Otto Cycle: Process, PV Diagram, Efficiency with Derivation & Applications [Explanation & PDF]
Hello readers, in this article I will discuss on Otto Cycle, after reading this article, we will understand the concept of Otto Cycle, it's processes, Pressure-Volume Diagram, Efficiency, and lastly the applications of this cycle.
So before dive into the otto cycle, I would love to discuss on the SI Engine, it will help you to understand the topic more easily.
SI engines are used in passenger cars, motorcycles, aircraft, agricultural equipment, etc.
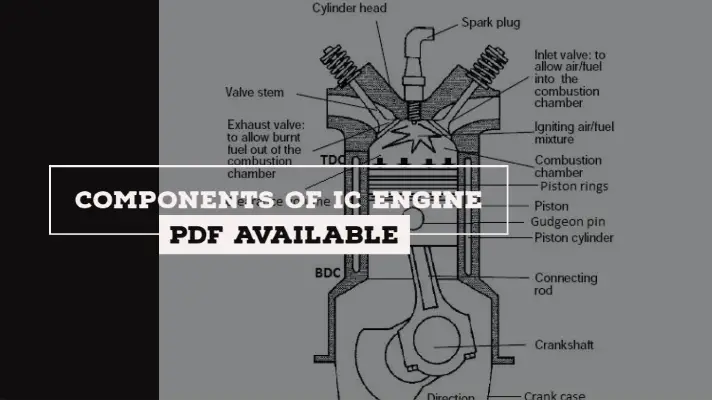
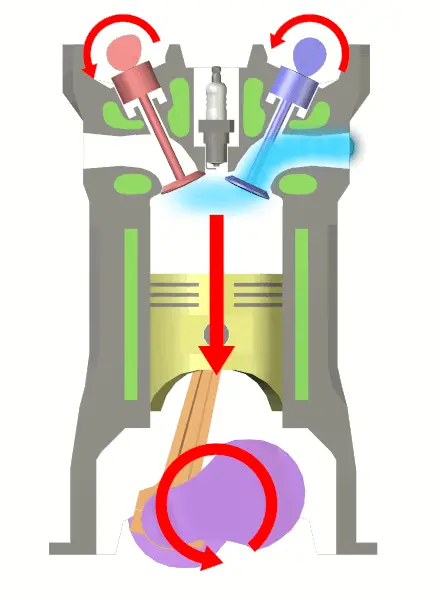
In a four-stroke engine, the cycle of operation is completed in four strokes of the piston or two revolutions of the crankshaft.
During the 4 strokes of the piston, there are five events to be completed and they are Suction, compression, combustion, expansion, and exhaust.
Each stroke consists of 180 degrees of Crankshaft rotation and hence a four-stroke cycle is completed through 720 degrees of crankshaft rotation.
Explanation of Four Strokes Occured in Petrol Engine:
The cycle of operation for the four-stroke engine consists of
- Suction stroke
- Compression stroke
- Expansion or power stroke
- Exhaust stroke
The working of 4 Stroke petrol(SI) engine was explained below.
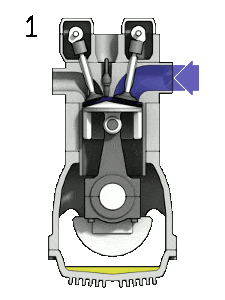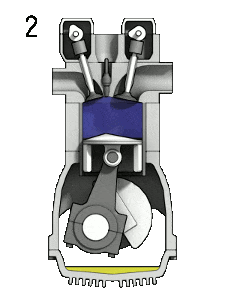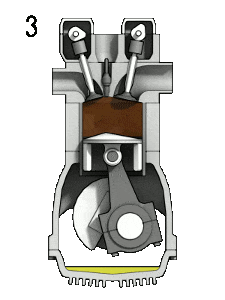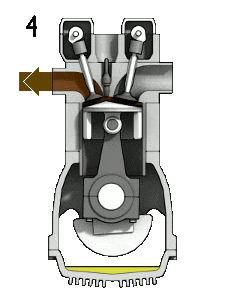
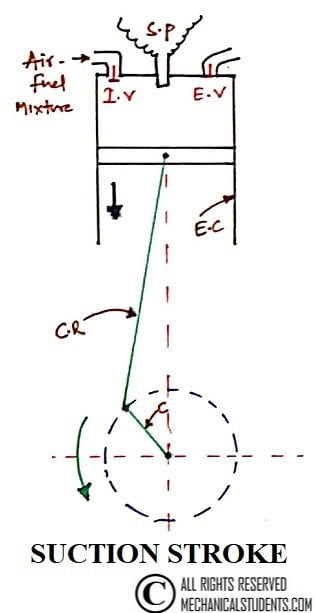
1. Suction stroke:
It starts when the piston is at the Top Dead Centre (TDC) and about to move downwards. During suction stroke, the inlet valve is open and the exhaust valve is closed.
Piston moving downwards creates a partial vacuum i.e. the pressure inside the cylinder is less than the atmospheric pressure. Due to pressure difference, the Air-Fuel mixture is sucked into the engine cylinder.
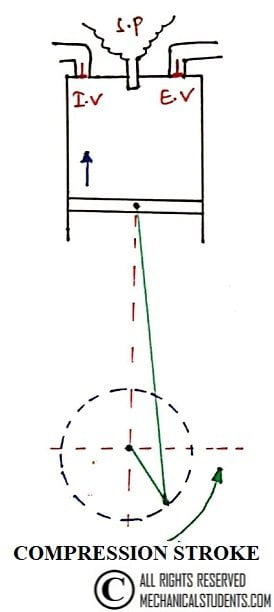
2. Compression Stroke:
During this stroke, the inlet and exhaust valves are in the closed position. The charge taken into the cylinder during the suction stroke is compressed by the return stroke of the piston.
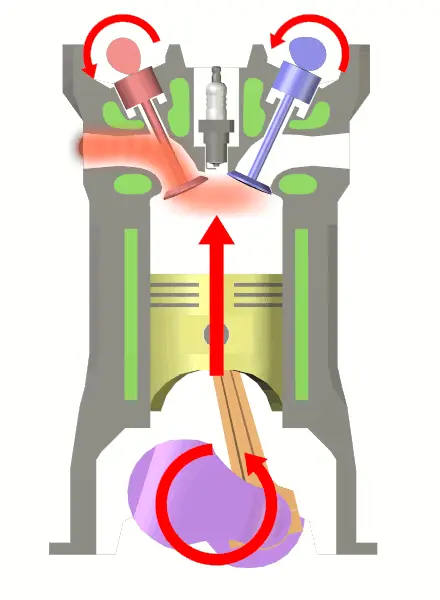
At the end of the compression stroke, the mixture is ignited with the help of an electric spark between the electrodes of a spark plug located on the cylinder head.
Burning takes place when the piston is at the Top Dead Centre (TDC). During burning, the chemical energy of the fuel is converted into heat energy and the pressure at the end of the combustion process is considerably increased due to heat release.
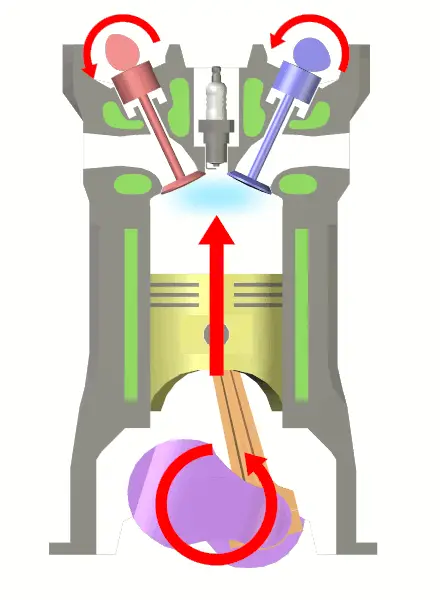
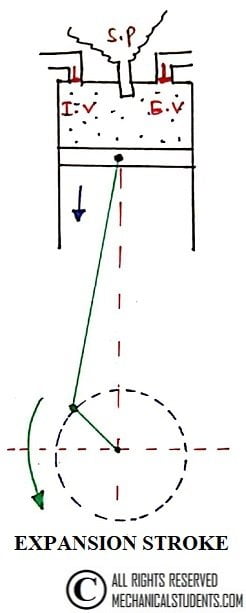
3. Expansion Stroke:
This is the Power stroke or Working stroke in which both valves are closed and high-pressure gas expands. At the end of the expansion stroke, the exhaust valve opens.
Some of the burnt gases come out through the exhaust valve. Due to this, the pressure decreases nearly at constant volume.
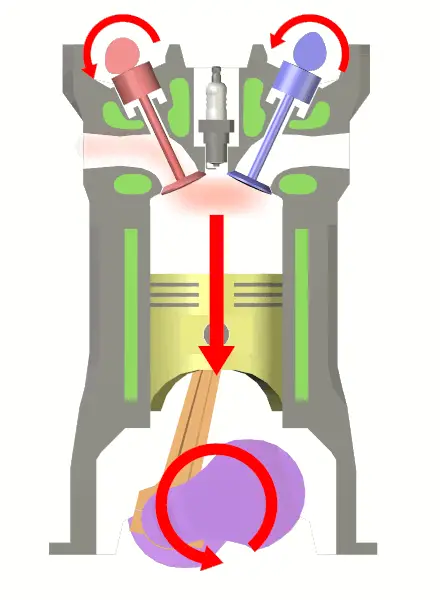
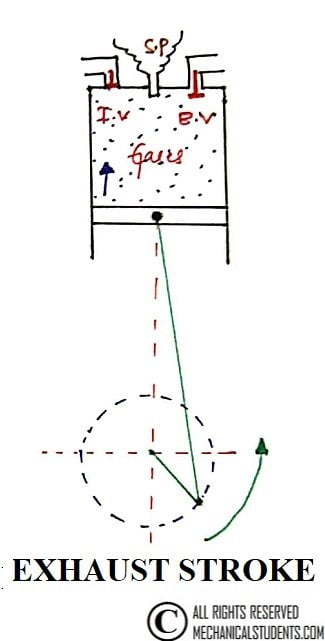
4. Exhaust Stroke:
During this stroke, the exhaust valve is open and the inlet valve remains closed. Piston moving upwards (BDC to TDC) forces the burnt gases through the exhaust valve.
At the end of this stroke, the exhaust valve closes and the inlet valve opens.
The fresh charge is taken into the engine cylinder while the Piston moving downwards. All the above events are repeated for the next cycle.
So now let's move to the cycle.
Explanation of Otto Cycle:
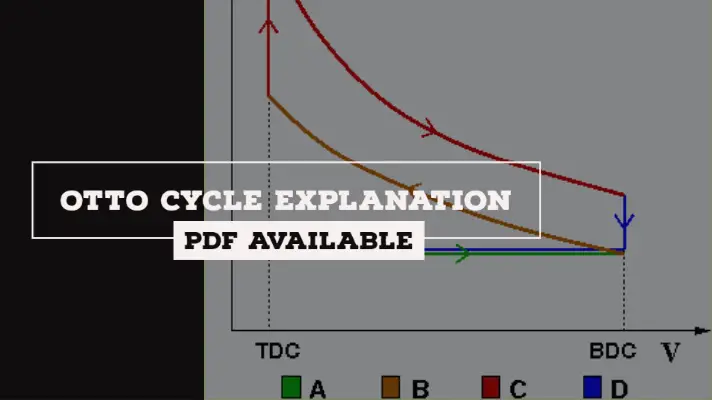
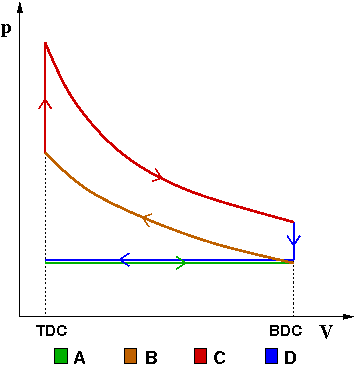
Otto Cycle is a constant volume cycle on which petrol and gas engines work. The Otto cycle consists of 4 processes and are as follows.
- Process 1-2: Reversible Adiabatic Compression or Isentropic Compression
- Process 2-3: Constant Volume heat supply
- Process 3-4: Reversible Adiabatic Expansion or Isentropic Expansion
- Process 4-1: Constant Volume Heat Rejection
The explanation of above processes are as follows.
Process 1-2: Reversible Adiabatic Compression or Isentropic Compression:
The air is compressed into the clearance volume of the cylinder and thus raising the pressure and temperature of the air. But, entropy remains constant as there is no heat transfer across the cylinder walls.
Process 2-3: Constant Volume heat supply (or) Heat Addition:
heat is supplied to air from hot body while the volume of the air remains constant. Thus the work done is zero but the pressure and temperature of the air increase further to the maximum value attained in the cycle. Due to heat supply(addition), there is an increase in entropy.
Qs = Cv(T3-T2)
Process 3-4: Reversible Adiabatic Expansion or Isentropic Expansion:
Air expands adiabatically causing the work-energy to be transferred to the surroundings at the expense of internal energy of the air.
Entropy remains constant as there is no heat transfer but the Pressure, Temperature and Volume decreases from stage 3 to 4.
Process 4-1: Constant Volume Heat Rejection
Heat is rejected from air to cold body. During the heat rejection, the air is maintained at constant volume and due to heat rejection, entropy decreases, pressure and temperature also decrease to initial state.
QR = Cv(T4-T1)
Thus, the cycle is completed.
Derivation of Otto Cycle:
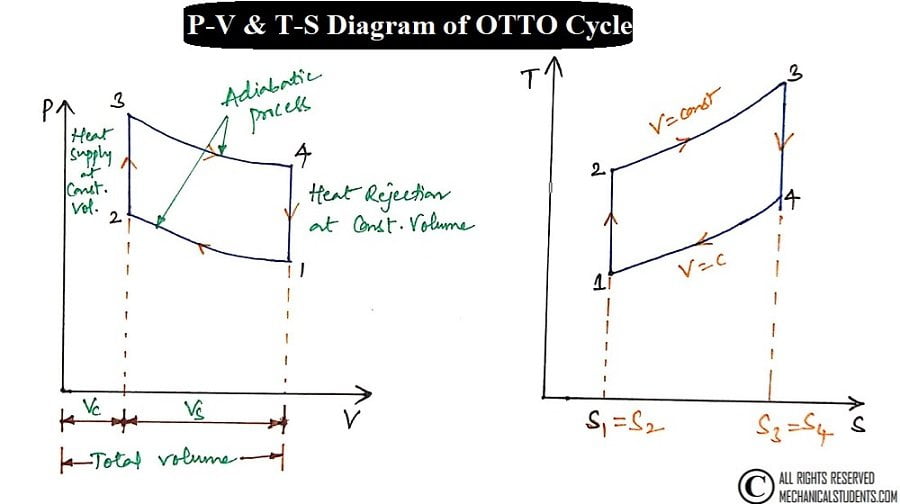
Follow the below derivation in order to calculate the efficiency of the Petrol engine by Otto Cycle.

Now, Let's consider the process from 1-2 as Adiabatic Compression & 3-4 as Adiabatic Expansion which was derived below in a hand written format.
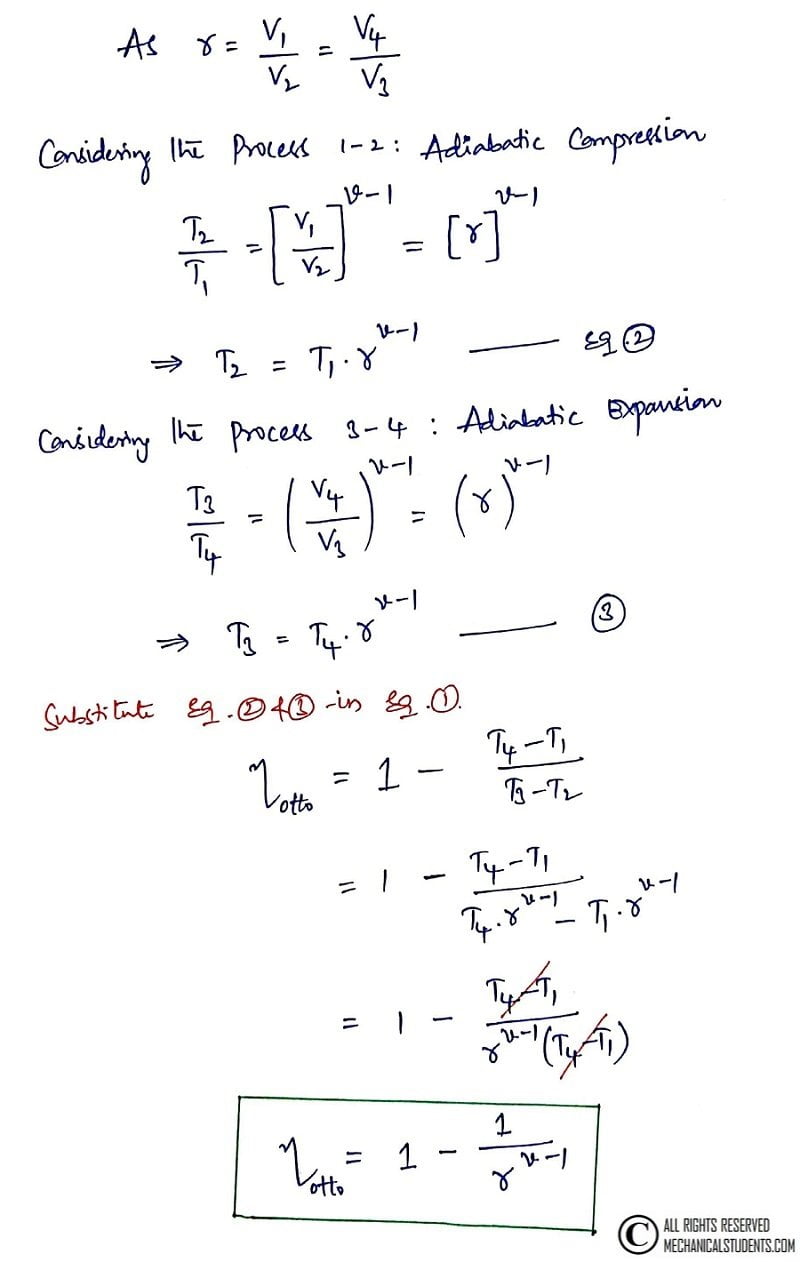
This is the detailed derivation of Otto Cycle and we can get the efficiency of the cycle by the derivation of Otto cylce.
Applications of Otto Cycle:
The applications of Otto Cycle are as follows.
- The Otto cycle was essential for the modern world where it can provide energy for most of the transportation.
- You can see the variety of automobiles seen on the road which uses the Otto Cycle to convert gasoline into motion i.e. Chemical Energy--> Heat Energy-->Mechanical Energy.
So this is all about Otto Cycle, I hope you liked this article, if so then don't forget to share this stuff among your friends.
More Resources:
Carnot Cycle
Diesel Cycle
References [External Links]:
- Spark Ignition Engine - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- SI engine combustion