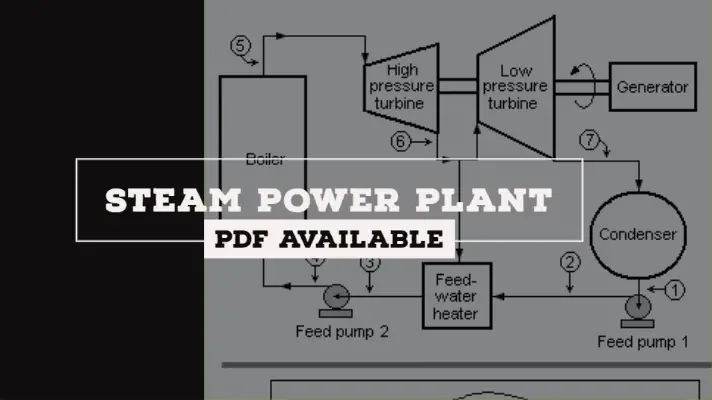
High-Pressure Boilers: Types, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications [PDF]
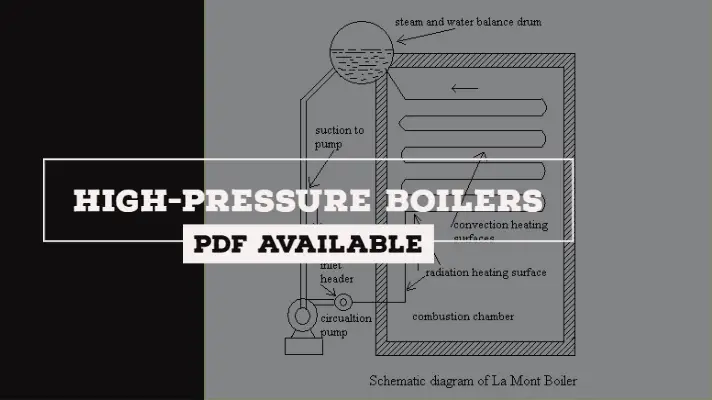
A high-pressure boiler is a type of boiler that operates at a pressure above 80 bars. They are widely used in thermal power plants for the generation of power. In this article, we can discuss high-pressure boilers along with its types, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications.
High Pressure Boilers Introduction:
The unique features of the high-pressure boiler are as follows.
- Method of water circulation
- Type of tubing and drums
- An improved method of heating
The explanation of the above features is as follows.
Method of water circulation:
The circulation of water through a boiler may be natural or Forced type. In all modern high-pressure boiler plants, water circulation is with the help of Pump i.e. by means of Forced Circulation.
Type of tubing and drums:
To avoid large resistance to the flow of water, these boilers have a parallel set of an arrangement of tubes.
high-pressure boilers are characterized by the use of very small steam separating drum or by a complete absence of any drum.
An improved method of heating:
Above the critical pressure, Saving of heat takes place by the evaporation of water.
Types of High Pressure Boilers:
There are two types of High pressure boilers and are as follows.
- Benson Boiler
- Lamont Boiler
The explanation of these type of high pressure boilers are presented below.
Benson Boiler:
In the Lamont boiler, the main difficulty experienced is the formation and attachment of bubbles on the inner surface of the heating tubes.
The attached Bubbles to the tube surfaces reduce the heat flow and steam generation, as it offers high thermal resistance than Water film.
Benson in 1922, argued that, if the boiler pressure was raised to critical pressure, the steam and water have the same density and therefore, the danger of bubble formation can be eliminated.
The Benson boiler also makes use of forced circulation but has a unique characteristic of the absence of the steam separating drum. Its main principle is that, at the critical pressure, the steam and water coexist at the same density, and heat is zero.
The water thus transforms into steam, without boiling and passes quickly from liquid to Vapor, without changing in volume.
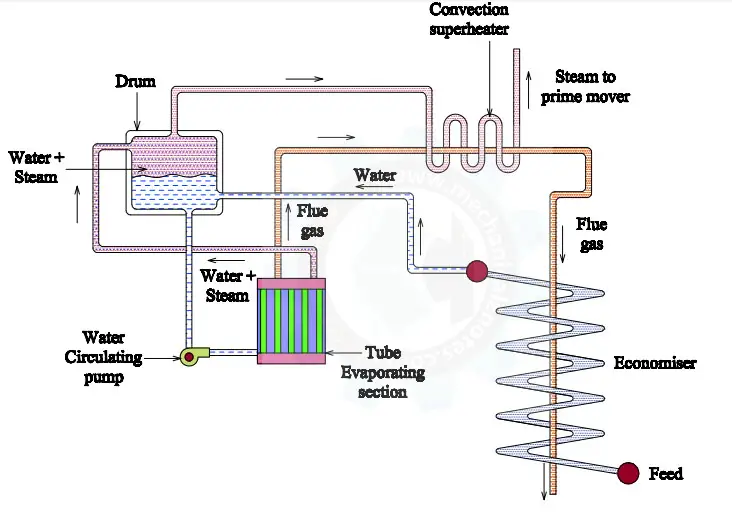
The figure above shows the representation of a Benson boiler.
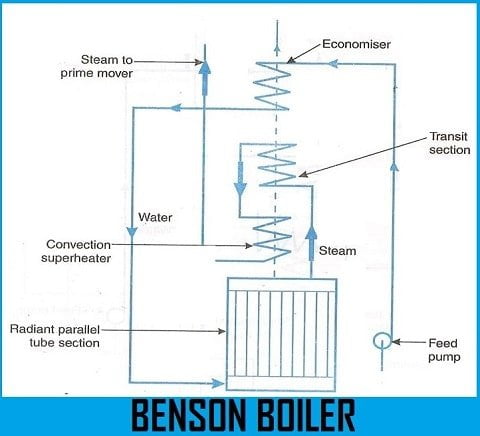
Parts of Benson Boiler:
The components or Parts of Benson boiler is as follows:
- Feed Pump
- Economizer
- Radiant Parallel tube section
- Transit section
- Convection Superheater
- Steam to the prime mover
The explanation for the parts along with Working, Advantages, Disadvantages and.Applications of Benson Boiler are presented in a detailed way in the below link.
Read: Benson Boiler: Definition, Parts, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications
Now let's dive into the concept of Lamont Boiler...
Lamont Boiler:
The definition, Parts, Explanation, Working principle of Lamont Boiler are presented below.
What is Lamont Boiler?
Lamont boiler is a high-pressure water tube boiler with internally fired furnace and the circulation is of forced type. An external agency is used to circulate throughout the tubes of the boiler.
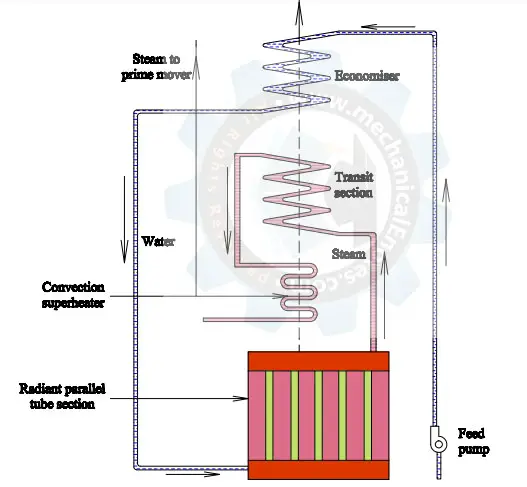
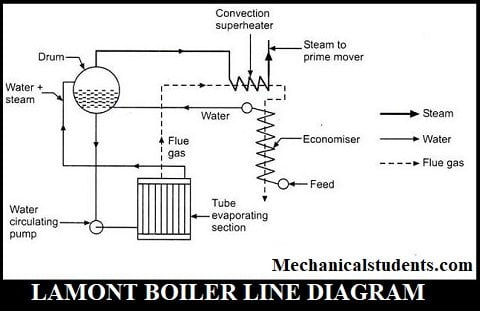
Parts of Lamont Boiler:
The Lamont boiler consists of the following parts:
- Feed Water
- Feed Pump
- Economizer
- Steam separating Drum
- Radiant Evaporator (Tube Evaporating section)
- Superheater
Explanation of Lamont Boiler:
This Lamont boiler works on the concept of forced circulation i.e. by the application of pump, the water is sent to various sections of the boiler unit and the circulation is maintained by means of a centrifugal pump which is driven by a steam turbine.
In this case, the steam from the boiler is used to drive a turbine and generate electricity or for doing any mechanical work.
And for emergency purpose, the pump which is driven electrically was also installed.
For working principle, Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications of Lamont boiler are presented below in the form of a link.
Read: Lamont Boiler-Definition, Parts, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications
Advantages of High-Pressure Boilers:
The advantages of High-Pressure Boiler are as follows.
- These boilers require less floor space to install the setup.
- Forced Circulation of water is used in High-Pressure boilers which ensures positive circulation of fluid/water.
- The tendency of scale formation is minimized due to the high velocity of the water.
- The steam generation is economical with the use of high-pressure boilers.
Disadvantages of High-Pressure Boilers:
The disadvantages of High-Pressure Boiler are as follows.
- If the water flow is insufficient, the tubes are possible to be overheated.
- High-pressure boilers can function on liquids or gaseous fuels.
- Bubble formation is taking place at the inner surfaces of the tube which reduces the heat transfer rate.
Applications of High-Pressure Boilers:
The applications of High-Pressure Boiler are as follows.
- For the production of electrical power, the supercritical boiler is used in various industries to generate steam.
- These high-pressure boilers are widely used to generate power from the steam in various types of boilers like Lamont Boiler, Benson Boiler, etc.
This is a detailed explanation of High-Pressure Boiler. If you have any doubts, you can ask us and I will answer them soon.
More Resources:
Lamont Boiler
Benson Boiler
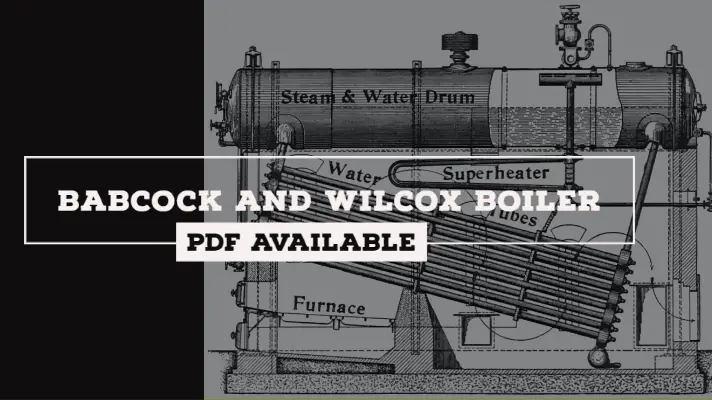
Babcock and Wilcox Boiler
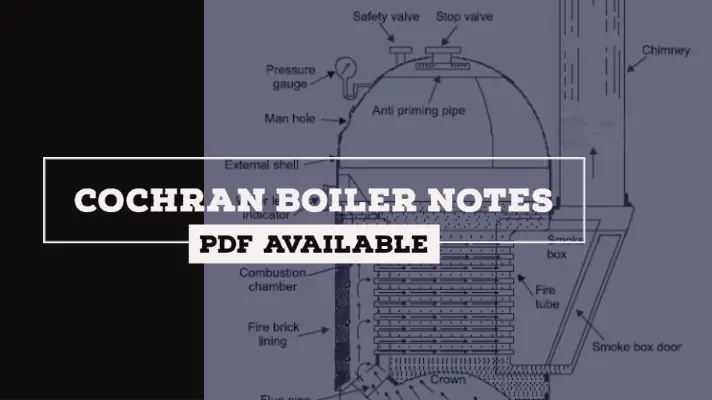
Cochran Boiler
References [External Links]:
- Steam Boilers-Researchgate