Battery Ignition System: Parts, Woking Principle, Advantages, and Disadvantages [PDF]
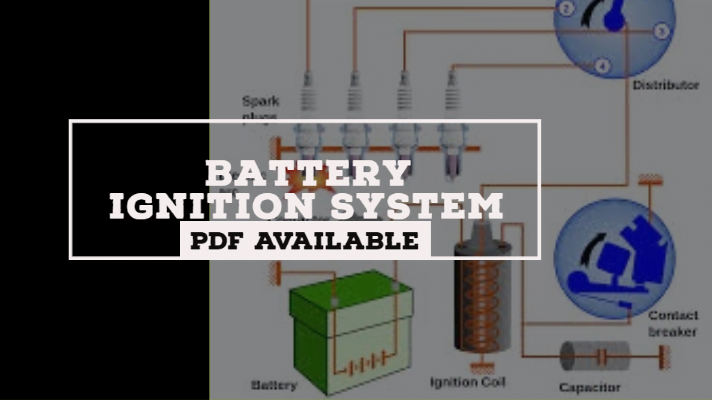
The function of the battery Ignition System is to initiate the spark in the cylinder for the combustion of fuel in the I.C. engine by means of a battery. This ignition system is used in automobiles and the main source for the generation of spark is the battery. It is mostly used in light commercial vehicles.
So, in this article, I will be explaining in detail about the Battery Ignition System.
Parts of Battery Ignition System:
The main parts of a battery ignition system are:
- Battery
- Ignition switch
- Ballast resistor
- Ignition coil
- Condenser
- Contact breaker
- Distributor and
- Spark Plug
Let's discuss each of these parts one by one.
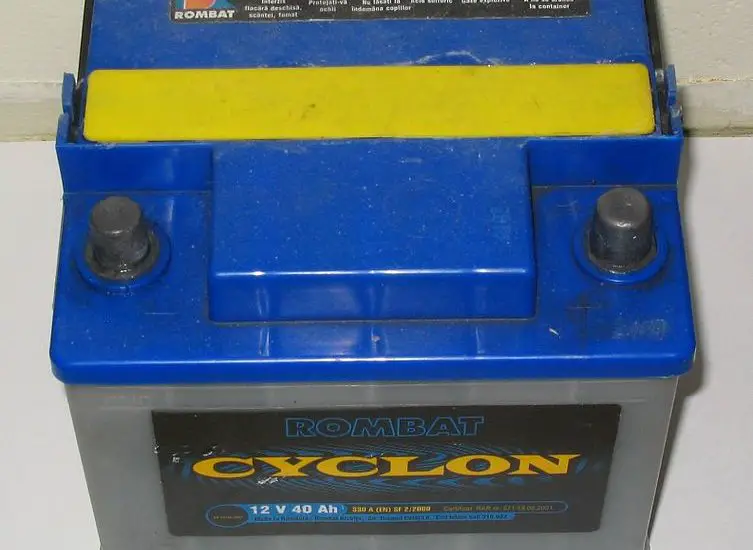
Battery:
A rechargeable Lead-Acid battery is used to provide electrical energy for ignition in the cylinder.
This battery is recharged by Dynamo which is driven by the Engine.

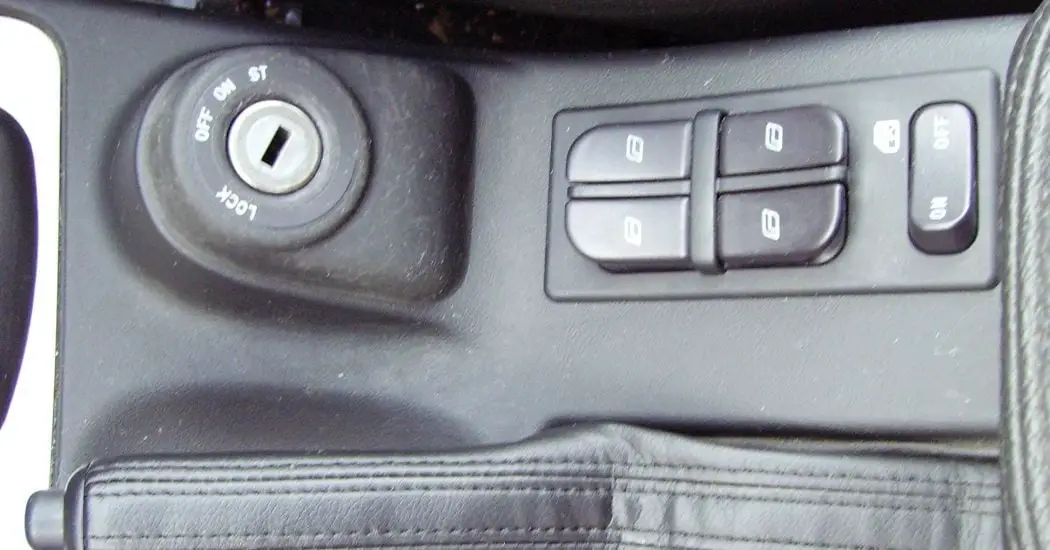
Ignition Switch:
One end of the battery is grounded and the other end (Positive Terminal) is connected to the primary winding of the Ignition coil using the ignition switch.
This switch(Key) is used to turn the Ignition system ON/OFF.

Ballast Resistor:
Under prolonged operations of the engine, the temperature of the ignition coil increases which can be dangerous. To prevent this, A ballast resistor made up of Iron wire is provided in series with the primary winding.
Iron has a property that it's resistance increases rapidly if a certain temperature is exceeded. Thus the ballast resistor helps to keep the current down to a safe value.
Ignition Coil:
Ignition coil is the source of ignition energy. Its function is to step up the Low voltage to high voltage to induce an electric spark in the spark plug.
An ignition coil consists of a magnetic Soft iron core and two insulated conducting coils known as Primary winding and Secondary winding. The Primary winding consists of 200-300 turns with it's both ends connected to exterior terminals.
The Secondary winding consists of 21000 turns with its one end connected to the high tension wire that goes to the Distributor and the other end is connected to the Primary coil.

Contact Breaker:
It is generally used for making and breaking of Primary circuit. It consists of 2 metal points and out of the two, one is fixed to the contact breaker assembly and the other is movable which is connected to a spring-loaded pivot arm.
The spring on this arm keeps both metal points in contact by closing the primary circuit. The pivoted arm has a heel attached in the middle which breaks the contact point due to the action of a cam (which is driven by the engine).
Now, as the high point on the Cam passes under the heel, the contact breaks and the current flow through contact breaker stops.

Condenser:
A condenser is connected in parallel with the contact breaker to prevent the burning of the metal points and also helps in providing ignition energy to the secondary winding.
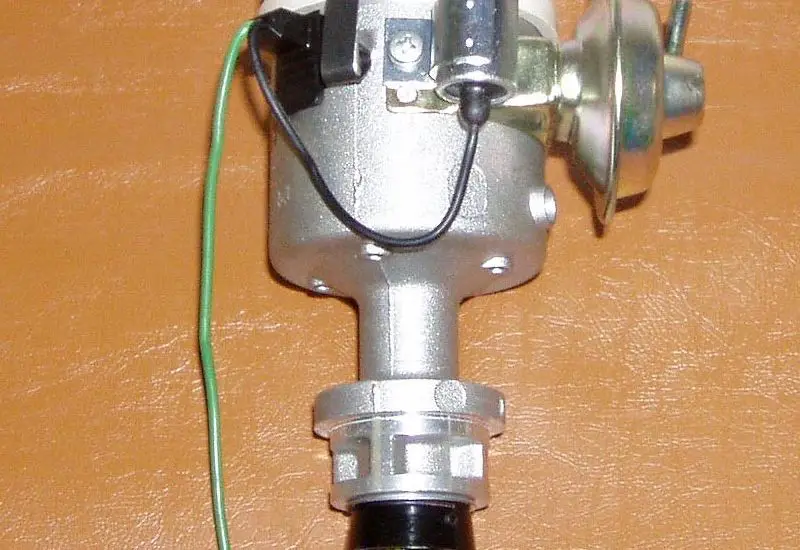
Distributor:
A distributor is provided for distributing the ignition surges to individual spark plugs in the correct sequence with respect to the firing order.
It consists of the rotor in the middle and the metallic electrode on the periphery. These metallic electrodes are directly connected to the spark plugs and are also known as Ignition harness
The Secondary winding of the ignition coil is connected to the rotor of this distributor which is driven by the camshaft. As the rotor rotates, it passes the high tension current to the ignition harness which then carried these high tension currents to the spark plugs.

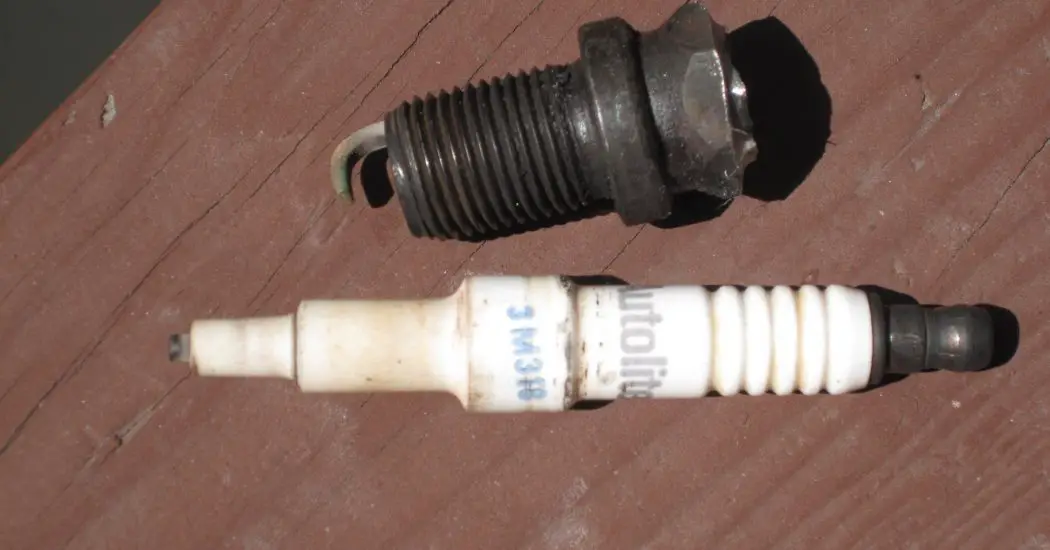
Spark Plug:
It is the output part of the whole ignition system.
It consists of 2 electrodes, one attached to the high tension current-carrying wires and the other is grounded. The potential difference between these electrodes ionizes the gap present between them and thus a Spark is generated which ignites the combustible mixture.

Working of Battery Ignition System:
When the ignition switch is turned ON, the primary circuit gets closed and current starts flowing through it. The current known as the primary current set up the magnetic field around the soft iron core of the ignition coil.
When the breaker points open by the action of Cam, the current which was flowing through the contact breaker starts flowing through the condenser. As the condenser charges, the primary current falls and the magnetic field collapses.
This change in the magnetic field induces a current in the primary winding which flows in the same direction as the primary current and charges the condenser to a voltage much higher than the battery voltage, thus stopping the current flow from the battery.
Due to this, the condenser then discharges into the battery, thus reversing the direction of both primary current and magnetic field. This rapid collapse and the reversal of the magnetic field induces a very high voltage in the secondary winding of the ignition coil.
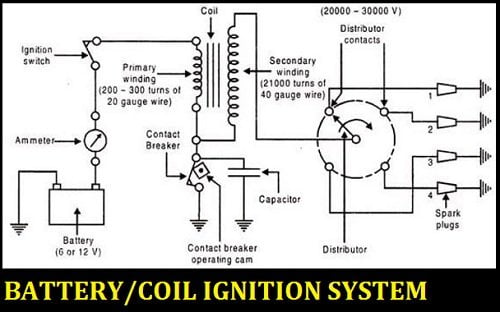
This high voltage is then carried through the high tension wires to the distributor rotor, where it passes through one of the ignition harnesses into the spark plug and produce a spark.
A very important function of the condenser is to prevent the arc across the breaker points. If the condenser was not connected in the primary circuit, the induced extra voltage due to the collapsing magnetic field would cause an arc across the breaker points which could be hazardous.
To prevent this, the condenser is used which absorbs all the voltage to charge itself above the voltage of the battery.
Advantages of Battery Ignition System:
Here are some advantages of battery Ignition System:
- In this, the maintenance is less because the moving parts are absent.
- Contact breaker points are absent-so no arcing
- Spark plug life increases by 50% and they can be used for about 60000 km without any problem.
- More power output.
- More fuel efficiency.
Disadvantages of Battery Ignition System :
The disadvantages of Battery Ignition System are the following:
- Because of arcing, the pitting of the contact breaker point will lead to problems.
- Poor starting: After a few thousand kilometers of running, the timing becomes inaccurate, which results in poor starting (Starting trouble).
- At very high engine speed, performance is poor because of inertia effects of the moving parts in the system
This is a detailed explanation of the Battery ignition system. If you have any doubts, feel free to ask from the comment section.
More on Ignition System
Magneto Ignition System
Electronic Ignition System
References [External Links]:
- IGNITION SYSTEM - Auto Creators
- Ignition Coil Function - Part Info
- ignition systems in automobiles - IJRDO Journal
Media Credits:
- Battery Image: By No machine-readable author provided. Shaddack assumed (based on copyright claims). – No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=401224
- Ignition Coil Image: By Sonett72 at English Wikipedia – Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=672379
- Distributor Image: By Riccardo Nicola – Own work, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=6214163
- Spark Plug Image: Industry shill – Own work by the original uploader, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=60305532
- Contact Breaker Image: By Sonett72 at English Wikipedia – Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1863764
- Capacitor Image: Public Domain
- Ignition Switch Image: By Ballista, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1012367
- Feature Image: Modified by Author