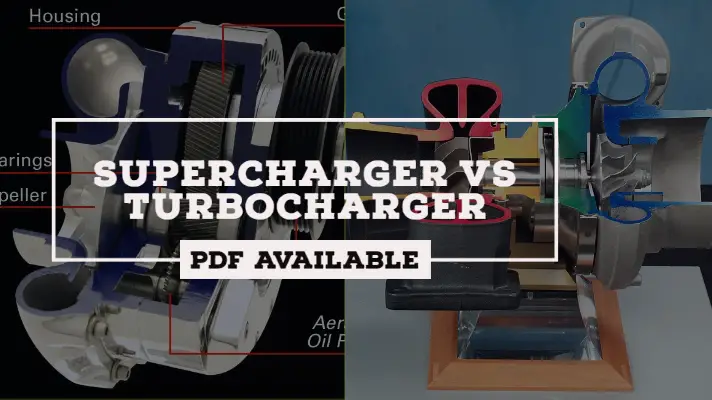
Turbocharger: Definition, Parts, Functions, Types, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications (With PDF)
A Turbocharger is a device that increases the air pressure in an IC engine, allowing it to burn fuel and produce more power. In the previous article, we discussed in detail about Supercharger, whereas in Today's article, we will discuss Turbocharger: Definition, Parts, Functions, Types, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications in a detailed way.
Let's start with the definition of a Turbocharger...
Turbocharger Definition:
Turbocharger is a device driven by a turbine, and it is used to increase the performance and efficiency of an IC Engine by putting more compressed air into the engine cylinder. A turbocharger is a device that increases the air pressure in an IC engine, allowing it to burn fuel and produce more power.
It can be achieved by using a turbine driven by exhaust gases to compress the incoming air, which leads to a denser air-fuel mixture and greater engine power output.
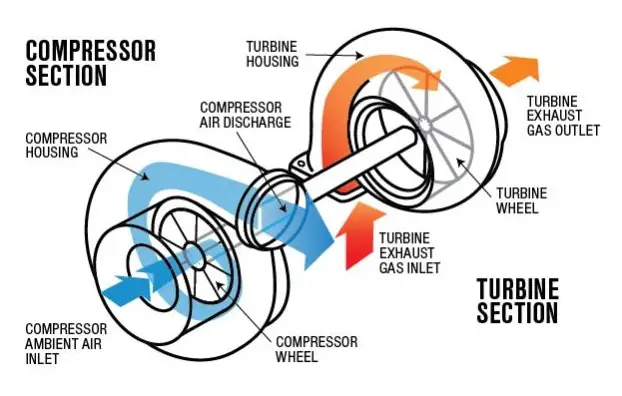
Turbocharger Diagram:
The diagram of the Turbocharger is shown below.

Parts of Turbocharger:
The main parts or components of a turbocharger are as follows.
Turbine wheel:
Exhaust gases spin the wheel by providing the energy to drive the compressor wheel.
Compressor wheel:
The rotating wheel compresses the incoming air and increases its density.
Housing:
The metal casing encloses the compressor wheel, shaft, and turbine wheel.
The rotational shaft:
It connects the compressor wheel and turbine wheel.
Wastegate:
A Wastegate is a valve regulating exhaust gas flow to the turbine wheel.
Working Principle of Turbocharger:
The working principle of a turbocharger is as follows.
Exhaust gases from the engine flow through the turbine housing and spin the turbine wheel. Through a rotational shaft, the spinning of the turbine wheel drives the compressor wheel.
The compressor wheel takes air from the atmosphere, compresses it, and increases its density. The compressed air is then directed into the engine's intake manifold, providing more air to burn with the fuel.
The increased air density results in powerful combustion leading to a greater engine power output. The Turbocharger's wastegate regulates the number of exhaust gases that reach the turbine wheel, allowing control over the boost pressure and avoiding engine overloading.
Functions of Turbocharger:
The main functions of a turbocharger are as follows.
- Providing a performance upgrade
- Reducing emissions
- Increasing engine power output
- Regulating boost pressure
- Improving engine efficiency
Types of the Turbocharger:
There are two main types of turbochargers:
Variable geometry turbocharger (VGT):
Variable Geometry Turbocharger is commonly used in diesel engines. This type uses a variable geometry turbine housing to regulate the boost pressure.
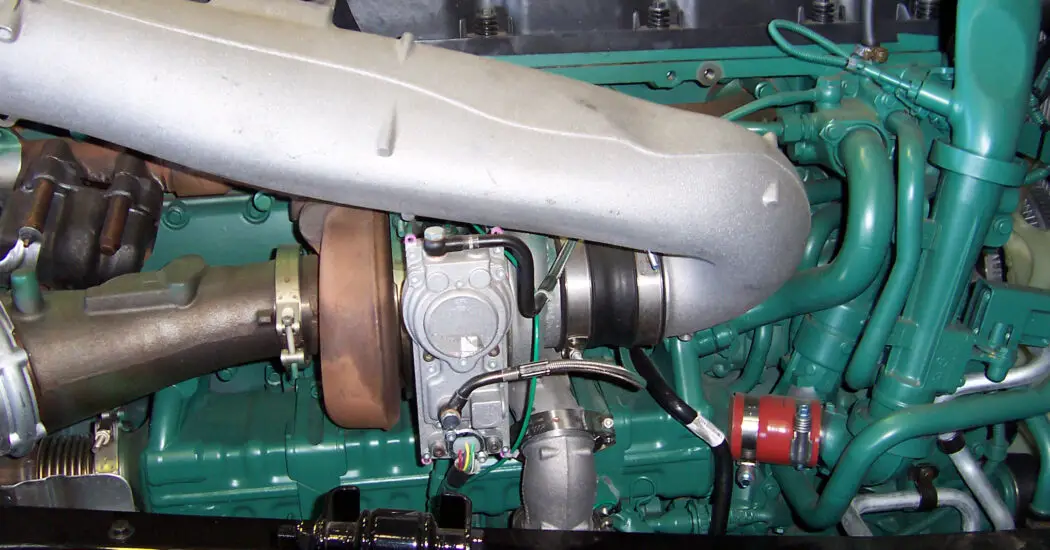
Wastegate turbocharger:
This turbocharger uses a wastegate to regulate the boost pressure. The wastegate opens to allow exhaust gases to bypass the turbine wheel which reduces its speed and thereby regulating boost pressure.

Other variations of these two types of turbochargers include twin-turbo systems, sequential turbocharging, and electric turbocharging.
Each type of Turbocharger has unique advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of Turbocharger will depend on the engine's specific needs and the vehicle.
Advantages of Turbocharger:
- A turbocharger can significantly increase engine power output by compressing incoming air and providing more air to burn with the fuel.
- By improving the engine's thermal efficiency, a turbocharger can improve fuel efficiency by burning more fuel and producing more power with the same amount of fuel.
- They can provide a significant performance upgrade to engines, especially in vehicles.
- A turbocharger can reduce emissions by burning more fuel with less waste improving engine efficiency.
Disadvantages of a turbocharger:
- Turbochargers require regular maintenance, including oil changes and regular cleaning.
- Turbochargers are more complex than naturally aspirated engines, requiring additional components and adding to the overall complexity of the engine system.
- Turbochargers generate heat during operation which leads to increased engine wear.
- They can experience a slight delay when the throttle is rapidly increased. It can result in a slower response from the engine.
Applications of Turbocharger
Turbochargers are widely used in a variety of applications, including:
- Industrial
- Aerospace
- Agriculture
- Marine
- Automotive field
- Power generation sector.
This is a detailed explanation of the Turbocharger. If you have any doubts, feel free to ask from the comments section and we will answer you within 24 hrs.
More Resources:
- Cooling Systems in IC Engines
- Lubrication Systems
- Ignition System-Battery, Electronic, and Magneto
- Supercharger in detailed