Pelton Wheel Turbine: Components, Working, Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages [PDF]

Pelton Wheel Turbine is the only impulse type of hydraulic turbine named after Lester A.Pelton, the American engineer. It is well suited for operating under high heads.
What is a Pelton Turbine?
- The turbine capable of working under the high potential head of water is the Pelton Wheel Turbine which works on the head greater than 300 m.
- The runner consists of a circular disc with a suitable number of double semi-ellipsoidal cups known as buckets which are evenly spaced around its Periphery.
- One or more nozzles are mounted so that, each directs a jet along the tangent to the circle through the centres of the buckets called the Pitch Circle.
- A casing is provided only to prevent the splashing of water and for discharging the water to the tailrace.
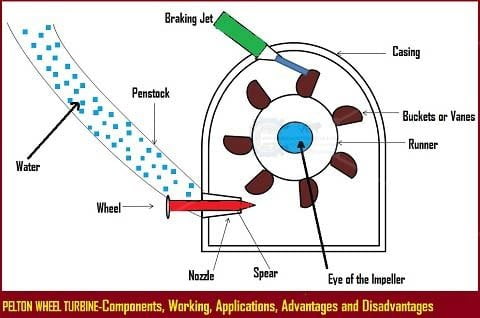
Components of the Pelton Wheel Turbine:
The Components of Pelton Wheel Turbine are as follows.
- Penstock
- Nozzle and Spear
- Runner and buckets
- Casing
- Breaking Jet
The explanation of the above components are as follows.

1. Penstock:
It is a channel or pipeline which controls the flow of water or it also acts as directing medium for the fluid flow.
2. Nozzle and Spear:
Nozzle:
The nozzle is used to increase the kinetic energy of water which is used to strike the buckets attached to the runner.
Spear:
Spear is used to control the quantity of water striking the buckets. It is a conical needle installed inside the nozzle to regulate the water flow that is going to strike on the buckets or vanes of the runner. It is operated by a handwheel.
The rate of water flow increases and decreases when the spear is moved in a backward direction and forward direction respectively and that can be handled by means of a hand wheel(It is operated in the axial direction).
The setup of Spear along with nozzle is shown in the below figure.
3. Runner and buckets:
The runner with buckets is shown in the figure given above.
- The rotating part of the turbine is a runner which is a circular disc and on the periphery of which a number of buckets are evenly spaced.
- The buckets are made of two hemispherical cups joined together. The splitter acts as a wall joining two hemispherical cups which can splits the water into two equal parts(i.e.on to the hemispherical cups.) deflected through an angle of 160 degrees to 170 degree.
- The buckets of the Pelton turbine are made up of cast iron, cast steel bronze or stainless steel.
4. Casing:
The case(outer cover) in which turbine is placed so that water can not splash outside(surroundings) called casing. The Pelton turbine with the casing is shown in the figure given below.
- It also safeguard and helps the water to discharge to the trail race.
- In order to make the casing, Cast iron or fabricated steel plates are used.
5. Braking Jet:
- The spear is pushed in a forward direction into the nozzle so that there should be no water jet impinging onto the blades of the turbine and making the turbine to stop. but the runner keeps moving due to the inertia.
- To stop the runner in the shortest period of time, a small nozzle is provided which directs a jet of water at the back of the vanes and that stops the runner of the turbine called as breaking jet.
Working of Pelton Wheel turbine:
The working of Pelton Wheel Turbine is as follows.
Water flows from the nozzle with high kinetic energy along the tangent to the path of the runner and when the jet of water comes in contact with the bucket, it exerts a force on the bucket called as Impulse force.
In order to control the quantity of water striking the runner, the nozzle fitted at the end of penstock is provided with a spear or needle fixed to the end of a rod.
In this process, the momentum of the water is transferred to the turbine. The impulse force produced due to this momentum of water causes the turbine to rotate.
The double Semi ellipsoidal buckets split the water jet into two halves which helps in balancing the wheel(runner). This ensures a smooth transfer of the fluid jet to the turbine wheel.
For maximum power and efficiency, the turbine is designed such that, the water Jet velocity is twice the velocity of the bucket.
Applications of a Pelton Turbine:
The applications of Pelton Wheel Turbine is as follows.
- To achieve maximum power and efficiency, the turbine blades are designed in such a way that water jet velocity is twice the velocity of rotating buckets.
- Pelton turbine, where the water available at the high head is from 150 m to 2000 m in a hydroelectric power plant.
- It is also used as set up in the labs of Educational Institutions.
Advantages of a Pelton Turbine:
The advantages of Pelton Wheel Turbine is as follows.
- It is easy to maintain.
- Intake and exhaust of water takes place at atmospheric pressure hence no draft tube is required.
- No cavitation problem
- It has simple construction
- It can work on high heads and low discharge
Disadvantages of a Pelton Turbine:
The disadvantages of Pelton Wheel Turbine is as follows.
- It requires a high head for operation
- Its efficiency decreases quickly with time
- Turbine size is generally large
- Due to the high head, it is very difficult to control variations in the operating head.
More Resources:
Hydraulic Turbines
References:
- Hydraulic Turbines - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- Governing of hydraulic turbines. - SlideShare