Supercharger: Definition, Types, Parts, Working Principle, Advantages and Disadvantages, Applications

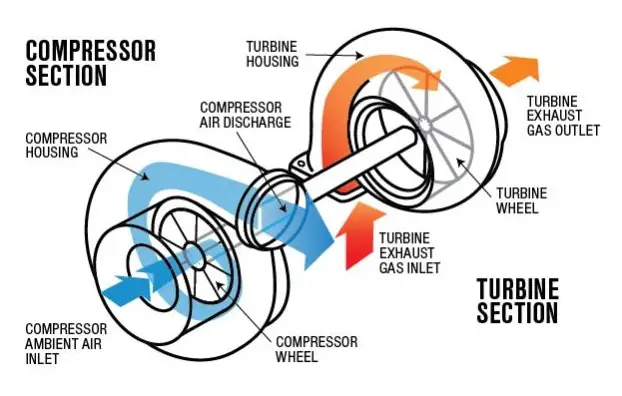
Supercharger is an air compressor used for forced induction of air into an internal combustion engine whereas Turbocharger works on the exhaust gases from the cylinder for better efficiency.
In this article, I will explain the Supercharger: Definition, Parts, Working Principles, Types, Advantages and Disadvantages, and Applications in a detailed way. Before discussing it in detail, let's start with the definition of it.
Supercharger Definition:
The process of forcing more charge into the engine cylinder than can be drawn by naturally aspirated piston action to get more power is called Supercharger.

Types of Superchargers:
According to the method of compression, there are two main types of superchargers.
- Dynamic compressors (Example: Centrifugal)
- Positive displacement (Example: Twin-screw, roots)
A Positive Displacement Pump has a decreasing cavity on the discharge side and an expanding cavity on its suction side.
Centrifugal Type Supercharger:
A/F mixture enters the impeller at the center and passes through the impeller and diffuser vanes. Finally, it enters the volute casing and the mixture goes to the engine from the casing.
- The pressure is increased by 30%
- Impeller speed → 80000 revs/min
- Impellers are made of duralumin/alloy steels to withstand high steels.
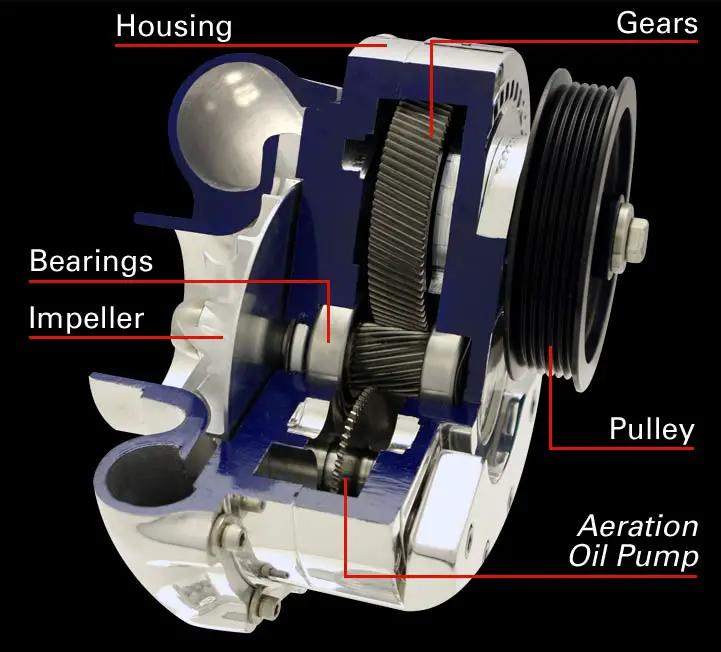
Twin-screw superchargers:
Twin Screw Supercharger works similarly to other superchargers that are driven via a gear drive or belt from the engine’s crankshaft. The name Twin screw has evolved as the supercharger uses a pair of the spiral rotor which is identical and are in the form of a screw.
The Twin Screw Supercharger comes under the positive displacement device and compared to Root's supercharger it was more efficient.
The Twin Screw Supercharger is used for increasing the air quantity in the engine cylinder for more combustion leading to more torque from the engine.
Parts of Twin-screw supercharger:
The main parts of the Twin-screw supercharger are as follows.
- Time Gears
- Housing
- Front Cover
- Drive Pulley
- Bypass Actuator
- Bearings
- Rotors
Root’s Supercharger:
In Root's Supercharger, there are two rotors of epicycloid shape, each rotor keyed to its shaft.
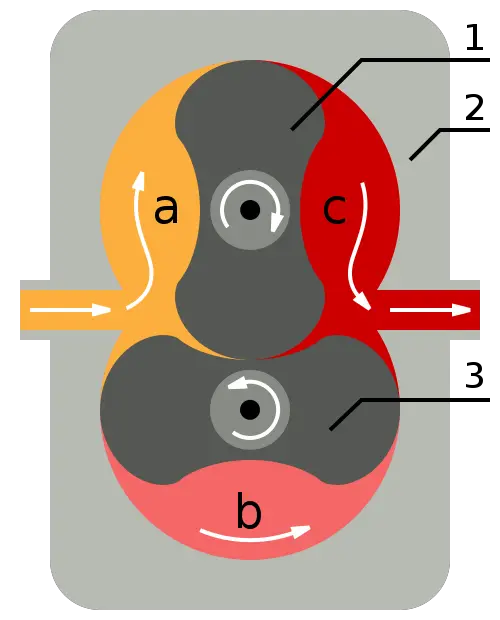
- One rotor is connected to others by means of gears.
- Gears are of equal size and two rotors rotate at the same speed.
- Operates like a gear pump.
- The mixture at the outlet of the supercharger is at high pressure.

Parts of Supercharger:
The four main components of a centrifugal supercharger are
- The Volute (compressor housing)
- Diffuser
- Impeller and
- Transmission.
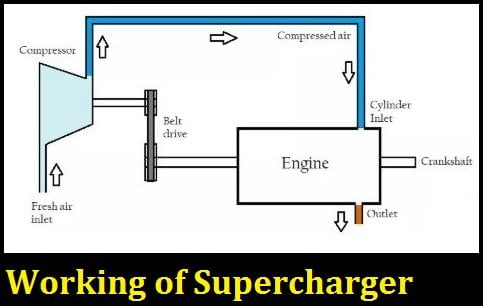
Working Principle of Supercharger:
It is fitted before the Intake valve of the cylinder so that air can be compressed in the supercharger and allowed to be forced into the cylinder via the Intake valve. It is used to increase engine power, efficiency, and torque by compressing the air in multi-stages for increasing the quantity of air, pressure, and temperature.
The greater mass flow rate provides more oxygen to support combustion in the cylinder compared to the naturally aspirated engine.
The supercharger allows more fuel to be burned and thereby more work is said to be done per cycle which increases the power output of the engine.
The Power to the supercharger comes mechanically from the engine's crankshaft via a belt, gear, shaft, or chain.
Super Charger increases the pressure of the A/F mixture and supplies at a higher pressure than atmospheric pressure.
The supercharged engine produces higher power up to 40% of that of the normal engine.
It also increases torque by 40%.
At higher altitudes, it helps by increasing the density of the air fed to the engine.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Supercharger:
The advantages and disadvantages of a supercharger are furnished below.
Advantages of Supercharger:
Here are some advantages of Supercharger:
- Higher power output.
- Quicker acceleration of the vehicle.
- Great atomization of fuel
- On the whole, a supercharger has good torque characteristics
- Reduced smoke from exhaust gases.
- The cost of a supercharger is cheaper than a turbocharger.
- Improvement of mechanical efficiency
- Smooth and complete combustion
- Better air/fuel mixture
- Improved cold starting
- Better scavenging products
Disadvantages of Supercharger:
There are some disadvantages of Supercharger and those are:
- Draws power from the engine.
- Fuel with poor ignition quality can be used
- High detonation tendency in SI engines.
- Due to increased turbulence, the heat loss can be increased.
- The cooling requirement of the engine is high
- Thermal stresses can be increased.
Applications of Supercharger:
The applications of the supercharger are as follows.
- As per the requirement of Aero engines, Superchargers are responsible for reducing the per horsepower weight of the engines.
- The superchargers can be used to improve low-speed transient response in downsized and down-speed engines.
More Resources:
Cooling Systems in IC Engines
Lubrication Systems
Ignition System-Battery, Electronic and Magneto
Media Credits:
- Image 1: By CZmarlin — Christopher Ziemnowicz. Thank you! - Own work, Public Domain,
- Image 2: By ATI ProCharger - www.procharger.com, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=18264092
- Image 3: By Inductiveload - Own work based on File: Rotary_piston_pump.svg, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=11297699
- Image 4: By No machine-readable author provided. Sfoskett~commonswiki assumed (based on copyright claims). - No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=423186