Cast Iron: Properties, Types, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications

In the last article, we had discussed the Mechanical properties of metals along with Non-Ferrous metals and Iron-Carbon diagram explanation. Whereas in today's article, we will discuss the properties, types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications of Cast iron in detail.
What is Cast Iron?
The cast iron is obtained by melting Pig iron with coke, limestone, and steel scrap in a furnace. It contains carbon ranging from 2.1% to 4.5%. Cast iron also contains a small amount of silicon, manganese, phosphorus, and sulfur.
Properties of Cast Iron:
The properties of Castiron are as follows.
- It is having low cost.
- Very brittle.
- It is having high compressive strength and high wear resistance.
- It is having good casting characteristics.
- Cast iron melting point is lower than steel.
- It is having excellent machinability.
- Most cast irons are not malleable at any temp.
- Cast iron has less ductility and cannot be rolled or drawn or worked easily at room temp.
Types of Cast Iron:
The 4 types of Cast iron are presented below along with its composition, Microstructure, properties, Fracture surface and applications.
- Gray cast iron
- White cast iron
- Malleable cast iron
- Nodular or SG or ductile iron
Grey Cast Iron:
- These types of cast iron are widely used.
- Presence of graphite in the form of flakes (like fibre)

Composition:
- 2.5% - 4% Carbon
- 1% - 3% silicon, rest iron
Microstructure:
- α-ferrite and flake graphite
Properties:
- High fluidity, very high compressive strength, very effective in damping vibrations, low cost.
Fracture surface:
- Greyish, blackish surface when fractured (because of graphite flakes), Hence the name grey iron too.
Applications:
- Pressure vessels, clutch plates, pistons, cylinder heads, base structure for machines and heavy equipment that are exposed to vibrations, fittings, levers, valves, etc.
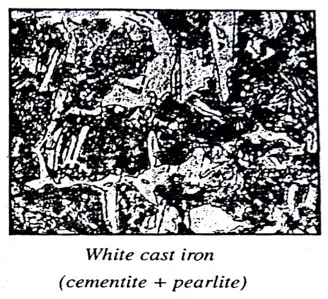
White Cast Iron:
The Characteristics of White Cast Iron are as follows.
Composition:
- 1.8% - 3.2% Carbon
- 0.3% - L8% Silicon, rest iron
Microstructure:
- Iron carbide (lightphase), pearlite (dark phase)
- No graphite
Properties:
- Very hard and brittle, highly wear resistant, no ductility and malleability, not machinable.
Fracture surface:
- Whitish surface (hence the name too).
Applications:
- Liners for cement mixers, certain types of drawing dies, ball mill, extrusion nozzles etc.
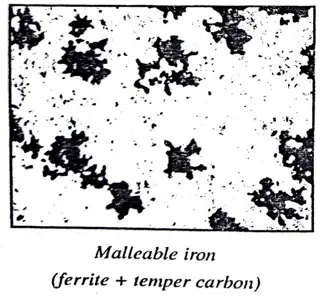
Malleable Cast Iron:
The Characteristics of Malleable Cast Iron are
Composition:
- 1.8% - 3.2% carbon
- 0.3%-1.8% silicon,rest iron.
Microstructure:
- Dark graphite rosettes in an α- ferrite matrix.
Properties:
- Highly malleable, very good machinability, good magnetic properties, wear resistance
Applications:
- Connecting rods, flanges, transmission gears, differential cases for the automotive industry, pipe fittings, valves, parts for railroads and marine works.
Nodular or Spheroidal Cast iron:
The Characteristics of Spheroidal Cast Iron are as follows...
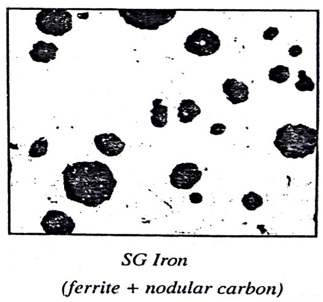
Composition:
- 3% to 4% Carbon, 1.6% to 2.8% Silicon, rest iron
- A very low percentage of phosphorus and sulphur
Microstructure:
- Dark graphite nodules surrounded by α- ferrite matrix
Properties:
- Highly ductile, very good machinability, high corrosion resistance and good creep properties at elevated temperatures.
Applications:
- Flywheel, wrenches, motor frames, furnace doors, lathe chucks, pump bodies etc.
Applications of Cast Iron:
The applications of Cast Iron are as follows.
- Machine tool structures. Example: bed, frame, etc.
- Pumps and compressors.
- Cylinder blocks and heads for I.C. engines.
- For transportation of fluids, cast iron is used for making pipes.
Cast Iron Advantages
The advantages of Cast Iron are as follows.
- The materials made up of cast iron are having good machinability(Grey Cast iron).
- It has good Casting properties.
- Comparing with steel, the cast iron has three to five times more compression strength.
- Cast iron has excellent resistance to wear.
- It has Resistance to deformation and has Low stress concentration.
Cast Iron Disadvantages
The disadvantages of Cast Iron are as follows.
- Cast iron has high brittleness.
- White cast iron is non-machinable.
- It has poor impact resistance and has a high weight to strength ratio.
- Machinability is poor.
This is the detailed explanation of Cast iron. If you have any doubts, you can ask us and we will reply you in 24hrs.
More Resources:
Types of steels and properties