Computer-Aided Process Planning (CAPP): Generative, Variant & Retrieval CAPP [PDF]
Process planning can be defined as an act of preparing, processing documentation for the manufacturing of a piece, part of an assembly is called Process Planning. In this article, I will be explaining about Process planning, Computer-Aided Process Planning (CAPP), Generative CAPP, Variant CAPP, Retrieval CAPP, and all its features in a detailed manner.
In order to know about Computer Aided Process Planning, you must know about Process Planning First which was mentioned below.
Steps of Process Planning in Manufacturing:
- Analysis of part requirements
- Selection of raw workpiece
- Determining manufacturing operations and their sequences
- Selection of machine tools
- Selection of tools, work holding devices, and inspection equipment
- Determining machine conditions (cutting speed, feed, and depth of cut)
- Manufacturing times (setup time, lead time, and processing time).
Two important areas in the life cycle of a product are design and manufacturing. Process planning serves as an integral link between design and manufacturing. i.e.
- Process Planning in Design
- Process Planning in Manufacturing
Process planning consists of preparing a set of instructions that describe how to fabricate a part or build an assembly which will satisfy engineering design specifications.
The resulting set of instructions may include any or all of the following:
- Operation sequence
- Machines
- Tools
- Materials
- Tolerances
- Cutting parameters
- Processes (such as how to heat-treat)
- Jigs
- Fixtures
- Time standards
- Setup details
- Inspection criteria
- Gauges
- Graphical representations of the part in various stages of completion.
Process Planning in Different Environments:
- In tool-room type manufacturing, “make a part as per drawing” is sufficient
- In a metal-forming type of operations, the process planning requirements are embedded directly into the die.
- Process planning is fairly trivial
- Job-shop type manufacturing requires most detailed process planning
- Design of tools, jigs, fixtures and manufacturing sequence is dictated directly by the process plan.
Requirements for Process Planner:
- Must be able to analyze and understand part requirements.
- Have extensive knowledge of machine tools, cutting tools, and their capabilities.
This is the detailed explanation of Process Planning. Now, let's discuss Computer-Aided Process Planning.
Computer-Aided Process Planning (CAPP):
It can be defined as an act of preparing processing documentation for the manufacturing of a piece, part or an assembly, etc. is called as process planning. If process planning was done by using a computer it is called Computer-Aided Process Planning(CAPP).
This post mainly focuses on, the structure of Computer-Aided Process Planning(CAPP) in a detailed manner.
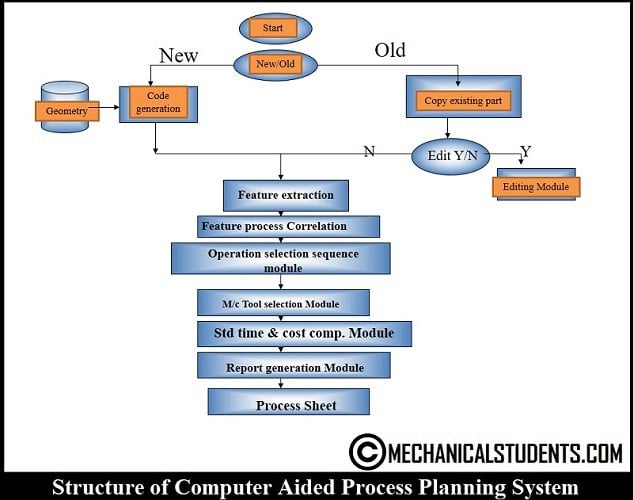
COMPUTER-AIDED PROCESS PLANNING(CAPP) METHOD:
- It can systematically produce accurate and consistent process plans.
- It can reduce the cost and lead time of process planning.
- Less skilled process planners may be employed.
- It increases the productivity of process planners.
- Manufacturing cost, manufacturing lead time and work standards can easily be interfaced with the CAPP system.
Why Computer Aided Process Planning(CAPP)?
- Understand the interactions between the part, manufacturing, quality, and cost.
- Systematically produce accurate and consistent process plans.
- Reduce the cost and lead time of process planning.
- Skill requirements of process planners are reduced.
- Increased productivity of process planner.
- Easily interface with other application programs for further analysis.
This is the detailed explanation of Computer-Aided Process Planning. Now, let's discuss the parts of it. They are:
- Generative Computer Aided Process Planning (G CAPP).
- Variant Computer Aided Process Planning (Variant CAPP).
- Retrieval Computer Aided Process Planning (Retrieval CAPP).
The detailed explanation of all these process planning is as follows:
1. Generative Computer Aided Process Planning(G CAPP):
A system which automatically synthesizes a process plan for a new component is called Generative Computer Aided Process Planning. It synthesizes the process information to create a process plan for a new part automatically without human intervention. This post mainly focuses on what is the Structure and Advantages of Generative Generative Computer Aided Process Planning(G CAPP) in a detailed manner.
Characteristics of Generative Computer Aided Process Planning(G CAPP):
- No existing standard plans.
- Able to generate process plans for both new and existing parts.
- Process plans are generated by means of:
- Decision logic.
- Formulas.
- Technology algorithms.
- Geometry based data.
- Geometry-based coding scheme.
- Process knowledge in the form of decision logic and data to perform uniquely the main decisions for converting apart from raw materials to a finished state.
A requirement of Generative Computer Aided Process Planning:
Part description:
- Part to be produced must be clearly and precisely defined in a computer compatible format (OPITZ, AUTAP).
Manufacturing databases:
- The logic of manufacturing must be identified and captured.
- The captured logic must be incorporated in a unified manufacturing database.
Decision making logic and algorithms:
- Decision trees.
- Expert Systems: AI-based approaches.
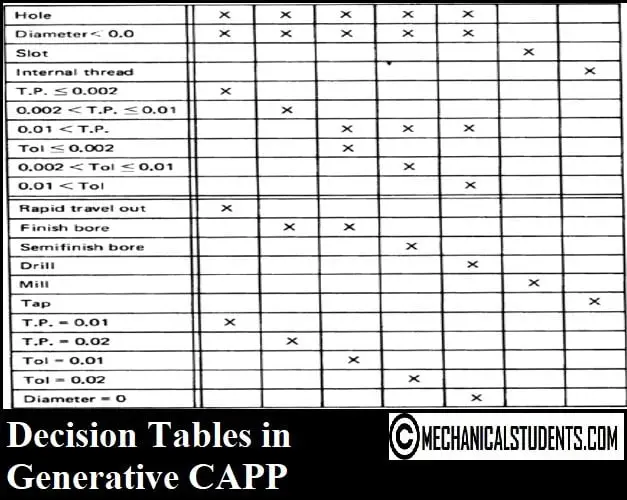
Decision Tables in Generative CAPP:
- A decision table program structuring tool provides readable documentation as an automatic by product.
- A decision table is portioned into conditions and actions.
- Can be used with pre-processor to eliminate some program coding to provide automatic checks for completeness, contradiction, and redundancy.
Techniques for Generative Computer Aided Process Planning (G CAPP)
- Identify the machinable volume and attach necessary technological details relevant for mfg.
- Do a preliminary sorting of pockets in order of levels that clearly indicate the likely sequence in the final process plan.
- Examine the pocket for any possibility of combining so that the machining operations could be reduced.
- Select the machine tools that can be used for each of the identified pockets.
- Identify the process sequence required for the machining of the pocket based on the technological requirements.
- For each of the pocket and the operation decided, select the cutting tool required.
- Sort the operations on the basis of the machine tools and cutting tools.
- Sequence the operations on the basis of the machine tools and cutting tools by making use of heuristic rules.
- Evaluate the machining time and idle time and select the final process plan based on the lowest cost and machining time.
- Present the final results in a suitable form.
2. Variant CAPP:
A process plan for a new part is created by recalling, identifying and retrieving the existing plan for a similar part and making necessary modifications for the new part. In this article, I am going to discuss Advantages and limitations of VARIANT CAPP (VCAPP) in a detailed manner.
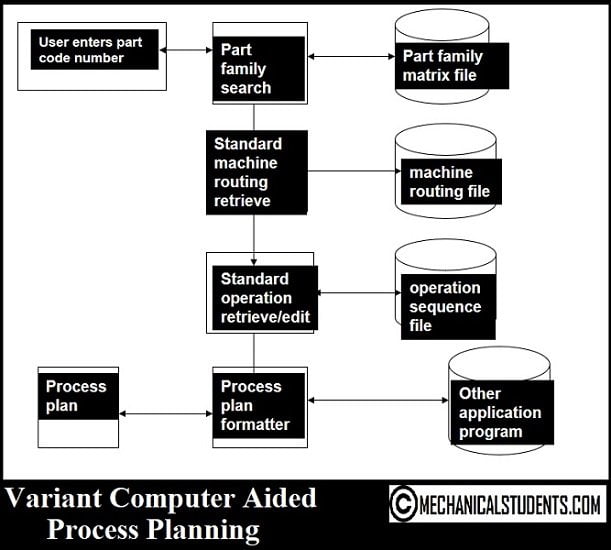
Steps involved in VARIANT CAPP are as follows:
- Define the coding system.
- Group the parts into part families.
- Develop a standard process plan.
- Retrieve and modify the standard plan.
3. Retrieval CAPP:
- Based on the principles of GT.
- Also called a VARIANT Computer Aided Process Planning(Variant CAPP).
- GT: Group Technology.
- The concept of grouping parts together depending upon their similarities in operation sequence or geometry is called Group technology.
- Experts’ knowledge and standard process plans as per GT are needed as a database.
- Considerable work is required to collect and organize data.
Salient points of VARIANT CAPP:
- Easy to build, learn and use.
- Experienced process planners are still required to edit the process plan.
- Cannot be used in an entirely automated manufacturing system without additional process planning.
Problems Associated with Variant PP:
- The components to be planned are limited to similar components previously planned.
- Experienced process planners are still required to modify the standard plan for the specific component.
- Variant planning cannot be used in an entirely automated manufacturing system, without additional process planning.
- These are the Advantages and Limitations of VARIANT CAPP.
Some FAQs Related to CAPP:
What is Computer-Aided Process Planning?
What is Process Planning?
What are the Steps of Process Planning?
1. Selection of raw workpiece
2. Determining manufacturing operations and their sequences
3. Selection of machine tools
What is Generative Computer Aided Process Planning?
What are the types of Computer aided process planning?
1. Generative Computer Aided Process Planning (G CAPP)
2. Variant Computer Aided Process Planning (Variant CAPP)
3. Retrieval Computer Aided Process Planning (Retrieval CAPP)
If you have any doubts, feel free to ask from the comments section. Please Share and Like this blog with your friends and social handles, so that it can reach to many.
References [External Links]:
- Computer Aided Process Planning - IGNOU
- Computer-aided process planning (CAPP)-archives.njit.edu
- (PDF) Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP) Approach