Boiler: Definition, Working, Classification, Selections, Essentials, Mountings, Accessories & Applications [PDF]
In the last session, we had discussed Lamont boiler, Benson boiler, Cochran boiler, Babcock and Wilcox boiler in a detailed way whereas, in today's session, we will discuss What is a Boiler? Selection of a boiler, Essentials of Good boiler, Classification of a boiler, Diagram of the boiler, Boiler Mountings, and Boiler Accessories in a detailed way.
Definition of Boiler:
The equipment used for producing steam is called Boiler or Steam Generator. Or it is also defined as “ A closed vessel in which steam is produced from water by the combustion of fuel.”
The steam generated is used for:
- Power generation
- Heating
- Utilization in industries like chemical industries, sugar mills, etc.
Working Principle of boiler:
The working principle of the boiler is very simple. Let’s understand it with a real-life example. For bathing, especially in winter, you need to heat water so you should not feel coolness around you.
but have you seen that when the temperature of the water increases beyond its saturation state, it starts vaporizing? However, at home, you cannot collect the steam but in the industries, that steam is used to generate electricity.
Now lets under What the working Principle of boiler is?
The boiler is a closed vessel that stores the water in it. Apart from water, boiler mountings and boiler accessories are also present which increases the efficiency of the boiler which are explained below. The Fuel(coal) is generally used as a furnace to heat the water present in the boiler shell.
The hot gases from the furnace touch the surface of the boiler shell and thereby steam is generated inside the shell which on further operations can drive the turbine. The driving of the turbine leads to the generation of electricity which will be used for various purposes.
This is the working Principle of Boiler. Now, let’s classify the boilers…
Classification of Boiler:
The boilers may be classified as follows:
- Horizontal, Vertical and Inclined Boilers
- Externally Fired and Internally Fired
- Fire-tube boiler and Water-tube boiler.
- Natural circulation and Forced Circulation
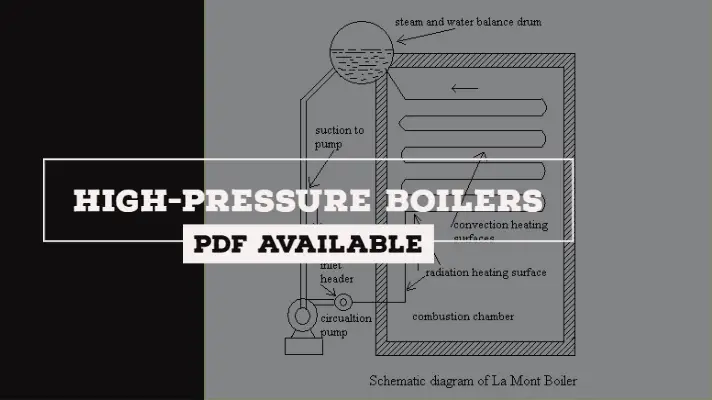
- High Pressure and Low-Pressure boilers
- Stationary and Portable boilers
- Single tube and Multitube boilers.
The explanation of the above types of boilers is as follows.
1. Horizontal, Vertical, and Inclined Boilers:
- If the axis of the boiler is horizontal, then the boiler is of horizontal type.
- If the axis of the boiler is vertical, then it is called a vertical boiler.
- If the axis of the boiler is inclined, then it is called an inclined boiler.
The parts of a horizontal boiler can be inspected and repaired easily. But, it occupies more space and the vertical boiler occupies less floor area.
2. Externally Fired and Internally Fired Boilers
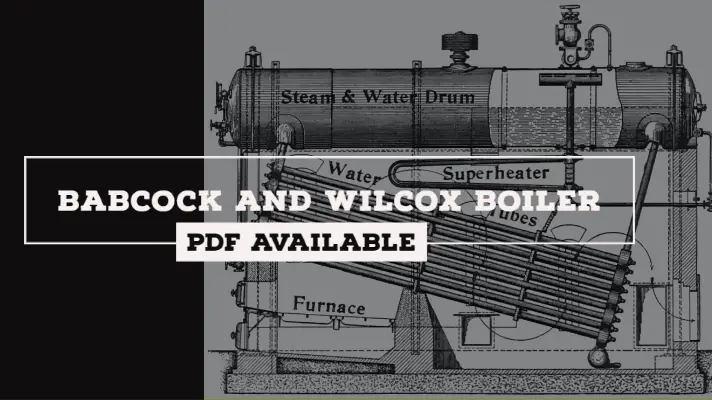
- The boiler is known as externally fired boiler if the fire is outside the shell.
For example, Babcock and Wilcox Boiler.
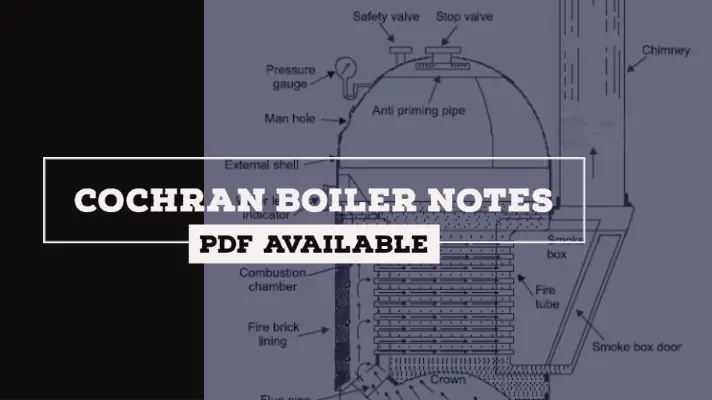
- In the case of internally fired boilers, the furnace is located inside the boiler shell.
For example, Cochran, Lancashire boiler, etc.
3. Fire-tube boiler and Water-tube boiler:
- In the fire tube boilers, the hot gases are inside the tubes and the water surrounds the tubes.
For Example, Cochran, Lancashire boiler, etc.
- In the water tube boilers, the water is inside the tubes and hot gases around them
For example, Babcock and Wilcox Boiler.
4. Natural circulation and Forced Circulation:
- In forced Circulation type of boilers, the circulation of water is done by a forced pump.
For example, Lamont Boiler, Benson Boiler, etc.
- In the natural circulation type of boilers, the circulation of water in the boiler takes place due to the natural convection currents produced by the application of heat.
Ex: Lanarkshire, Babcock and Wilcox boiler.
5. High Pressure and Low-Pressure boilers:
High-Pressure Boilers:
The boilers which produce steam at pressures of 80 bar and above are called high-pressure boilers.
For example, Babcock and Wilcox, Lamont, Benson boilers.
Low-Pressure Boilers:
The boilers which produce steam at a pressure below 80 bar are called low-pressure boilers.
For example, Cochran, Lancashire, and locomotive boiler.
6. Stationary and Portable Boilers:
- Primarily, the boilers are classified as either stationary or mobile(marine and Locomotives)
Stationary boilers are used for power plant steam for Central station utility power plants.
Portable Boilers:
Portable or mobile boilers include the locomotive type and other small units for temporary usage at sites(Just as in small coal-field pits).
7. Single tube and Multi-tube Boilers:
- If a fire tube is just one, then it is called a Single tube boiler.
For example, Cornish, Simple Vertical Boiler.
- If fire tubes are more than one, they are called as Multi-tube boilers.
Selection of Boiler:
The selection of Boilers is based on below conditions:
- Floor area available
- Portable load factor
- Erection Facilities
- The fuel and water availability
- Accessibility for repair and inspection
- Comparative initial cost
- Steam generation rate
- Operating and maintenance cost
Essentials of Good Boiler:
These are some essential qualities for a good boiler:
- The boiler should produce the maximum weight of steam of the required quality at minimum expenses.
- We should have easy access to various parts of boilers for inspection and repairs.
- The Installation of the boiler should be simple.
- Boiler components should be such that they would be transportable from one region to another without any difficulty.
- Steam production rate should be as per requirements
- Reliable.
- It should have to occupy in a minimum space.
- Tubes should not accumulate soot and water deposits.
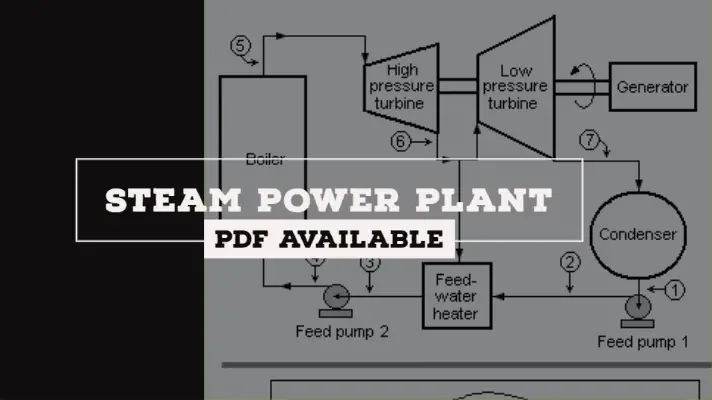
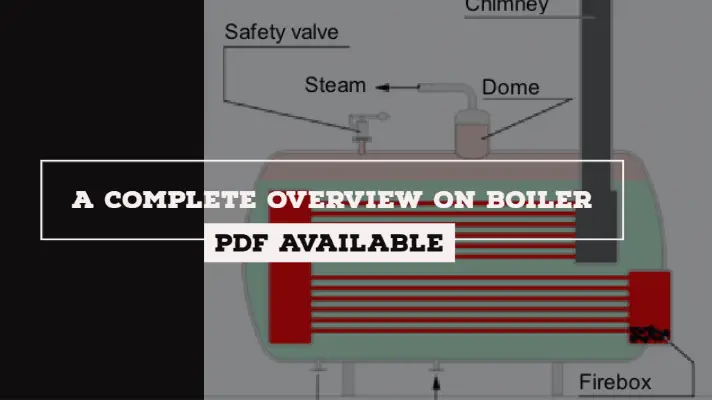
Diagram of the Boiler:
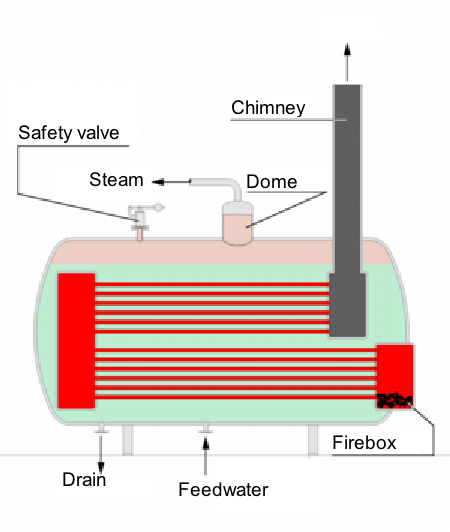
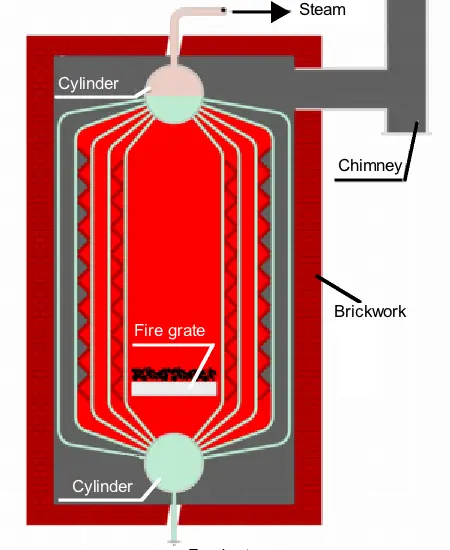
Boiler Mountings and Accessories:
The detailed explanation of Boiler Mountings and Accessories are presented below.
Boiler Mountings:
The Boiler Mountings are as follows:
- Water Level Indicator
- Blow off cock
- Feed check valve
- Safety Valves
- Pressure Gauge
- Fusible Plug
An Explanation of Boiler Mountings:
The detailed explanation of Boiler Mountings are shown below.
Water Level Indicator:
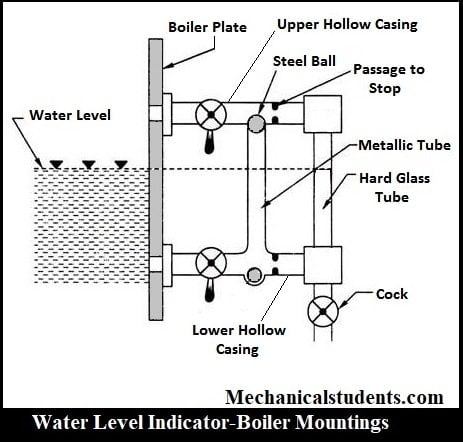
It is fitted on the boiler so that we can come to know, how much water level was present in the bolier such that suitable steam can be generated from it.
Blow off cock:
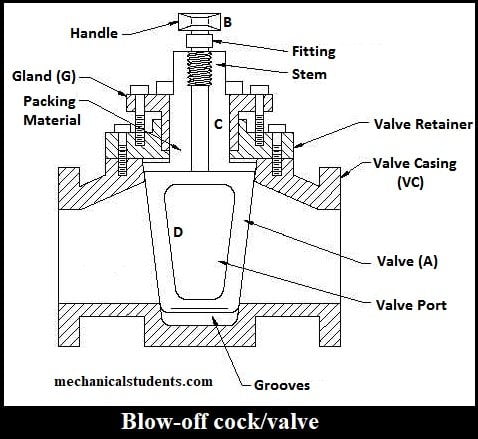
The function of Blow off cock is to empty the boiler by removing water, mud and sediments which are collected at the bottom of the boiler shell.
Feed check valve:
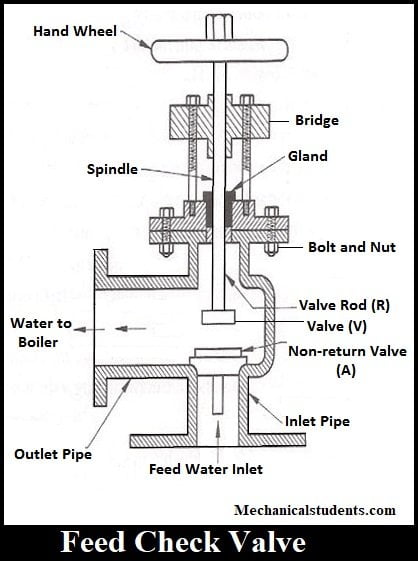
The main function of Feed Check Valve is to regulate the supply of water which is pumped into the boiler by employing feed pump.
Safety Valves:
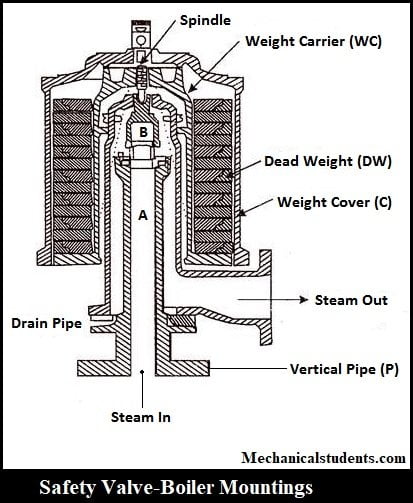
They are generally used to avoid the exposion takes place inside the boiler shell due to the excess pressure. When the pressure crosses the critical pressure, then the safety valve opens which allows excess steam to escape into the atmosphere untill the pressure inside the shell reaches normal pressure.
Pressure Gauge:
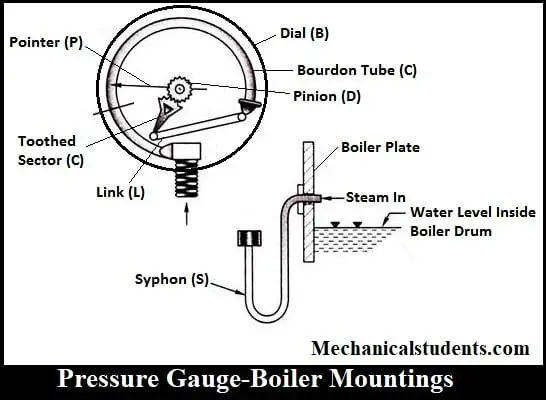
The Pressure gauge used in the boiler is especially of Bourdan type which is used to measure the pressure inside the boiler shell.
Fusible Plug:
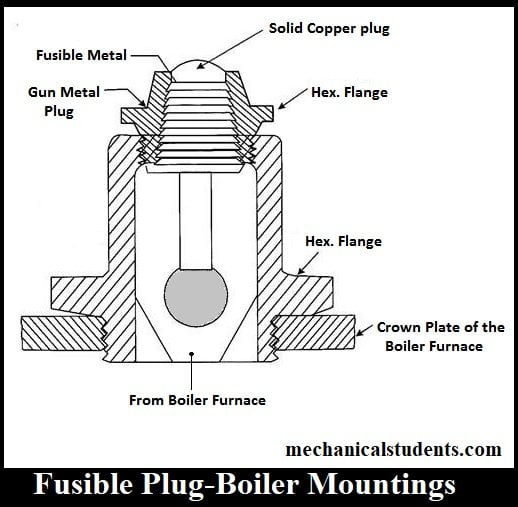
The fusible plug is placed at the top of the firebox whose duty is to avoid the explosion taking place due to the overheating of furnace when the water level in the boiler falls to an unsafe limit and it extinguish fire in the furnace.
Boiler Accessories:
The Boiler Accessories are presented below:
- Feed Pumps
- Steam Separator
- Economizer
- Air Preheater
- Superheater
An Explanation of Boiler Accessories:
A detailed Explanation of Boiler Accessories are explained below.
Feed Pumps:
A feed pump is one of the accessories of the boiler which is used to force the feed water into the boiler at high pressure. There are two types of Feed pumps,
- Rotary pumps
- Reciprocating pumps
Steam Separator:
This accessory of the boiler is used to separate the steam from the water in the boiler shell. If it is not taken, then an increase in furnace vaporizes the steam present in the boiler.
Economizer:
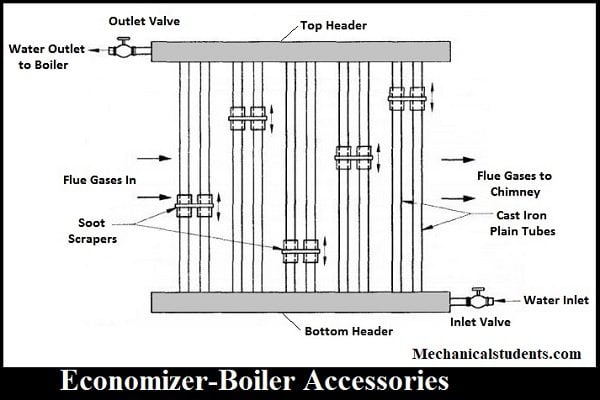
It is used to heat the feed water coming out from the boiler before it leaves the chimney to the atmosphere so that, the heat from the flue gases can be used as a preheat to other elements.
The usage of the Economizer increases the overall efficiency of the boiler.
Air Preheater:
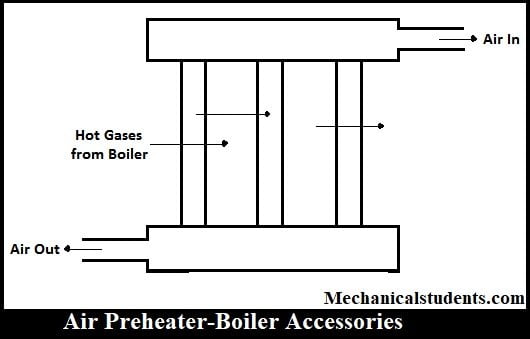
It is placed or installed between the Economiser and Chimney and it has to supply preheated air into the furnace such that an increase in temperature takes place which accelerates the combustion of the fuel.
Thus by the usage of Air Preheater, the thermal efficiency of the plant will be increased.
Superheater:
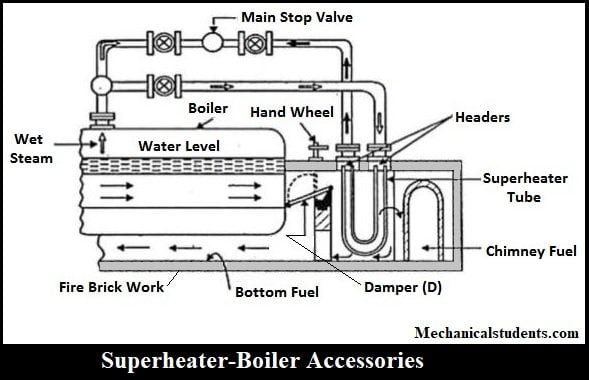
The function of Superheater is to increase the temperature of the steam about the saturation temperature. It is also a device that is used to convert saturated steam into supersaturated steam.
This steam is used to drive the turbines and generate electricity.
Difference between Water Tube Boiler and Fire Tube Boiler:
| Criterion | Fire Tube | Water tube |
|---|---|---|
| Position of hot gases and water | Hot Gases in tubes surrounded by water outside | Water in tubes and Hot gases flow outside |
| Mode of firing | Internal fired | External fired |
| Floor area | For a given power, it occupies more floor area. | For a given power, it occupies less floor area. |
| Capacity | 10000kg.hr | 50000kg/hr |
| Evaporation | Slow | Fast |
| Operating Pressure range | 15 to 20 bar | 170 to 200 bar |
| Suitability | Not suitable for large power plants. | Suitable for large power plants. |
| Risk on burning | Involves Lesser risk of explosion due to lower Pressure | Involves more risk on bursting due to High Pressure |
| Application | Not suitable for large power plant | Suitable |
| Requirement of Skill | Requires Less skill for efficient and economic working | Requires more skill for efficient and economic working |
| Water Treatment | Not so necessary | More necessary. |
| Construction | Difficult | Simple |
| Shell Diameter | More | Less |
| Transportation | Difficult | Simple |
| Accessibility of various parts | Not easily accessible for cleaning, repairing and inspection. | Easily accessible |
This is the complete explanation of the Boiler. If you have any doubts feel free to ask in the comment section.
FAQ's:
What are the 3 types of boilers?
Horizontal, Vertical and Inclined Boilers
Single tube and Multitube boilers.
Externally Fired and Internally Fired
Stationary and Portable boilers
Fire-tube boiler and Water-tube boiler.
Natural circulation and Forced Circulation
High Pressure and Low-Pressure boilers
What is the Definition of Boiler?
What are the boiler accessories?
What are boiler mountings?
More Resources:
Babcock and Wilcox Boiler
High-Pressure boilers
Cochran Boiler
Lamont boiler
Benson boiler
References [External Links]:
- Boilers - Bureau of Energy Efficiency
- Industrial boiler technology for beginners - Bosch