Forging Process: Definition, Types, Diagram, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications [PDF]
Forging Process is a metal forming process in which the forces are applied on the material such that the stresses induced in the material are greater than the yield stress and less than the ultimate stress so that the plastic deformation produced in the material will be used for changing the shape of the component is called as Metal Forming Process.
Advantages of Metal Forming Process:
- Wastage Of material will be minimum or sometimes zero.
- The grain orientation is possible.
- In some material forming processes, an increase in strength and hardness of the material will be taking place.
- The production rate is high.
Now, let's dive into the main concept i.e. Forging Process.
Forging Process Definition:
Forging is a Metal Forming Process in which the workpiece is heated to higher temperatures and is placed on the die(work region). Now, a large amount of compressive force is applied to the workpiece with either similar die or hammers in a vertical direction so that the shape change(deformation) takes place.

In the forging process, the forces applied are either continuous or intermittent impact loads.
Forging Process Types:
The various types of Forging process is as follows.
According to Temperature:
- Hot Forging
- Cold Forging
According to the Arrangement of Die:
- Open Die Forging
- Closed Die Forging
According to the Forging Equipment:
- Smith forging
- Drop Forging
- Press Forging
- Machine Forging
Now let's discuss one by one...
According to Temperature:
Hot Forging Process:
Deforming the material at a temperature greater than or equal to recrystallization temperature is called a hot forging process.
Cold Forging Process:
Deforming the material at a temperature, less than recrystallization temperature is called a Cold Forging Process.
Note:
Recrystallization temperature is the minimum temperature at which the grains start changing their behavior.
Let's know about Hand Forging Process and Machine Forging Process.
Hand Forging Process:
Hand Forging is also called as Smithing or Blacksmithing. It is the simplest form of forging in which the metal to be heated to high temperatures in the fire of a forge, and then it is beaten into shape on a metal anvil with sledges or hammers in order to get the required shape.
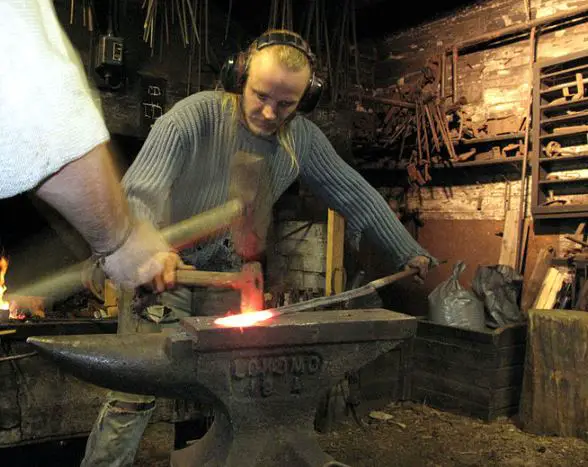

Hand forging always uses drop hammer type because the continuous force due to the human hand is not sufficient to produce the deformation in the workpiece.
- The workpiece is compressed between two flat or simple shaped dies.
- It is similar to a compression test when the work part has a cylindrical cross-section and is compressed along its axis or its sides.
- This Deformation operation reduces height and increases the diameter of the work or Cross-section.
Machine Forging Process:
In machine forging, because the force required is obtained from a machine, it is possible to use either continuous force application or intermittent impact load application known as drop hammer type.
Applications of Forging Process:
The applications of Forging Process are as follows.
- Agriculture tools, Cutting tools, nails, machine parts spring, hook, screw, pin, etc.
- Furniture manufacturing.
- Aircraft and missile product.
- Building materials like a handle, bolt, hinge, etc.
- Home appliance and military products.
This is the detailed explanation of Forging Process. If you have any doubts, ask us and we will reply it soon.