38 Recent Trends in Mechanical Engineering in 2022 PDF
Everyone who is in the field of Engineering has to know the recent trends in their fields so that they can understand things very easily in their own domain. Considering that, I had written a detailed article with related figures on 38 Recent Trends in Mechanical Engineering in the year 2022.
According to a report...
"Mechanical engineers are at the forefront of developing new technology for farming, transportation, environmental remediation, safety, food production, housing, security, water resources, healthcare, etc." says the report, based on the proceedings of The Global Summit on the Future of Mechanical Engineering, held April 16-18, 2008, Washington, D.C.
Let's dive into the topic...
38 Recent Trends in Mechanical Engineering:
I have listed 38 Trends in Mechanical Engineering. Students can take Individual Topics and can make the PPTs for their Technical Seminars so that they can know about the latest technologies in the field of mechanical engineering.
Apart from that, in this article, detailed information was given on all the latest technologies in Mechanical Engineering which were listed below.
Mechanical engineering is at the forefront of developing the latest technology in the following areas of
- 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
- Interconnected Machines
- Internet of Things
- Industry 4.0
- Digital Manufacturing
- Bio-Medical Engineering
- Green Manufacturing
- Nano-Technology
- Alternative Energy(Solar energy and Other Renewable energies)
- Mechatronics
- Robotics
- Smart Materials/Composites
- Automation and Intelligent System
- CAD-CAM Sustainability
- Agricultural Technology (Equipment used in Agriculture)
- Energy Solutions
- Textile Industry
- Self Driving Cars and New Automated Transport solutions
- Manufacturing Optimization
- Rapid Tooling
- Project Management
- Laser Cooling
- Cryogenics
- 4D Printing Technology
- Nano Electro-Mechanical Systems
- Digital Twins
- Hyperloop Technology
- Computational Fluid Dynamics
- IIOT (Industrial Internet of Things)
- Beamed Energy Propulsion
- Autonomous Vehicle
- A scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet)
- Fuel-Efficient Engine Technologies
- High-Speed Machining
- Advances in Gas Turbine Technology
- Stir Friction Welding
- Agile Manufacturing
- Advances in Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning.
Let's discuss each in detail.....
1. Additive Manufacturing (AM) or 3D Printing:
As the name implies, additive manufacturing adds the material to create a 3D object. Additive Manufacturing is also called 3D Printing.
Additive Manufacturing is a process in which the model of an object has to be created in any Modelling Software(CAD Software) and has to save in the format of.STL.
[.STL stands for Standard Triangular Language]
This format essentially "slices" the object into ultra-thin layers. Each successive layer bonds to the preceding layer of partially melted or melted material.
This file has to be sent to an Additive Manufacturing machine or 3D Printing Machine to produce a 3D object in the form of fine layers.
The 3D Printing Machine understands the data in the(.STL) file created in CAD software by CAD Engineer and processes accordingly in the form of smooth and Fine layers of plastic to create precise geometry shapes.
Additive Manufacturing Materials:
They are a variety of materials used in the Additive Manufacturing machine to create 3D objects and some of them are as follows.
Plastics: (Thermoplastics)
One of the most popular materials used in Additive Manufacturing machines is Thermoplastics.
They are used because of the following reasons:
- When it is heated, it turns soft and at this point, we can change the shape of the component.
- Light Weight.
- It is recyclable.
Ex: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), Polycarbonate (PC) and Polylactic Acid (PLA) offer distinct advantages in various applications.
Ceramics:
A variety of ceramics are also been used in additive manufacturing such as Zirconia, Tricalcium phosphate, alumina, etc.
Metals:
Metals and Metal alloys are used in additive manufacturing machines from precious metals like gold, silver, etc. to strategic metals like stainless, etc.
Additive Manufacturing Applications:
Aerospace:
Additive Manufacturing excels in producing the components for aerospace applications that are light in weight and stronger enough to withstand the desired load.
Ex: Jet engine parts.
Automotive Industry:
Aluminum alloys are used to produce exhaust pipes and parts of the pump, and polymers are used to produce bumpers of an automobile.
Health Care:
- At, the New York University School of Medicine, a study of 300 patients will evaluate the efficacy of patient-specific, multi-colored kidney cancer models using additive manufacturing.
- 3D printed surgical implants for patients suffering from bone cancer disease.
Advantages of Additive Manufacturing:
- AM creates the components which are lighter, stronger, and which otherwise by conventional methods(machining, etc) takes huge time, money, etc.
- In AM, which offers a digital-to-digital process eliminates traditional machining and offers a more dynamic, design-driven process.
- The Lead time is frequently reduced in AM compared to Traditional.
- The parts which are assembled in traditional methods can be eliminated by fabricating into single components in Additive Manufacturing.
Additive Manufacturing Technologies:
There are various Additive Manufacturing Technologies and a few of them are as follows.
- Fused Deposition Modelling(FDM)
- Selective Laser Sintering(SLS)
- Vat Photopolymerization
- Material Jetting
- Binder Jetting
- Direct Energy Deposition
Two of the popular additive manufacturing Technologies are presented below
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM):
It is one of the Rapid Prototyping techniques which fuses or melts the material(similar to the extrusion Process) and deposits in the form of layer by layer in order to construct a component whose data had been taken from the cad(.stl) file.
Parts of Fused Deposition Modelling:
- Base(For Support)
- Filament (Plastic Material)
- Feed Rollers (Provide the proper amount of material)
- Supply Rollers (Supply plastic material at the beginning)
- Heating Elements (Heats the Plastic to a semi-liquid state)
- Nozzle or Extrusion Chamber
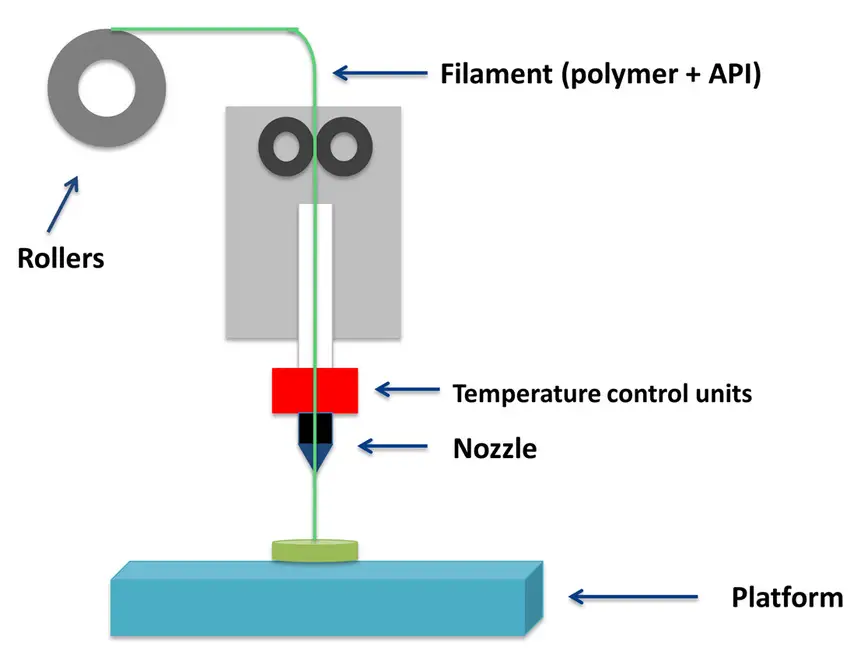
Working of Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM):
In this process, the raw material is a plastic component, which is also called a filament in the FDM technique is drawn by means of rollers and is to be passed into the heating chamber by means of Feed rollers.
The plastic material is to be heated up to the formation of semi-liquid and is to be passed into the extrusion chamber.
In the Extrusion chamber, it has to be passed through a nozzle(similar to the extrusion process) and the product is obtained in the form of layers.
This is a detailed explanation of the working of the fused deposition modeling technique in additive manufacturing.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS):
It is also one of the Rapid Prototyping Technique which uses laser machine for sintering the raw material to get the desired shape in the form of layer by layer.
Sintering means heating the raw material(Powder) so that it is melted and converted into a thick layer called sintering.
It is a process that creates a physical object from a digital design. The engineering design of a model can be prepared in CAD software.
The design file(.stl) is then sliced Into small layers of equal thickness and Uploaded to an additive manufacturing machine.
The above figure shows the sintering of the material layer by layer to form a final component.
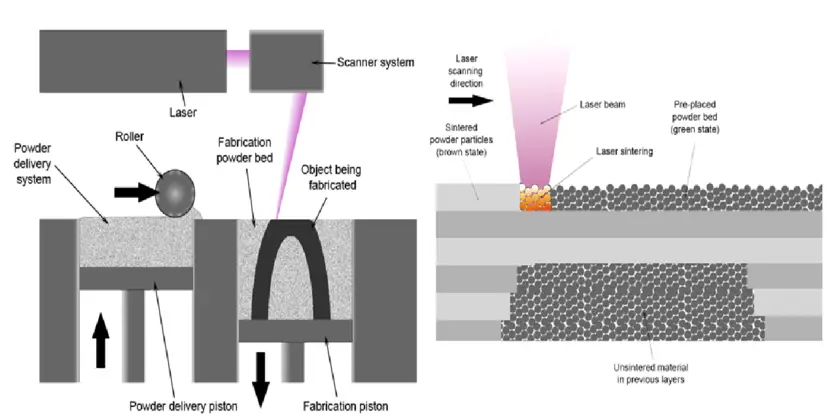
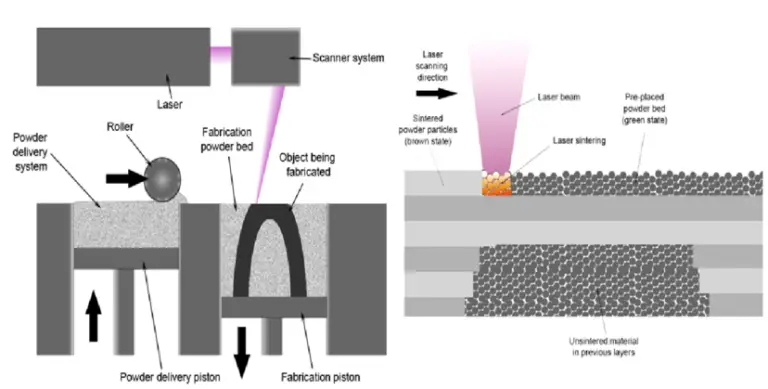
Parts of Selective Laser Sintering:
- Laser
- Scanner
- Powder
- Chambers with Piston Arrangement
- Roller
Working of Selective Laser Sintering:
The manufacturing process begins once the thin layer of metal powder is spread across the platform.
On the Platform, two chambers are present with Piston arrangement. One piston is moving up and the other piston is moving down as shown in the figure.
The First Chamber Piston pushes up the powder so that it is above the platform. Now roller will push and spread the powder to another chamber.
The Second chamber whose piston is pushed down so that the powder material has to be filled in the form of layer by layer.
Now, a heat source such as a laser or electron beam then notes the first layer of the 3D design, and the scanner can scan the work region and post the laser so that the powder melts and deposits on the work platform in the form of layers.
The platform is loaded again and the layer of metal powder is spread across the platform.
The layering and melting process is then repeated until the process is complete.
The metallic powder is removed and the physical object is revealed or taken out from the powder and was cleaned so that impurities cannot be deposited.
Watch the video below to understand the concept of the SLS Process:
The parts produced by the Selective Laser Sintering are lighter, stronger, and more adorable than traditional or Conventional parts.
This is the explanation of Additive Manufacturing. Let's discuss the rest of the technologies in Mechanical Engineering.
2. Interconnected Machines:
Machines Interconnected or Machine to Machine(M2M) in the sense there is a direct communication either in the form of wired or wireless between devices using a communication channel.
Machines Interconnection includes industrial instrumentation that enables the sensors to communicate the information.
While using less power, the expansion of IP networks has made machine-to-machine communication faster and easier around the world.
These networks allow new business opportunities for suppliers and consumers.
Applications of Interconnected Machines:
- Machine-to-machine communication is used for remote monitoring.
- M2M is vital in warehouse management systems
- Machine-to-machine communication also plays a vital role in supply chain management.
3. Internet of Things (IoT):
In this system, there is no need for human intervention. Each and every system is under the control of devices connected around it.
It is a system of mechanical and digital machines which are provided with UIDs in order to transfer the data over a wide variety of networks.

It actually involves Machine learning with real-time analytics.
Traditional fields of wireless sensor networks, embedded systems, automation, control systems, and all other contributors for enabling the Internet of Things.
Examples that can come under the Internet of Things include thermostats, security systems, cars, alarm clocks, electronic appliances, lights in commercial and household environments, vending machines, speaker systems, and more.
Applications of IoT:
- Commercial applications like medical and health care, building and home automation, transportation, etc.
- Industrial applications like manufacturing and agriculture.
- Infrastructure applications like environmental monitoring, energy management, etc.
- Military applications like Ocean of things, Internet of battlefield things, etc.
4. Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is one of the trends of Mechanical Engineering which focuses on Data exchange and Automation in manufacturing technologies and processes which include the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, Cloud computing, Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT).
"Industry 4.0" factories have machines that have sensors and other parts with wireless connectivity which can visualize the entire production line and make the decisions on its own.
The Components of Industry 4.0 includes:
- Smart factory
- Internet of Things for manufacturing
- Smart Manufacturing
- Dark factories also known as Lights out Manufacturing
- 3D printing
- Big data analytics and advanced algorithms
- Data visualization
5. Digital Manufacturing:
As there are more automated tools in the manufacturing industry, it is the duty of the industry to model, run the simulation and analyze the machines, input materials, and tooling.
The name indicates that the manufacturing is controlled by means of numbers or numerals in the digital form i.e. write the G codes and M codes in a program and that can be operated by means of a central computer.
In order to meet the market demand, there will be a need for a large number of goods for the consumers. Making a few things or goods does not sustain the environment, therefore there is the need for Digital Manufacturing.
With the rise in the quality and quantity of computer systems in manufacturing plants, the transition to digital manufacturing has become popular.
As you can see that digital manufacturing would be sharing the same goals of
- Flexible Manufacturing
- Lean Manufacturing
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing
- Design for Manufacturing
But you can see a difference that digital manufacturing was evolved for the use of the computer world.
6. Biomedical Engineering:
Biomedical engineering (BME) is also known as medical engineering is the application of design concepts and engineering principles to biology and medicine for healthcare purposes.
This can solve advanced health care treatment which includes
- Diagnosis
- Monitoring
- Therapy
The contents which you can listen to in Biomedical Engineering are
- Biomedical optics
- Biomaterial
- Genetic engineering
- Biomechanics
- Tissue engineering
- Bioinformatics
- Pharmaceutical engineering
- Neural engineering
Some of the examples of medical devices are
- Dialysis machines
- Pacemakers
- Artificial organs
- Dental implants etc.
7. Green Manufacturing:
The “greening” of manufacturing in the sense of reducing waste and pollution by minimizing natural resource use, reusing and recycling waste, and reducing emissions.
Step by step procedure for Green Manufacturing:
- Design
- Procure
- Manufacture
- Packing and Distribution
- Customer used to the end of life
- Remanufacture
And the cycle continues….
Applications of Green Manufacturing:
- Lean Manufacturing
- Green Chemistry
- Automobile design and Manufacture+
- Product Design
Benefits of Green Manufacturing:
- Company Benefits
- Environmental Benefits
- Technological Benefits
Implementation of Green Manufacturing:
- Production Process
- International Organisation for standardization
- Regulations
Challenges of Green Manufacturing:
- Investment
- Long term effort
- Increase in production cost
- Engineers
This is the explanation behind Green Manufacturing.
8. Nano Technology:
It is defined as the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1-100nm.
Nanotechnology defined by its size is very broad, including fields of science such as
- surface science
- molecular biology
- microfabrication
- molecular engineering
- organic chemistry
- semiconductor physics
- energy storage
The current research is based on the following areas
- Nanomaterials
- Top-down approaches
- Bottom-up approaches
- Functional approaches
- Speculative
- Biomimetic approaches
- Dimensionality in nanomaterials
Applications:
Nano Electronics
The rest of the Recent trends in Mechanical Engineering will be updated soon...
Media Credits:
- Fused Deposition Modelling took from Youtube channel
- Selective Laser Sintering taken from Youtube channel





