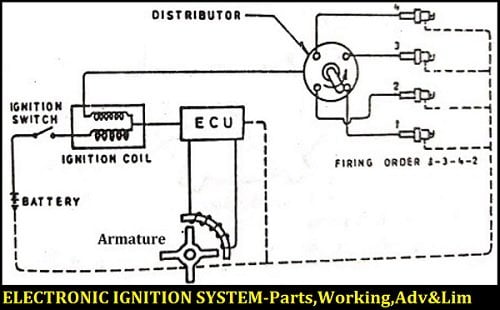
When the armature tooth moves away from the pickup coil, a voltage signal is not generated and due to this, the timing circuit inside the ignition module turns ON and thereby the current will flow again into the circuit.
Due to the continuous make and break of the current, a magnetic field is generated in the ignition coil. Due to the magnetic field, an electromotive force(EMF) is induced in the secondary winding causing the voltage to increase up to 50,000 volts.
This high voltage is then transferred to the distributor. The rotor inside the distributor rotates according to the ignition timing. When the rotor comes exactly in front of the distributor point, the voltage jumps due to the air gap from the rotor to the point.
A high voltage is then transferred from the distributor to the spark plug terminal via a high tension cable. A voltage difference is generated between the central electrode and the ground electrode. The voltage continues to transfer through the central electrode which is sealed using the insulator.
When the voltage exceeds the dielectric strength of the gases between these electrodes, the gases are ionized. Due to ionization, gas becomes a conductor and allows the current to flow through the gap and thus, the spark is finally produced.
This is the detailed explanation of the electronic ignition system if you have any doubts feel free to ask from the comment section.
Advantages of Electronic Ignition System:
Some of the advantages are as follows.
- This system does not have any moving parts in it because it is been under the control of the Electronic Ignition Module or Electronic Control Unit(ECU).
- Due to this, the accuracy increases w.r.t. the spark distribution.
- This increases the reliability and long life of the rest of the components in the circuit.
- This reduces maintenance requirements.
Disadvantages of Electronic Ignition System:
The disadvantage of Electronic Ignition System is:
- The cost of the entire system is very high
So this is all about Electronic Ignition System, I hope you have got an overview of Electronic Ignition System. If you have any doubt don't forget to ask me in the comment section, and don't forget to share this article on your favorite social platforms.
More on Ignition System
Battery Ignition System
Magneto Ignition System
References [External Links]:
- How the ignition system works | How a Car Works
- How Ignition System Works - YouTube
Media Credits:
- Battery Image: By No machine-readable author provided. Shaddack assumed (based on copyright claims). - No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=401224
- Ignition Coil Image: By Sonett72 at English Wikipedia - Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=672379
- Distributor Image: By Riccardo Nicola - Own work, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=6214163
- Spark Plug Image: By User:Industry shill - Own work by the original uploader, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=60305532
- Armature Image: By (Lucas Richardson) - Own work, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1511733
- Feature Image: Modified by Author, Source IGNOU