Linear Measurements: Definition, Standards, Methods & Instruments [PDF]

Metrology is defined as the science of measurements or the precision of measurements. Even it can be defined as the accuracy of measurements.
The science which is dealing with measurements and their conditions is called measurement science or metrology.
In this article, we will discuss Methods, Standards, and Instruments for Linear Measurements.
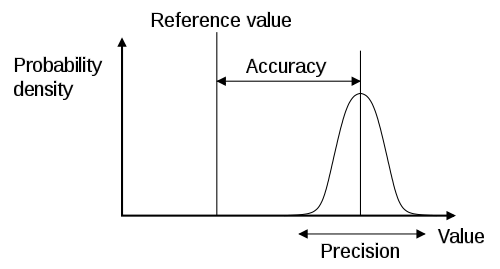
But before that, we should have to know about Precision and Accuracy.
Definition of Precision:
It is the repeatability or reproducibility of measurements.
Whatever the number of times a given dimension is measured by using given measuring equipment if the same dimension is obtained every time called repeatability or reproducibility of measurements.
When Precision is important?
Whenever only one measuring equipment is involved in the measurement of the dimensions, the Precision is important.
Definition of Accuracy:
The nearness to the true value is called accuracy.
The precise measurements made by using standard measuring equipment or non-errored measuring equipment is called Accuracy of measurements.
Whenever more than one measuring equipment is involved in measuring dimensions, accuracy is important.
Definition of Linear Measurement:
The measurement of lengths, thickness, diameter, and heights including external and internal measurements is called Linear measurement.
Standards used for Linear Measurements:
They are 3 standards used for Linear Measurements and are as follows:
- Imperial Standard Yard
- International Prototype Meter
- Wavelength Standard
The explanation is as follows...
1.Imperial Standard Yard
- 1Yard = 3 feet
- 1 feet = 12 inches
2.International Prototype Meter
- 1m = 100 cm= 1000 mm
3.Wavelength Standard
- 1m = 1650763.73 light waves of a red-orange line of Krypton-86.
Methods used for Linear Measurements:
These are the following methods used for Linear Measurements:
- Line Standard Method of Measurements
- End Standard Method of Measurements
- Line & End Standard Method of Measurements
The detailed explanation for the Methods of linear measurements is as follows.
Line Standard Method of Measurements:
If the lines of measuring equipment are coincided with the ends of a measurand, by counting the number of lines in between the coincidence lines and multiplied by one scale division, the dimension of the component will be obtained called line standard measurement.
For Example, Scale, tape, etc.
No.of lines = 95-32 = 63.
L= n*one scale division
= 63*1
= 63
End Standard Method of Measurements:
If ends of measuring equipment are coincided with the ends of the measurand and by adding the individual dimensions of the end standards used. The dimensions of the component will be obtained called End Standard Measurement.
For example, Slip gauges, end bars, etc.
L= 60+20+10+5+1 = 96 mm.
Line & End Standard Method of Measurements:
If the ends of measuring equipment are coincided with the ends of a measurand and by using the lines if the dimension of the component is obtained called as Line and End standard method of measurement.
For example, Vernier Caliper, Screwgauge, etc.
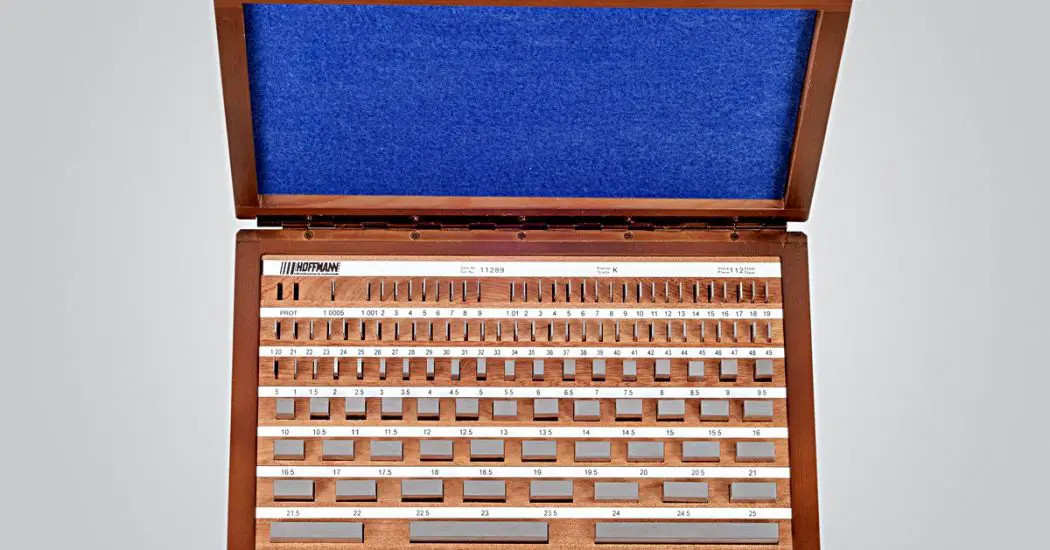
Slip Gauges:
A Slip gauge is specified by using its height only.
They are made by using high carbon steel as a material.
The top and bottom surfaces of the slip gauge are lapped with other slip gauges so as to construct a given height to measure the angle of the given specimen by sine bar and for that, a final machining operation is to be done on the slip gauges to get a very high degree of surface finish.
Points to be considered during the building of a given dimension using Standard set are as follow:
- Every slip gauge used for building must be available in the standard set.
- Do not repeat the same dimensions of slip gauge during one setting. In the sense, you should not use the same value to construct a given height such as 8 + 8(or any number).
- Use a minimum number of slip gauges as possible.

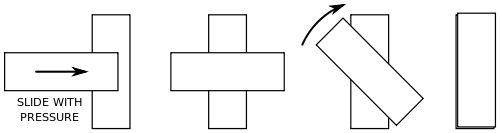
Wringing:
Building a given dimension using more than one slip gauge by forming a temporary bond between the slip gauge surfaces is called the Wringing of slip gauges.
Explanation of Wringing:
Atoms present on the highly polished surface are more active to share the energy with the other atoms.
Therefore, when two slip gauge surfaces are contacting and placed at 90° and rotated with the application of the little amount of force so that the temporary Bond formation is taking place between the two slip gauge surfaces. This is called as wringing of slip gauges.
Differences Between Line and End Standard Measurements:
Here are some differences between Line and End Standard:
- By using a 1 m scale, it is possible to measure nearly 200 varieties of dimensions. Therefore the measurements made by using line standards are simple, easier and faster. Whereas by using end standard methods, just for measurement of one dimension, there are many slip gauges required. Therefore, measurements made by using End standards are difficult and time-consuming.
- The accuracy made by using Line standards is up to 0.5 mm only. but the accuracy made by using End standards is up to 0.001 mm.
- In the case of line standards, there is no wear and tear problem whereas in the case of End standards because of wringing of measuring and measurand, the wear and tear will be taking place.
- Parallax error problem is always existing inline standards where there is no parallax error problem in case of end standards.
- There is no built-in datum present in the case of line standards but it always exists at both the ends of End standards.
Linear Measurement Instruments:
They are classified as Direct and indirect measuring instruments.
- Direct measuring instruments.
- Graduated Measuring instruments
- Non Graduated measuring instruments
- Indirect measuring instruments.
Direct Measuring Instruments:
The direct measuring instrument is divided into two types.
Graduated Measuring instruments:
Here are some Graduated Measuring Instruments:
- Ruler or Scale
- Vernier Caliper
- Micrometer
- Vernier Height Gauge
- Vernier Depth Gauge
- Dial Indicators
Non Graduated measuring instruments:
These are some Graduated Measuring Instruments:
- Trammel
- Caliper
- Telescope Gauges
- Slip Gauges
- Screw Pitch Gauges
- Surface Gauges
- Wire Gauges
- Straight Edges
- Radius Gauges
- Thickness Gauges
A Numerical on Linear Measurement:


Therefore, this is the detailed information about the Linear Measurements. If you have any doubts, feel free to ask in the comments section.
More Resources:
Sine Bar
Vernier Caliper
References:
- Engineering Metrology - IIT Kanpur
- Linear Measurement: Metric and Imperial [PDF]
Media Credits:
- Image 1: By Pekaje at English Wikipedia - Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons., GFDL, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1862863.
- Image 2: By Speedy1910 - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=81800683.
- Image 3: By Wizard191 - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=12424242.
- Numerical: Engineering Metrology Prof. J. Ramkumar Dr. Amandeep Singh Oberoi Department of Mechanical Engineering & Design Programme Department of Industrial & Production Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur National Institute of Technology, Jalandhar.
- Feature Image: By Solaris2006 - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1175333, Modify and Edited by Author.