Condition Monitoring: Definition, Types, Maintenance, Structural Health, Need, Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages [PDF]
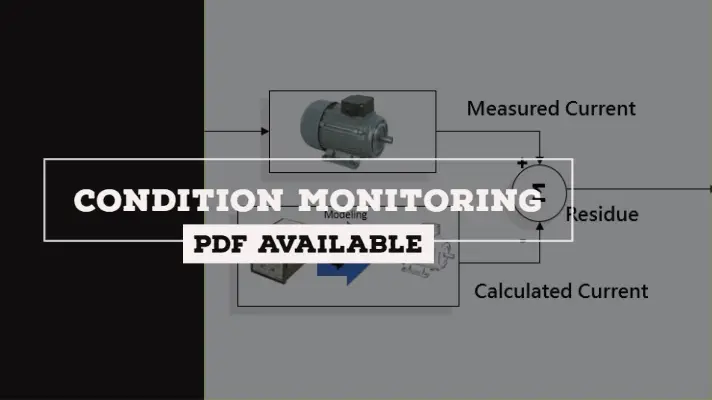
Condition Monitoring technology is applied in transportation and industrial sectors which includes vibration analysis and diagnostics, acoustic emission, oil condition sensors, etc.
In today's session, we will discuss on Condition Monitoring along with its Definition, Types, Maintenance, Structural health, Need, Machine fault signature, Applications, Advantages, and disadvantages.
Let's dive into the topic...
Condition Monitoring Definition:
Condition monitoring is the process of monitoring a parameter of condition in machinery (vibration, temperature, etc.), in order to identify a significant change which is indicative of a developing fault is called Condition Monitoring.
Condition Monitoring Types:
The types of Condition Monitoring are as follows:
- Route Monitoring
- Portable Machine Analysis
- Online Machine Monitoring
- Factory Assertion Test
- Online Machine Protection
The explanation for the types of Condition Monitoring are as follows.
Route Monitoring:
Within a prescribed route, the shop floor operator records the data of machine periodically with the help of a device and this data is to be studied to determine whether there is a need of advanced analysis or not.
Portable Machine Analysis:
PMA is the Abbreviation of Portable Machine Analysis. It is a system in which portable devices are attached to the machines to monitor their health and collect the data simultaneously.
Online Machine Monitoring:
OMM is the Abbreviation of Online Machine Monitoring. It is a system in which tools and machine equipment are monitored and diagnosed in the running state itself by embedding devices and servers for scheduling and analysis.
Factory Assertion Test:
FAT is the Abbreviation of Factory Assertion Test. It is a system that is used to assure that the finished goods have met the criteria up to the norms or not and also record the possible failures of equipment.
Online Machine Protection:
OAT is the Abbreviation of Online Machine Protection. In this system, a routine of continuos monitoring of the machine can done as it starts running and the machines can be turned ON/OFF by the setting mechanism. The embedded devices are used to record and diagnose the failures.
This is the explanation for the types of Condition Monitoring.
Condition Monitoring Maintenance:
- The use of Condition Monitoring allows maintenance to be scheduled or other actions to be taken to avoid the consequences of failure before the failure occurs.
- Machines with defects are more at risk of failure than defect-free machines. Once a defect has been identified then it is very easy to solve the problem.
- It can only measure the deterioration of the condition.
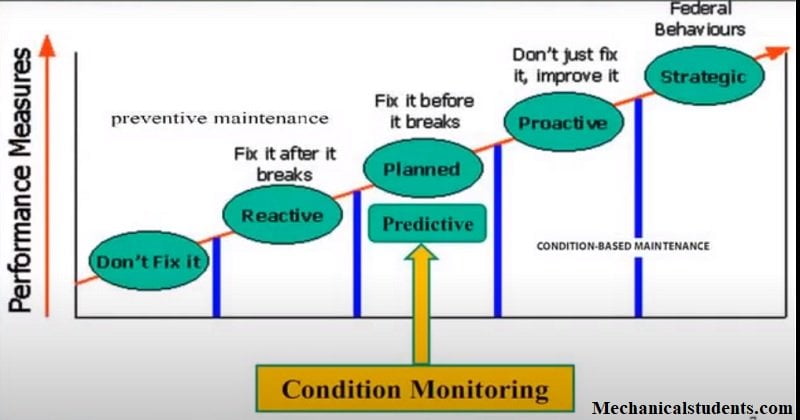
Types of Maintenance:
There are four types of maintenance in Condition Monitoring.They are:
- Periodic Preventive Maintenance
- Predictive Maintenance
- Proactive Maintenance
- Reactive Maintenance
Structural Health Monitoring:
As the name indicates that, it will monitor the health of the structure during the running conditions i.e. working of a machine under the control of computers. It is also named as Active Control Structure in Condition Monitoring.
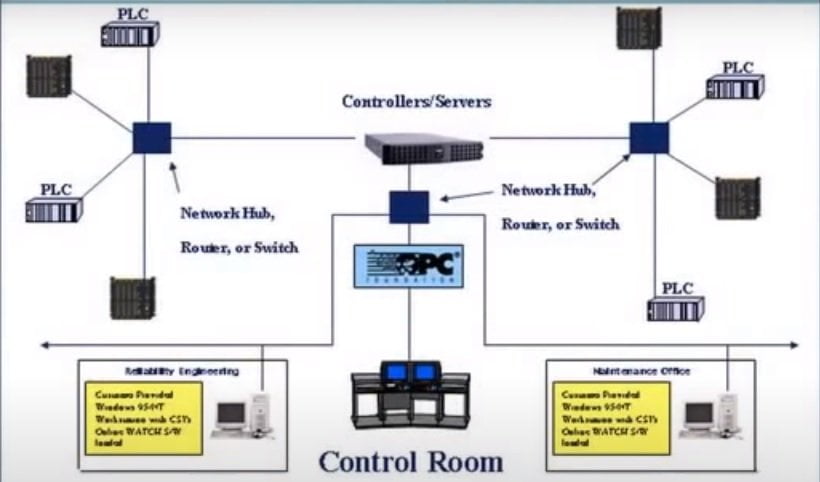
The Active Control Structure consists of PLC, Control room, OPC, Controllers/Servers, Network hubs, etc.
It can detect machinery problems if the system is:
- Unbalance
- Misalignment
- Looseness
- Shaft cracks
- Oil whirl
- Phase
- Rubs
- Gear and bearing problems
It can pass the information to DCS plant information systems via OPC.
It uses existing plant LAN Ethernet infrastructure.
Confirmation of mechanical conditions to reach plant for planned shutdown or remedy
Fix what is 'broke' before failure.
The need for Condition Monitoring:
- It is a major component of predictive maintenance.
- The use of condition monitoring allows maintenance to be scheduled or other actions to be taken to prevent failure and avoid its consequences.
- Condition monitoring techniques are normally used on rotating equipment and other machinery (pumps, internal combustion engines, presses).
Condition Monitoring can be discussed on various aspects and some of them are as follows.
- What is a machine?
- What is Life cycle cost ownership?
- Why machine health gets affected?
- What is Bath Tub Curve and what is its importance?
- Failure data results
- Aging of moving components
- Healthy machine requirement
- What happens when oil films break?
- What is a sick machine?
- What are the symptoms of a sick machine?
Machine Fault Signature Analysis:
Machine Fault can be defined as any change in machinery part or component which makes it unable to perform its function satisfactorily is called a machine fault.
Objectives of Machine Fault Signature:
- Prevention of future failure events.
- Assurance of reliability, maintenance, and safety of machinery.
Machinary problems are due to:
- Unbalance
- Shaft cracks
- Looseness
- Oil whirl
- Misalignment
- Gear and Bearing Problems.
Failure Occurences:
- An inherent weakness in material, manufacturing, and design.
- Gradual deterioration due to Wear, Tear, Stress, Fatigue, Corrosion, etc.
- Misuse or applying stress in an undesired direction.
Detection Techniques:
The detection techniques are shown below and are as follows.
- Visual Inspection
- Aural
- Wear debris
- Operation variables,Temperature etc.
Condition Monitoring Issues:
- Condition monitoring has a unique benefit in that conditions that would shorten normal lifespan can be addressed before they develop into a major failure.
- While periodic inspection uses non-destructive testing techniques and fits for service (FFS) evaluation which is used for stationary plant equipment such as steam boilers, piping, and heat exchangers.
- The criticality of inspected part/machine/process
- The sensitivity of faults-parameter to monitor
- Offline Inspections/Online Inspections
- Optimum inspection Interval.
Condition Monitoring Applications:
The applications of Condition Monitoring are as follows.
Condition Monitoring for:
- Mining Industry
- Cement Industry
- Pulp and paper processing Industry
- Steel production industries
- Food manufacturing units
- Oil industries
- Transport
- Military etc.
Condition Monitoring Advantages:
The advantages of Condition Monitoring are as follows.
- The maintenance cost is lower
- Increase the life span of machinery
- Maximizes the production output
- Accurate Analysis
- Perfect ordering of maintenance tasks.
Condition Monitoring Disadvantages:
The disadvantages of Condition Monitoring are as follows.
- Short-term investment is required.
- The equipment for condition monitoring is expensive.
- The sensors of condition monitoring may not survive depending upon the environment.
- It exhibits unpredictable maintenance periods.
Some FAQ on Conditioning Monitoring:
What is condition based monitoring?
What are the advantages of condition monitoring?
1. The maintenance cost is lower.
2. Increase the life span of machinery.
3. Maximizes the production output.
4. Accurate Analysis.
What are the 4 types of maintenance?
1. Periodic Preventive Maintenance.
2. Predictive Maintenance.
3. Proactive Maintenance.
4. Reactive Maintenance.
What are condition monitoring techniques?
1. Visual Inspection
2. Aural
3. Wear debris
4. Operation variables,Temperature
So this is the detailed information on Condition Monitoring. If you have any doubts, ask us and we will answer you as soon as possible. Happy learning!