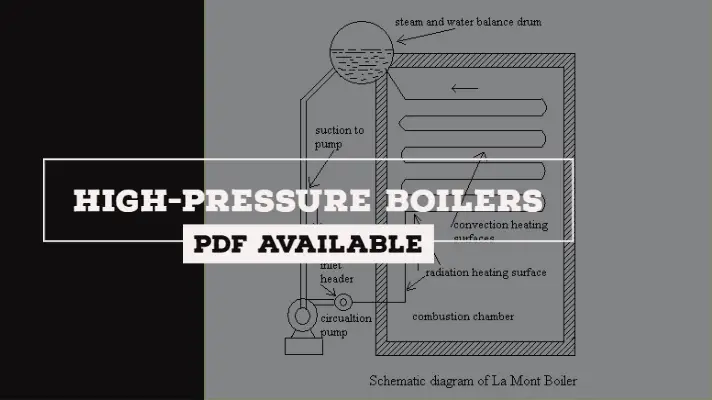
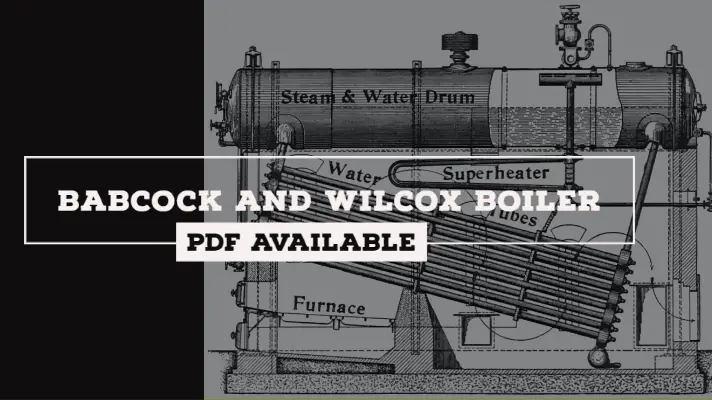
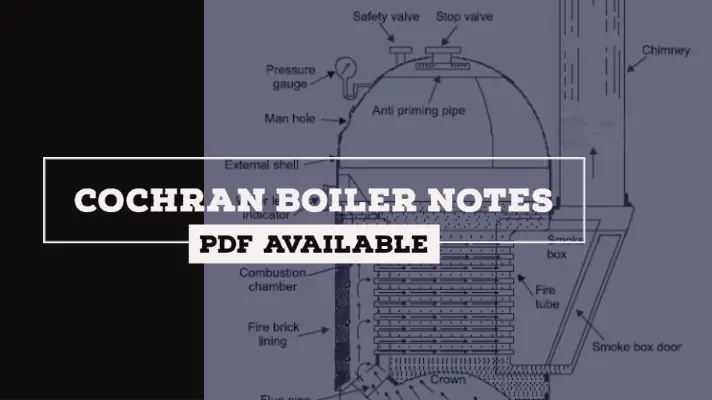
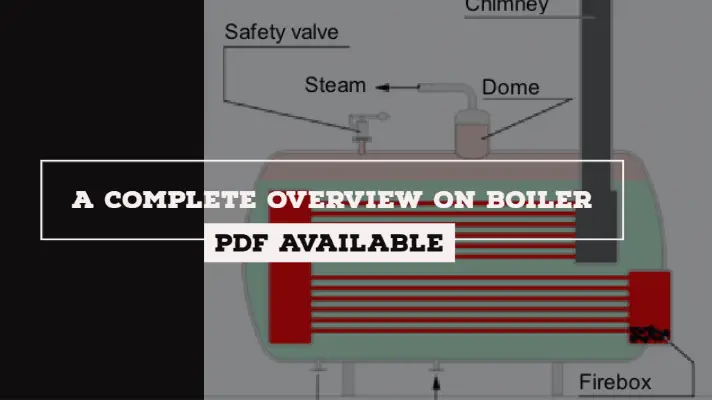
Steam Power Plant: Definition, Components, Layout, Working Principle, Uses, Advantages & Disadvantages [PDF]
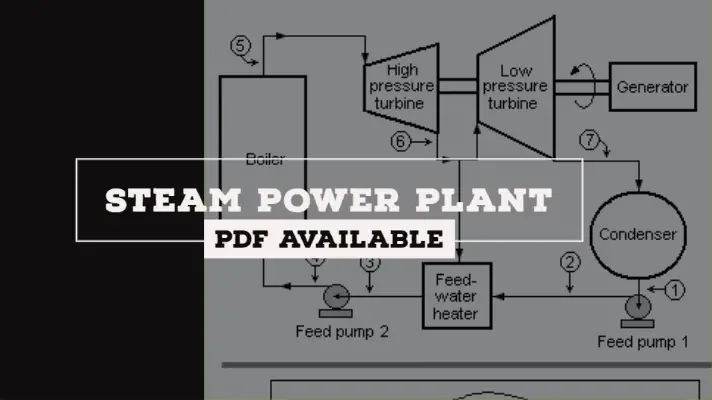
The steam power plant is also called a Thermal Power plant. The steam power plant is an important source for producing electricity.
The major source of electricity to our homes is through the thermal power plant. In this article, we will discuss the construction, working, components, advantages, and disadvantages of the steam power plant along with the diagram.

Definition of Steam Power Plant:
Steam Power Plant is defined as a power station, where we generate electricity using a steam-driven electric generator.
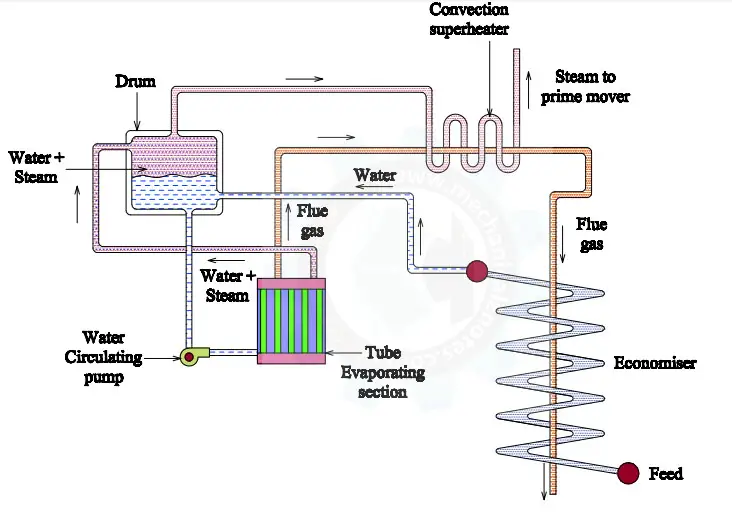
Layout or Schematic Diagram of Steam Power Plant:
The Layout or Schematic Diagram of Steam Power Plant is shown below.
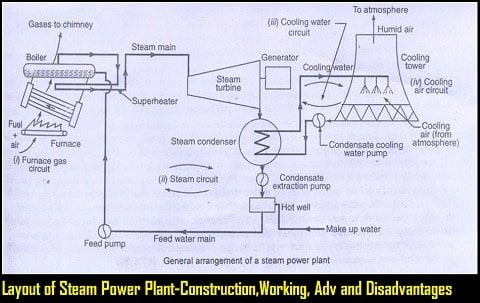
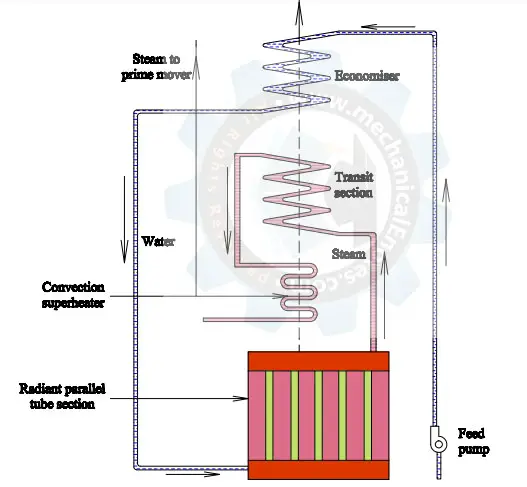
Another Diagram of Steam Power Plant Running on Rankine Cycle:
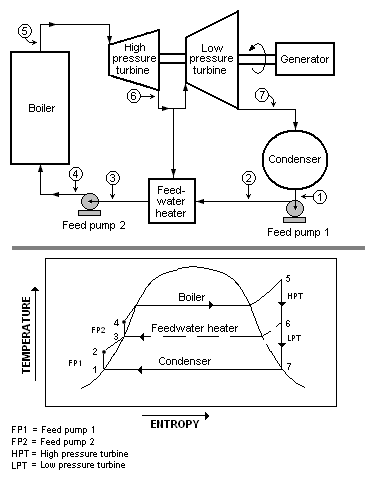
Construction Details of Steam Power Plant:
The layout of the steam power plant consists of the following parts. Those are:
- Coal and Ash Handling Unit
- Boiler
- Superheater
- Steam Turbine
- Generator
- Condenser
- Economizer
- Feed Pump
- Cooling Tower
- Chimney
An Explanation for the Components of Steam Power Plant:
The detailed explanation for the components of Steam power plant are as follows.
Coal and Ash Handling Unit:
Before feeding the coal to the furnace, It is to be converted into the pulverized form and after the combustion, the ash is collected in the ash handling unit.
Boiler:
The equipment used for producing steam is called Boiler or Steam Generator.
The steam generated is used for:
- Heating
- Power generation
- Utilization in industries like sugar mills, chemical industries, etc.
Superheater:
The steam is taken out from the boiler and is superheated so that, the steam should be free from the water molecules.
Steam Turbine:
The steam which is free from water molecules are used to strike the blades of the turbine so that large amount of power can be generated.
Generator:
A generator that converts one form of energy to another is attached to the rotor of the turbine and as the turbine rotates, it also rotates with the speed of the turbine.
Condenser:
The steam after striking on the blades of the turbine enters into the condenser where it gets condensed with the help of cold water from the cooling tower.
Economizer:
The economizer adds the feed water to extract a part of the heat from the condensate by increasing the feedwater temperature.
Feed Pump:
This feedwater is to be sent to the boiler using a feed pump only.
Cooling Tower:
The water that is used to condense the steam in the condenser was supplied from the cooling tower.
Chimney:
It is the last stage where only the air particles will enter into the atmosphere by reducing the heat from steam by the usage of the water sprinklers.
These are the various parts of the Steam Power Plant. Let's understand the Working Principle of it...
Working Principle of Steam Power Plant:
A Steam Power Plant working phenomena will be discussed using 3 circuits:
- Furnace Circuit
- Steam Circuit
- Cooling Water circuit
The explanation of these circuits is as follows.
1. Furnace Circuit:
Before feeding to the furnace, the coal is to be converted into the pulverized form and after combustion, the ash is to be collected into the Ash Pit (Ash handling unit).
2. Steam Circuit:
The water present in the boiler is heated up by means of a furnace and as the density of steam is less than the density of water, the steam will deposit on the surface of the water.
The steam is taken from the boiler and is superheated so that, the steam present should be free from the water molecules. Thus the superheated steam strikes the turbine blades with a high speed which makes the turbine rotate.
A generator is attached to the rotor of the turbine and as the turbine rotates, it also rotates with the speed of the turbine. The generator converts one form of energy to another i.e. mechanical energy of the turbine into electrical energy.
After striking the turbine, the steam enters into the condenser where it gets condensed with the help of cold water from the cooling tower.
The condensed water(also known as condensate) along with the feedwater, enters into the economizer.
The economizer must extract a part of the heat from the condensate by adding the feed water to increase the feedwater temperature before supplying it to the boiler.
This feedwater is sent to the boiler using a feed pump.
3. Cooling Water Circuit:
The water that is used to condense the steam in the condenser was supplied from the cooling tower. The hot steam cannot be released directly into the atmosphere from the chimneys and by doing so, the hot steam will affect the atmosphere.
For this reason, the hot steam along with water particles was released from the larger heights in the cooling tower, so that the water will fall down and the air particles will escape into the atmosphere.
After burning of the coal, it is transported to ash handling plant and finally to the ash storage.
In this way, the feed water rotates throughout the circuit with few losses of water, and the power is generated from the steam which is used to drive the turbines.
Uses of Steam Power Plant:
The uses of Steam Power Plant are as follows.
- It generates electricity from steam.
- It can be used in the automotive industry.
Advantages of Steam Power Plant:
The advantages of Steam Power Plant are as follows.
- The coal for the combustion is to be transported via railways and roadways.
- The fuel used is quite cheaper compared to other modes of power generation processes.
- The setup cost is also very low compared to others.
- Space accommodation is less compared to the hydropower plant.
Disadvantages of Steam Power Plant:
The disadvantages of Steam Power Plant are as follows.
- The steam power plant produces smoke and fumes at the end of the combustion process which can pollute the environment.
- Time Consumption is more for those power plants which are away from the Coalfield.
References [External Links]:
- Power Plant | Student Energy
- Power plant - Energy Education