Sliding Mesh Gearbox: Components, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications [PDF]
In automobiles, Sliding Mesh Gearbox is one of the transmission systems which is of the oldest type. As we have two types of Transmission systems, one is Manual Transmission and the other is Automatic Transmission.
In the last session, we discussed the Cone clutch, Electromagnetic clutch, and Single Plate Clutch, and we are moving towards the Transmission system i.e. Gearbox where we can discuss different types of Gearbox in detail.
Sliding Mesh Gearbox will come under Manual Transmission and overcome the limitations of Sliding Mesh Gearbox, Constant Mesh Gearbox, and Synchromesh Gearbox has come into the picture.
Now, Let's dive into the concept of Sliding Mesh Gearbox.
Components of Sliding Mesh Gearbox:
The Components of the Sliding Mesh Gearbox are as follows:
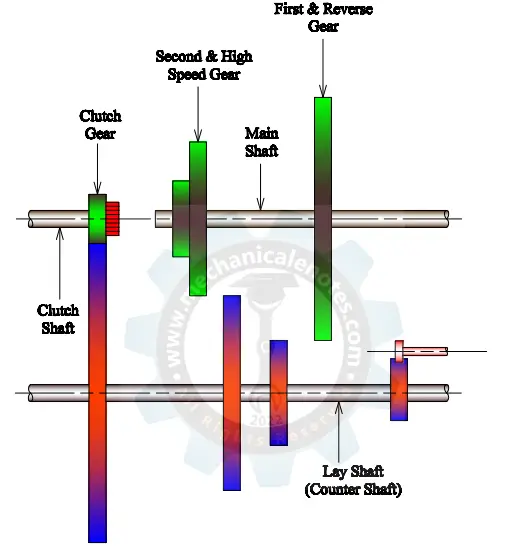
1. Shafts
- Clutch shaft
- Lay Shaft
- Main Shaft
2. Gears
- Fixed Gears
- Movable Gears
- Idler Gear
- Clutch Gear
3. Gear Lever
The explanation for the Components of Sliding Mesh Gearbox
#1 Shafts:
The shaft is generally used to transmit the power from one end to another end. There are three types of shafts in the case of Sliding Mesh Gearbox.
Clutch Shaft:
The clutch shaft is used to transmit the power from the engine when the clutch is in an engaged position. When the clutch shaft is rotating, the clutch gear which is attached at the end of it also rotates along with the clutch shaft.
Lay Shaft:
The lay shaft is an intermediate shaft between the clutch shaft and the Main shaft which provides meshing of fixed gears to the movable gears to provide the output appropriately.
The fixed gears are attached to the lay shaft and they are in mesh with the gears of the main shaft and the gear of the clutch shaft.
Main Shaft:
This shaft acts as an output shaft for the transmission of power from the engine shaft via a lay shaft. The gears with internally splined grooves are arranged on the main shaft so that they can mesh easily with the gears of the lay shaft.
#2 Gears:
Fixed Gears:
These gears are attached to the lay shaft for proper mesh with the gears of the main shaft. As they are fixed, if one gear rotates then all the gears rotate along with the lay shaft also.
Movable Gears:
These gears are attached to the Main shaft and are independent. It means, that if one gear rotates, then other gears do not rotate w.r.t. the shaft. As the vehicle has to move in any of one gear (might be 1st,2nd,3rd, or 4th), there is no need for the rotation of another gear.
Idler Gear:
This gear is used when the vehicle needs to move in the reverse direction. This gear places its position in the center of lay shaft gear and main shaft gear and thus the reverse action is taking place in the vehicle.
Clutch Gear:
This gear is attached at the end of the clutch shaft for transmitting power from the engine to the lay shaft and main shaft respectively.
#3 Gear Lever:
This lever is used by the driver to change the gear by means of a selective mechanism.
Working of Sliding Mesh Gearbox:
The Sliding Mesh Gearbox uses Spur Gears for the transmission of power from the engine shaft to the main shaft. It generally consists of 3 shafts i.e. Clutch shaft, Lay shaft, and Main Shaft whose explanation was given above.

It is a transmission mechanism of Just 4 gears and out of these 4, one is the reverse gear. So here we have 1st gear, 2nd gear, Top gear, and the Reverse gear.
The power comes from the engine to the clutch shaft and thence to the clutch gear which is always attached at the end of the clutch shaft. All the gears on the lay shaft are fixed and are in mesh with the clutch gear and main shaft gears.
Let’s understand how the 4 gears mesh for the transmission of power. Here, the driving shaft is the Lay shaft and the driven shaft is the Main shaft.
Power Transmission by the First Gear:
As you know that the vehicle moves slowly in the first gear compared to all the other driving gears this is because the gear of the driving shaft (lay shaft) is small compared to the gear of the driven shaft (Main Shaft).
Due to this, it acquires maximum torque at low speed and this can be obtained by meshing the smallest gear (C) on the lay shaft to the biggest gear (D) on the main shaft.
Power Transmission by the Second Gear:
The Torque acquired is smaller and the speed acquired is larger than the first gear and this can be obtained when the middle size gear (F) of the main shaft meshes with the second smallest gear (E) of the lay shaft.
Power Transmission by the Third Gear:
The third Gear is the Top gear which provides Maximum speed and Minimum Torque and this is obtained when the middle gear (F) of the main shaft is in mesh with the clutch gear (A) by means of a dog clutch.
Due to this, at top gear, the vehicle moves at a higher speed because the engagement of the clutch shaft is equal to the main shaft.
Therefore, with the speed of the clutch shaft, the main shaft rotates for the transmission of power.
Power Transmission by the Reverse Gear:
Here the idler gear is to be placed in between the bigger diameter gear (D) of the main shaft and the smaller diameter gear (G) of the lay shaft. Therefore, the vehicle moves in the reverse direction.
In this way, by the usage of 3 driving gears and 1 reverse gear, the power transmission takes place in the Sliding Mesh Gearbox.
Advantages of Sliding Mesh Gearbox:
Here is some advantage of the Sliding Mesh Gearbox:
- The mechanism of this gearbox is simple compared to Constant Mesh Gearbox and Synchromesh Gearbox.
- There should be fewer fluctuating loads because only one gear is in mesh at a time.
Disadvantages of Sliding Mesh Gearbox:
These are some disadvantages of the Sliding Mesh Gearbox:
- The Mechanical Efficiency was very low in the case of the Sliding Mesh Gearbox.
- The driver requires considerable skill for changing the gears because the gears of the main shaft and lay shaft are away from each other.
Applications of Sliding Mesh Gearbox:
- Renault Voiturette used a manual 3-speed transmission.
- Mercedes 35HP used 4-speed manual transmission
To avoid the disadvantage of Sliding Mesh Gearbox, Constant Mesh Gearbox has come into the picture and that concept will be discussed in the next article.
More Resources:
Single Plate Clutch
Electromagnetic Clutch
Cone Clutch
Reference [External Links]:
Media Credits:
Feature Image: Modified By Author