Differences between SI and CI Engine [With PDF]
Hello Readers... In the last session, we had discussed SI Engines along with the working of the SI Engine and also derived the equations to calculate the efficiency of the Otto cycle whereas, in today's session, we will discuss the differences between SI Engine and CI Engine in a detailed way.
Before diving into the differences, you need to know the basics of Spark-Ignition Engine and Compression Ignition Engine.
What is the Spark Ignition (SI) Engine?
Spark-Ignition Engine is also known as SI Engine which can run by taking the fuel as Petrol.
The basic SI Engine works on a two-stroke, four-stroke, and Eight strokes of piston operation.
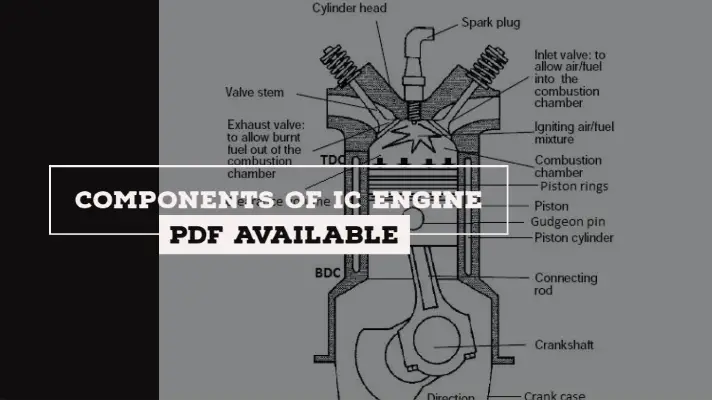
In a four stroke engine, the cycle of operation is completed in four strokes of the piston or two revolutions of the crankshaft.
What is the Compression Ignition (CI) Engine?
Compression-Ignition Engine is also known as CI Engine which can run by taking the fuel as Diesel.
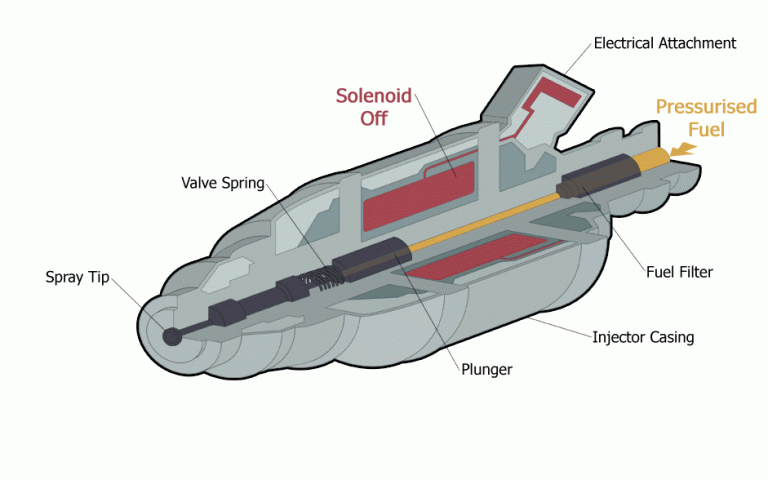
Fuel is directly injected as droplets into Combustion Chamber passing through the fuel injectors.
Later on, the injectors are been used in SI Engines because of the improper distribution of fuel by the carburetor at different speeds.
Let's dive into the concept of Differences between SI and CI Engine which was presented below in a tabular column.
Differences between SI and CI Engine:
The Differences between SI and CI Engine are listed below in the form of a table.
| DESCRIPTION | SI ENGINE | CI ENGINE |
|---|---|---|
| Basic cycle | Otto cycle (const.Volume heat addition) | Diesel cycle (const. Pressure Heat addition) |
| Fuel | Gasoline (petrol) Highly volatile – Self-ignition temp. | Diesel oil Non-volatile Self-ignition temp. |
| Introduction of fuel | 1.A gaseous mixture of fuel + air introduced during the suction stroke 2. Carburetor and Ignition system are required. | 1. Fuel directly injected as droplets into Combustion Chamber at high pressure at the end of compression Stroke 2. Fuel pump and Injector are necessary. |
| Load Control | Throttle controls the air-fuel mixture introduced. | A quantity of fuel is regulated. Air quantity is not regulated. |
| Ignition | Requires an ignition system with a spark plug in the combustion chamber. The primary voltage provided by a battery or a magneto | Self-ignition occurs due to a high temperature of air because of compression. Ignition system and spark plug are not required. |
| Compression ratio | 6 to 10. An upper limit is fixed by the anti-knock quality of the fuel. | 16 to 20. An upper limit is set by the weight increase of the engine. |
| Speed | Due to lightweight and homogeneous combustion, they are high-speed engines | Due to heavyweight and due to heterogeneous combustion, they are low-speed engines. |
| Thermal efficiency | Because of the lower compression ratio, the max. value of thermal efficiency that can be obtained is lower. | Because of the higher compression ratio, the max value of thermal efficiency that can be obtained is higher. |
| Weight | Lighter construction due to lower peak pressures. | Heavier due to higher peak pressures |
These are major diffrences between SI and CI Engine, I hope you liked this article if so then don't forget to share this stuff with your friends.
References [External Links]:
- CLASSIFICATION OF INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
- (PDF) CI Engine Modeling Techniques - ResearchGate