What are the Components of an IC Engine?
Hello readers, In today’s article, I will discuss some important components of an IC engine with their functions.
Internal Combustion Engine aka IC Engine is a heat engine which works on either the Otto cycle or diesel cycle.
In this type of engine, the combustion of the fuel occurred inside the engine. And produced thrust which applies to some components of the Engine. Also, this thrust or force produces a vertical or horizontal movement on the components.
By this process, chemical energy is converted to mechanical energy.
So let's dive into the article.
Major Parts of an IC Engine with their Functions:
An Internal Combustion Engine consists of several important parts, and those are:
- Cylinder
- Cylinder Head
- Piston
- Piston Ring
- Gudgeon pin or Piston Pin
- Connecting Rod
- Small End and Big End Bearing
- Crank Shaft
- Cam Shaft
- Crank Case
- Valves or Ports
- Manifold
- Push Rod
- Rocker Arm
- Spark Plug or Fuel Injector
- Cooling Jackets or Fins
- Flywheel
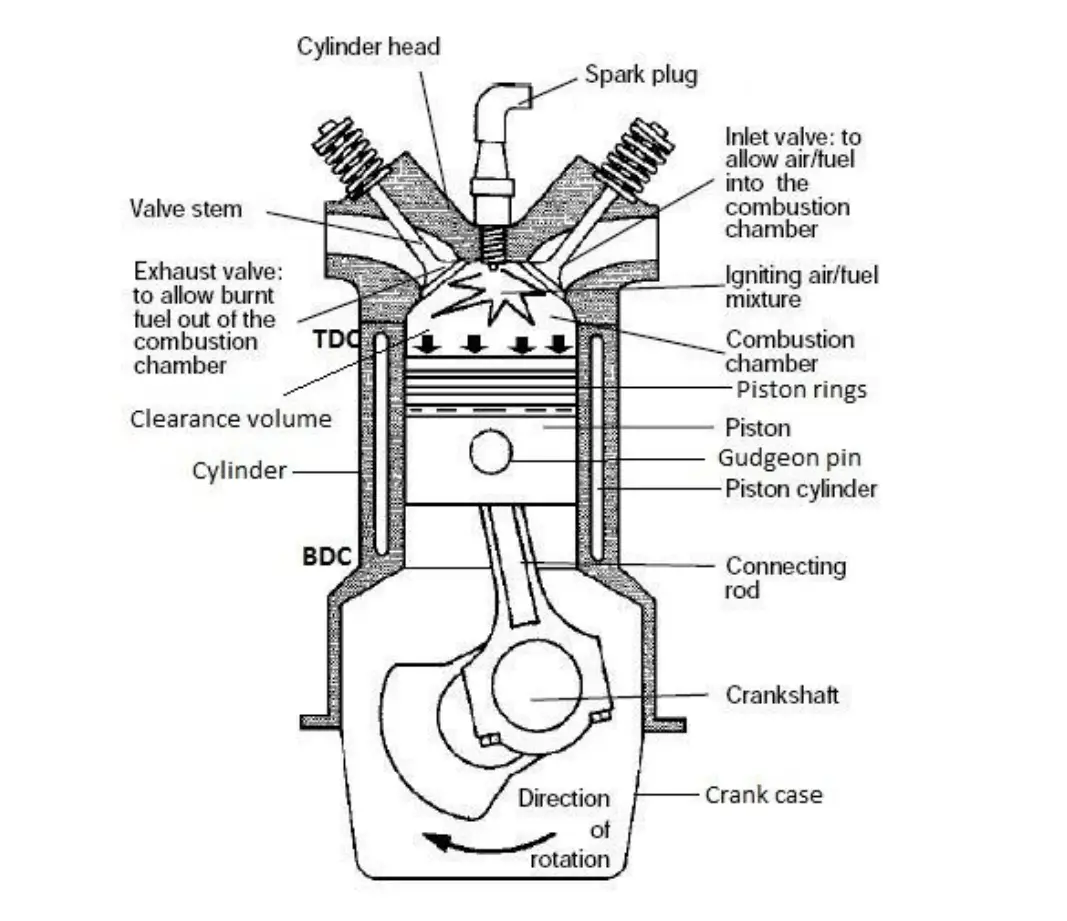
These are the major parts which an Internal Combustion Engine has. So let's discuss these components one by one!
Cylinder:
It is one of the important parts of an IC Engine. Within this, the piston reciprocates.
Generally, a cylinder block made of cast iron to withstand pressure above 50-100 bar.
Also, when designing a cylinder block we need to keep in mind that it should bear the heat also. According to NCERT the temperature of Engine Cylinder can be raised to 2600 degree centigrade.
According to science direct nowadays cylinder blocks made of grey cast iron, compact graphite cast iron, nodular cast iron and cast Al alloy.
The Functions of Cylinder Head:
- In this chamber, the ignition of the charge [Air+Fuel] happens.
- It guides the piston to reciprocates.
Cylinder Head:
The cylinder head is fitted over the Cylinder Block.
As of the cylinder block, the cylinder head is also made of same material [Cast Iron].
Generally, cylinder and cylinder head both are made by casting.
There are Valves [Inlet or Exhaust], Spark Plug [SI Engine] or Fuel Injector [CI Engine] are mounted on it.
A gasket is provided on the Cylinder Head to avoid the leakage of the compressed fuel and make the cylinder block air-tight.
The Functions of Cylinder Head:
- It is used for closing the Cylinder block.
- The Valves and Spark Plug or Injector are mounted over it.
Piston:
The piston is generally made of Aluminium Alloy, which is good for heat transfer.
Piston converts the to-fro motion or the reciprocating motion to the rotary motion.
A piston is also used to transfer the energy [after Power Stroke] to the connecting rod.
The Functions of Piston:
- Piston provides the to and fro movement.
- It converts the reciprocating movement to rotary motion.
- It helps to transfer the energy to the connecting rod.
Piston Ring:
Piston Rings are attached to the periphery of the Piston, generally made of steel alloys.
In an Internal Combustion Engine, three piston rings are used.
The top one is named the compression ring, and the bottom one is named the oil ring.
The Functions of Piston Rings:
- The compression ring is used for preventing the leakage of burnt gases into the lower chamber.
- And Oil Ring is used for preventing the leakage of oil inside the engine block. Also, it scrapes the oil from the cylinder wall.
- Lastly, the middle ring is for safety purposes if by chance the leakage of burnt gas or oil happened than it can prevent that.
Gudgeon Pin or Piston Pin:
Gudgeon Pin [Piston Pin or Wrist Pin] is used to connect connecting rod with the piston.
It is made of Steel alloy to bear the high strength.
And, it is generally, made by forging process.
The Functions of a Gudgeon Pin:
- To connect the piston with the connecting rod
Connecting Rod:
Connecting Rod is generally used to transfer the reciprocating motion to the rotary motion of the crankshaft.
The one end [smaller] is connected with the Piston with the help of piston pin, and the other end [bigger] is connected with the crankshaft with the help of a crank pin.
Connecting rod is made of Steel Alloy or Aluminium Alloy. However, in recent days connecting rod is also made of T6-2024 and T651-7075 aluminium alloys. These alloys are so lighter and capable of bear the high strength and high impact. [Source VLABS]
Else, Titanium is also used to make a connecting rod.
Connecting rod is made by Forging Process.
The Functions of Connecting Rod:
- It is used to convert the to and fro [reciprocating motion] of the piston to circular motion.
Small End and Big End Bearing:
As we already know that connecting rod has two different ends [Small and Big End], so for smoother movement of the connecting rod these two bearings are used.
Small end bearing attached in inside the joining of the piston and connecting rod, and big end bearing is attached inside the joining of connecting rod and crank.
The Functions of Small End and Big End Bearing:
- To provide smoother functioning between the piston, connecting rod and crank.
- To minimize power loss due to friction.
Crank Shaft:
This is the rotating member of an IC Engine which covert the reciprocating movement of the piston to rotary motion.
All the pistons of the engine are connected with the crankshaft by the help of connecting rod and one end of this crankshaft is connected with Flywheel. [I will discuss flywheel later on this article].
It is made of forged steel or Cast Iron. [Source Science Direct]
A crankshaft is consisted of the number of Crank and Crank Pin, according to the size of the engine it can be defined. If the engine is 6-cylinder then the amount of crank and crankpin is 6, and when it goes down to 3 or 4, then the number of crank and crankpin reduces accordingly.
A crankshaft consists of four major parts,
- Main Journal
- Crank Pins
- Crank Webs
- Counterweights
Main Journal:
Main Journal is a bearing which helps to determine the rotation of the motion.
Crank Pins:
Crank pins are used to connect one end of the connecting rod.
Crank Webs:
Crank webs are used to connects the crankpins with the main journal.
Counter Weights:
And lastly, counterweights are used to balance the crankshaft.
The Functions of Crank Shaft:
- The crankshaft converts the reciprocation movement of piston o the rotary motion.
- It drives the flywheel and camshaft.
Cam Shaft:
It is a vital part of an IC Engine, it is used for opening and closing of Valves at the right time [Follow the Valve Timing Diagram].
The rotation of the camshaft is half of the crankshaft in a four-stroke engine, and a two-stroke engine rotation of both crank and camshaft is same.
It is made of Cast Iron or Steel.
The Functions of the Cam Shaft:
- It helps to open the poppet valves [Inlet and Exhaust] at the proper time.
Crank Case:
It is the place where the crankshaft is located. Also in some engines, lubricating oil is stored inside it, especially on two-stroke engine.
It is located below the cylinders.
The crankcase is also made of Cast Iron.
If we deeply analysis the crankcase, we can see that it consists of intermediate walls, sidewalls, and end walls, and an upper cover plate. [The detailed analysis of Crank Case can be found here]
The Functions of the Crank Case:
- It protects the crankshaft and connecting rod from debris.
- In some engines, the crankcase is used for sump of lubrication oil.
Valves or Ports:
Valves or Port is a basic and important part of an IC Engine. So let me first tell you whare valve and where a port is used! So in a four-stroke engine, we use a valve and in case of the two-stroke engine, we use ports.
In a four-stroke IC Engine, there are two valves. one is Inlet Valve, and the other one is Exhaust Valve.
Valves are fitted in the valve spring, which driven by a camshaft with the help of rocker arm and pushes rod.
These valves are located on the cylinder head.
Valves are available in a wide range of material like Stainless Steels, Martensitic Valve Steel, Austenitic Valve Steel, Nickel Alloy, Stellite Alloy, Nimonic / Inconel / Monal Superalloys. [Source Shailesh Industries]
The Functions of Valves:
- During suction stroke inlet v/v allow the charge [Air+Fuel or only Air] to go inside the engine cylinder.
- And after the exhaust stroke, through exhaust v/v the burnt gas is going out of the cylinder.
- They also seal the piston-cylinder when compression stroke happens.
Manifold:
This is also an essential part of an engine. There are two types of a manifold, one is inlet other is exhaust manifold.
Through inlet manifold, the charge [Air+Fuel or Air] is entered to the engine cylinder.
And the burnt gases from all the cylinders exit through the exhaust manifold.
There is also a term Manifold Pressure, so it is the pressure which formed between the air or fuel mixture in the throttle section to the inlet manifold. When we increase the RPM the manifold pressure is also increased due to the increase in ambient air pressure.
Functions of Manifolds:
- Through the manifold, the fresh charge comes into the engine cylinder and brunt gases come out from the engine cylinder.
Push Rod:
It is a rod which is operated by the camshaft to open or close the valves.
Functions of Push Rod:
- It is used for opening and closing of Poppet Valves
Rocker Arm:
It is an oscillating lever, which converts the radial movement of the cam to verticle or linear movement of the poppet valve.
In general rocker arm is made of Aluminium alloy, but for heavy engines like bus, trucks we use cast iron or carbon steel.
Functions of Rocker Arm:
- Rocker arm converts the radial movement of the Cam to the linear movement of the Valve in IC Engine.
- It is used for the opening of Valves.
Spark Plug or Fuel Injector:
Spark Plug and Fuel Injecter, these two things are different and also use in different engines.
The spark plug is used in Spark Ignition Engine [SI Engine] where Fuel Injector is used in Compression Ignition Engine [CI Engine].
The Function of Spark Plug:
- Spark Plug is used to generate the spark in SI Engine [Petrol].
Functions of Fuel Injector:
- The fuel injector is used for injecting the fuel inside the engine cylinder, in atomised form.
Cooling Jackets or Fins:
As we already know, inside the engine cylinder the temperature can be raised to 3000-degree centigrade, so to avoid wear and tear we need to use the cooling system.
In four strokes engines, there are two types of a cooling system can be noticeable.
One is liquid colling and other is Air cooling. Air cooling is used for small engines like a motorcycle, and for a larger engine like 4 to 6 cylinder engines, we need to use liquid cooling, as heat transfer rate is more.
Functions of Cooling Jackets or Fins:
- To reduce the temperature of the engine.
- To protect the engine from wear and tear.
Flywheel:
It is a big circular shaped wheel mounted on one end of the Crank Shaft. It is designed so well that it can store the rotational energy quite easily.
During the power stroke, the excessive amount of energy is being stored by the flywheel, and deliver that store energy to the rest of the threes strokes.
The Functions of Flywheel:
- The main function of the flywheel is to store excess energy during the power stroke and supply that energy to the rest of the threes strokes to complete the cycle.
Some FAQs on IC Engine:
What are the main parts of internal combustion engine?
Cylinder, Cylinder Head, Piston, Piston Ring, Gudgeon pin or Piston Pin, Connecting Rod, Small End and Big End Bearing, Crank Shaft, Cam Shaft, Crank Case,Valves or Ports, Manifold, Push Rod, Rocker Arm, Spark Plug or Fuel Injector, Cooling Jackets or,Fins, and Flywheel
What are examples of internal combustion engines?
Is IC Engine is a Heat Engine?
So this is our whole topic on Parts of Internal Combustion Engine with their Function. I hope I am able to describe this well for your understanding. So now I want to hear from you.
So My question for you, What is the top half of the engine called? Let me know your answer in the comment section.
And finally, don't forget to share this stuff with your friend, groups and social handles. Happy Learning. BYE!
References [External Links]:
- Contributor: Charles Lafayette Proctor
- Article Title: Internal-combustion engine
- Website Name: Encyclopædia Britannica
- Publisher: Encyclopædia Britannica, inc.
- Date Published: June 01, 2020
- URL: https://www.britannica.com/technology/internal-combustion-engine
- Access Date: June 21, 2020