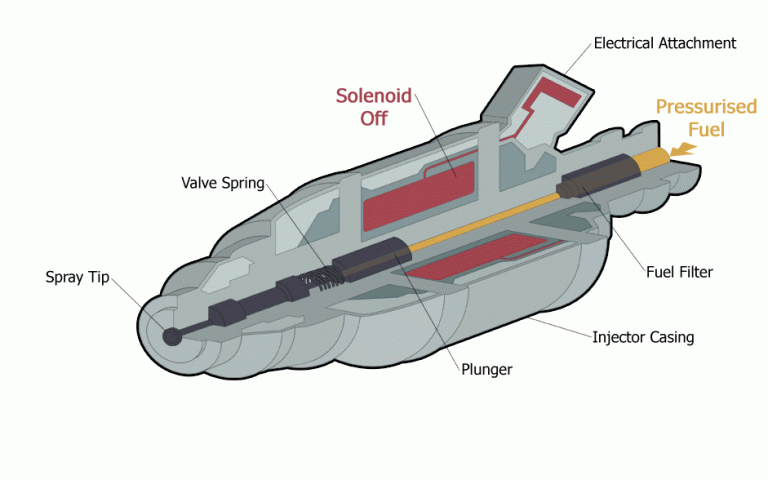
Magneto Ignition System: Parts, Working Principle, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications [PDF]
Magneto Ignition system applies to 2 wheelers and racing cars. It is similar to the Battery Ignition System but the magnet is used here instead of a battery to generate a high spark at the Spark Plug. It is used in SI engines. A rotating magnet produces a high voltage (there is no need for battery) and in this ignition system, a magnet ? is used in the place of a battery.
Parts of Magneto Ignition System:
Magneto Ignition system is consist of the following parts:
- Transformer Core
- Magnet
- Cam
- Capacitor
- Ignition switch
- Contact breaker
- Distributor
- Spark Plug
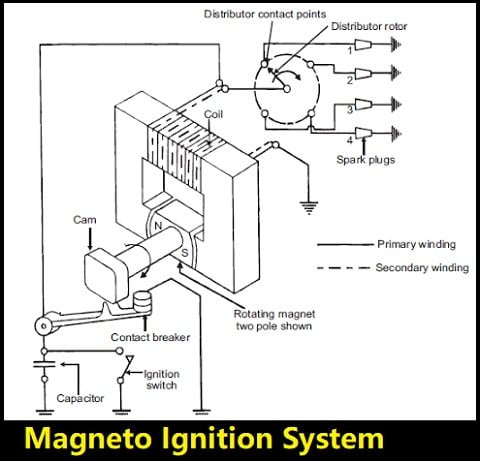
Here are the explanation of all these parts.
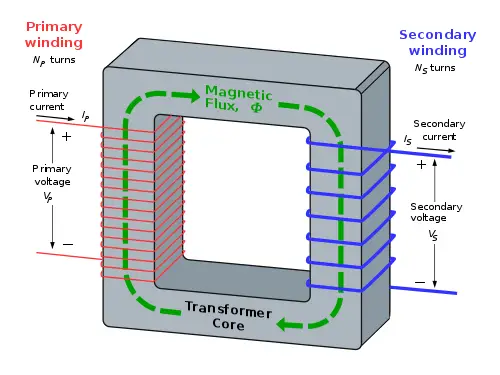
Transformer Core:
The main part of the Magneto ignition system is the Transformer Core which consists of two types of windings.
One is the Primary winding and the other is the Secondary winding. The primary winding is also called the low tension winding and the Secondary winding is called the high tension winding.
One end of the primary winding is grounded and the other end is connected with the link, contact breaker and the capacitor.
Contact Breaker:
The upper contact is grounded and the lower contact point is connected with the link.
It is generally used for making and breaking of Primary circuit. The pivoted arm(link) has a heel attached in the middle which breaks the contact point due to the action of a cam (which is driven by the engine).

Cam:
One end of the shaft is connected with the cam and the other end is connected with the magnet which has two poles, North and South.
Capacitor:
One end is connected with the primary winding and the other end is grounded and it is generally used to store the charge coming from the primary winding.
Ignition Switch:
It is placed parallel to the capacitor to avoid excessive power passing through it.[If you have seen, the ignition switch is in series in battery ignition system whereas here, it is in parallel]
One end of the ignition switch is in contact with the capacitor and the other end is grounded which is generally used to ON/OFF the engine by means of a key.

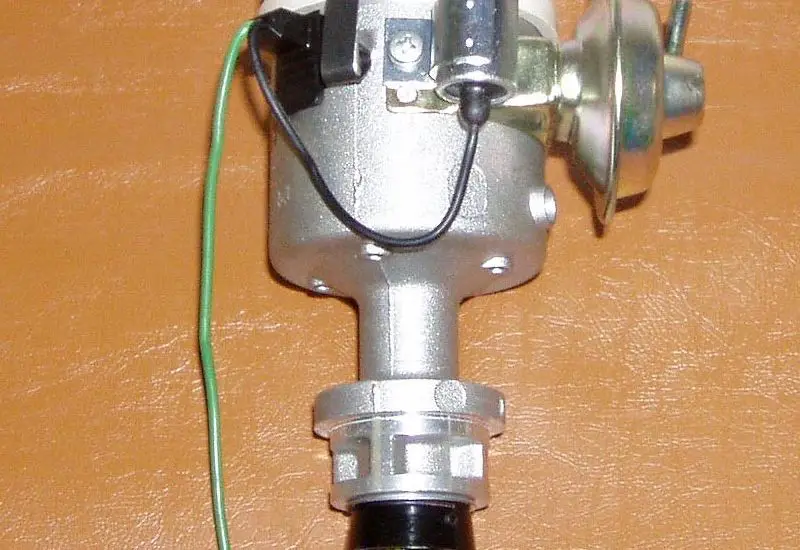
Distributor:
A distributor is provided for distributing the ignition surges to individual spark plugs in the correct sequence with respect to the firing order.
It consists of the rotor in the middle and the metallic electrode on the periphery. These metallic electrodes are directly connected to the spark plugs and are also known as Ignition harness.
As the rotor rotates, it passes the high tension current to the ignition harness which then carried these high tension currents to the spark plugs.

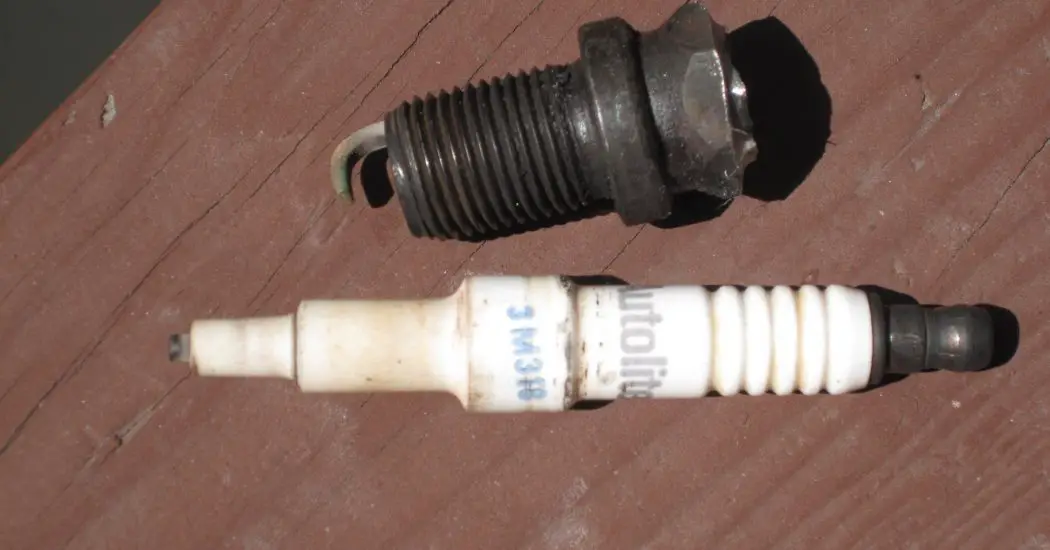
Spark Plugs:
It is the last component of the Magneto Ignition System. It consists of 2 electrodes, one attached to the high tension current-carrying wires and the other is grounded.
The potential difference between these electrodes ionizes the gap present between them and thus a Spark is generated which ignites the combustible mixture.

Working Principle of Magneto Ignition System:
When the engine starts, the cam rotates which also rotates the magnet connected on the other end of the shaft.
When the magnet rotates from North to South, the magnetic flux is generated which can travel in the direction from north to south and because of this flux, the current will be produced in the primary winding.
As the secondary winding is connected with the primary winding, the current also travels in the secondary winding.
When the poles are reversed from South to North, the flux is generated from South to North which will reverse the flux and current compared to North and South Pole so therefore in both the ways from north to south or South to North, the current will be produced which will induce the current in the secondary windings.
Note that we will get AC current when the magnet rotates in the core. At the maximum current, the flux starts reducing and it will be zero at a particular point and at that point, the contact breakers will open and the circuit will break.
When the contact breakers open, the current from primary winding will enter into the capacitor and charges it.
Due to this, the primary current falls and the magnetic field collapses. A large amount of current from the capacitor enters into the secondary winding which will step up the voltage.
The voltage generated is sent to the distributor for distributing the ignition surges to individual spark plugs in the correct sequence with respect to the firing order.
In this way, the current will be produced which is sufficient to produce for spark plugs in 2 wheeler engines.
Note: At the start, as the engine speed is low, the current generated by the magneto is quite small. As the engine speed increases the flow of current also increases. Thus there is always a starting problem with the magneto ignition system and sometimes there is a need for a separate battery for stating.
Applications of Magneto Ignition System:
This ignition system is best suited at high speed. So it is used in racing cars, aircraft engines, 2 wheelers, etc.
Advantages of Magneto Ignition System:
These are the following advantages of using Magneto Ignition System:
- This system is more reliable at medium speeds and high speeds.
- It requires less maintenance.
- It is more reliable, because of no battery usage.
Disadvantages of Magneto Ignition System:
Although there are some disadvantages of Magneto Ignition System, and those are:
- It has a starting problem.
- It is more expensive than the battery ignition system.
- There is a possibility of misfire due to leakage of current between the windings and the wires that carry current to the other parts.
More Resources for You
Battery Ignition System
Petrol Ignition System
Electronic Ignition System
So this is all about Magneto Ignition System, I hope you liked the whole paper, however, feel free to ask me any doubts in the comment section.
References:
- How Ignition Systems Work | Champion Tech Tips
- spark ignition system: Topics by WorldWideScience.org
Media Credits:
- Feature Image: By Andy Dingley (scanner) - Scan from (1911) Mechanical Transport, HMSO, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=10723920, Modified by Author.
- Image 1:
- Image 2: By BillC at the English language Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=27407689
- Image 3: By Sonett72 at English Wikipedia - Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1863764
- Image 4: By No machine-readable author provided. Borowski~commonswiki assumed (based on copyright claims). - No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=969167
- Image 5: Public Domain
- Image 6: By Ballista, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1012367
- Image 7: By Riccardo Nicola - Own work, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=6214163
- Image 8: By User:Industry shill - Own work by the original uploader, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=60305532