Electrical Engineering Workshop: A Detailed Explanation [PDF]
A network of cables connecting various electrical accessories for distribution of electrical energy from the supplier to various electrical energy consuming devices such as fans, lamps, radio, TV, and other domestic appliances through controlling and safety devices known as wiring system.
In the last session, we had discussed Engineering Fitting Workshop whereas, in today's article, we will discuss in detail about all the concepts of Electrical Engineering Workshop.
Electrical Engineering Workshop:
The main concepts which we can discuss here are, Types of supply systems, Wires, and Wire sizes along with Wiring boards in a detailed way.
Types of Supply Systems:
• For Domestic installations, the Power supply is supplied through a phase and a neutral forming a single-phase A.C. 230 V
• For industrial establishments, power is supplied through a three-phase 440V. Also called as 3-Phase, 4 wire system.
What is Wire?
A wire is defined as an insulated conductor consisting of one or several flexible strands for the flow of current.
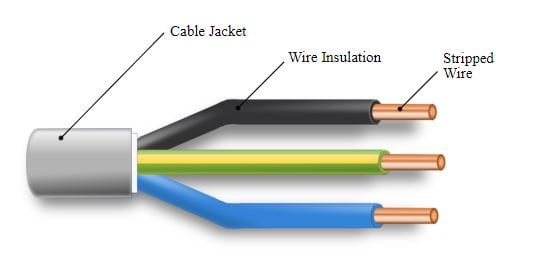
A wire can be used as the passage of electrical energy (current) in various forms such as
• Overhead Transmission and distribution lines
• Giving service connection to various consumers
• Winding coils of electrical machines
• Domestic and industrial wiring
• For laying underground cables etc.
What is Conductor?
The material which has free electrons to conduct “current” through it is called as Conductor.
Ex: Cu, Al etc.
What is Insulator?
The material which doesn't have free electrons and will not allow the current to pass through it is called as Insulator.
Ex: PVC, Rubber, Bakelite etc.
Wire Sizes:
• As per AWG (American wire gauge), the diameter of the wire is inversely proportional to the AWG number.
Example:
For Household applications, the diameter of the wire is small but its AWG No. is large I.e.14 AWG whereas, for Industrial Applications, the diameter of the wire is large but the AWG No is small i.e. 1 AWG.
• But, the Diameter of the wire is directly proportional to the current-carrying in the wire.
• Most household wiring is usually 12 or 14 AWG Wire Size
• Some of the wires are Solid and some are stranded.


Wiring Boards:
- A Printed Circuit board (PCB) is the combination of electrical or Data circuits on a horizontal layer of material.
- PCBs can be found in many electronic devices. They can be used to connect LCD monitors or computers.

Types of Wires:
The types of wires were classified based on Domestic and Industrial Applications and are as follows.
- V.I.R.( Vulcanized India Rubber) wire.
- T.R.S.(Tough Rubber Sheathed) wire.
- Weatherproof wire.
- L.C.(Lead Covered) wire.
- MICC (Mineral Insulated Copper Covered) wire.
- PVC (Poly Vinyl Chloride) wire.
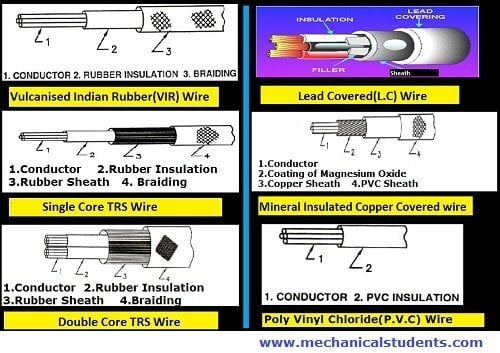
The detailed explanation of above mentioned wires is as follows.
1. V.I.R.( Vulcanized India Rubber) wire
• In this type of wires, the conductors are made up of aluminum or copper.
• In VIR, the conductor is covered by Rubber insulation and Braiding.
• It has greater properties of durability, mechanical strength, and wear resistance.
• It is suitable for moderate and low voltage cables.
2. T.R.S.(Tough Rubber Sheathed) wire
• In this type of wires, a layer of strong and durable rubber is provided over the conductor.
• Additionally, the TRS wire is coated with rubber sheath compared with VIR wire i.e. The TRS wire is covered with rubber insulation, rubber sheath, and Braiding.
• The strength of the TRS wire is more than VIR wire.
• Effect of heat, moisture, and water is less in it.
• It is used for both Domestic wiring and Industrial Wiring.
• Single core TRS wire is shown in the figure.
3. Weatherproof wire
• There is no effect of the atmosphere on Weather Proof wire.
• Rubber layer is provided on copper-conductor.
• Braiding of cotton is provided on this.
• An outer sheath is inflammable and it is not used in casing-capping type wiring.
• It is useful in service connections and Its use is nowadays has become limited.
4. L.C.(Lead Covered) wire
• A Coating of insulated rubber is provided on the conductor.
• A tube made up of lead is kept over it. Due to that, there is no effect of moisture on the rubber. So it can be used in the presence of moisture.
• As Lead is soft. It is easily affected by mechanical stresses. So care has to be taken while using these types of wire.
5. MICC (Mineral Insulated Copper Covered) wire
• In this type of wire, a coating of magnesium oxide is provided as insulation on the copper conductor. Over this copper, a sheath is provided.
• When this wire has to be used in a moist atmosphere, a serving made of PVC is provided over this.
• This wire is less affected by temperature.
• This type of wire is used in wiring in factories, boilers, mines, furnace, rolling mills etc.
6. PVC (Poly Vinyl Chloride) wire
• In this type of wire, insulation made of polyvinyl chloride is provided over copper or aluminum conductor.
• By the usage of PVC wires, the rubber insulated wires are reduced. This wire is generally used in Voltage rating of 11KV.
• PVC is very resistant to corrosion, impact, weathering etc.
This is the detailed explanation of all the types of wires used in Electrical Workshop. Now, let's discuss about House wiring methods or House Wiring Connections.
House Wiring Methods or House Wiring Connections
Whenever a question is asked related to House wiring Methods or Methods of House wiring or House Wiring Connections, you need to answer like this as shown below.
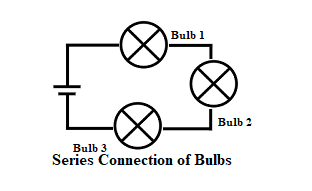
Series Method or Joint Box System or Tee System:
- The series circuit provides a single and continuous path through which the current flows.
- Even, if one device breakdown, the remaining devices will not operate.
- This method of wiring does not consume too many cables.
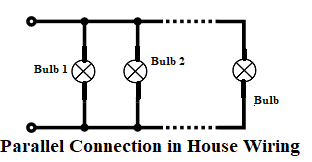
Parallel Method or Loop-in System:
- All devices (Ex. Bulbs) are connected in parallel so that the current flows in no. of parallel paths.
- Each device is connected across the power source. Therefore, if one device breakdowns, other devices continue to operate.
Types of Internal Wiring or Wiring Installations or House Wiring systems:
The following are the different types of house wiring system in Electrical Engineering Workshop
- Cleat wiring
- Wooden casing and capping
- Batten wiring or TRS wiring
- Lead (or metal) Sheathed Wiring
- Conduit Wiring
The detailed explanation is as follows.
Cleat Wiring:
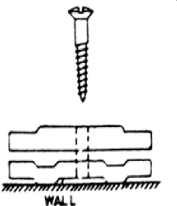
- In this type, wires are clamped by means of porcelain cleats.
- The cleat is of two halves.
- One half is grooved through which wire passes while the other fits over the first.
- The whole assembly is then mounted on the wall or wooden beam with the help of screw.
Wooden Casing and Capping:
- VIR or PVC insulated wires are used.
- Wires are carried through a wooden casing.
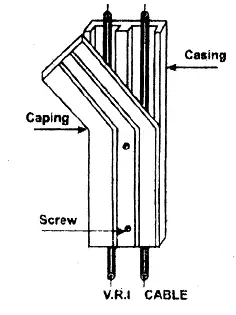
- The casing is covered with a rectangular strip of wood or PVC of the same width, called capping. The capping is screwed into the casing by means of screws fixed.
- It is most commonly used in domestic wiring installations.
Batten Wiring or TRS wiring:
- In this type, the wooden batten(atleast a thickness of 10mm) is fixed on the surface of the wall, by means of screws and raw plugs.
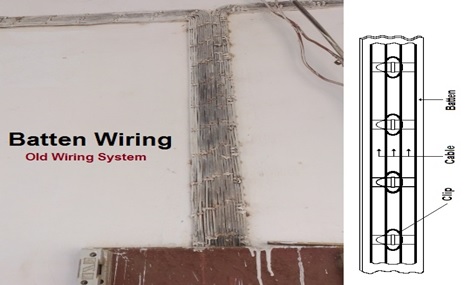
- Circular Oval shape cables are used in this wiring.
- The wire runs on the batten and is clamped using the metal clips
- This type of wiring is cheap and can be used in residential wiring.
- CTS or TRS cables are chemical-proof, waterproof, and steam proof.
Lead Sheathed Wiring:
- In this type of wiring, Vulcanized India Rubber(V.I.R) conductors covered with lead alloy sheath are used. It is similar to surface wiring.
- The sheath gives protection from mechanical damage, Moisture and Atmospheric corrosion.
- The wires with metal sheath are fixed on wooden batten by means of metal clips.
- This type of wiring is suitable for places which are exposed to sun or rain but unsuitable for the corrosive environment.
Conduit Wiring:
There are two types of conduit wiring and are as follows
- Surface Conduit Wiring
- Concealed Conduit Wiring
Surface Conduit Wiring:
If conduits are installed on either wall or roof, It is known as surface conduit wiring. In this wiring method, holes are made on the surface of a wall or on the roof at equal distances and the conduit is installed.

Concealed Conduit Wiring:
If the conduit was hidden inside the wall slots with the help of plastering, it is called concealed conduit wiring.
Nowadays, It is the most popular, stronger and common electrical wiring system.

House Hold Electrical Appliances:
There are many household electrical appliances are there but I will be explaining one of its types i.e. Automatic Electric Iron box. Let's discuss it...
Automatic Electric Iron box:
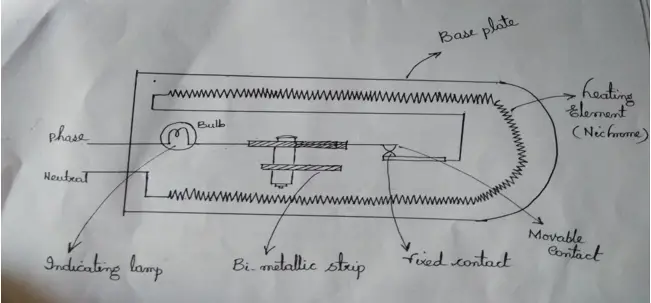
Operation: whenever current passes through normally closed contact and heating element, heat is produced due to "i^2Rt" losses.
•That heat is uniformly spread over the base plate through a mica(insulation) sheet. During this period, the Bi-metallic strip arrangement will be as shown.

when the required heat is produced, the bi-metallic strip on one side bends and pushes up the closed contact as shown.
•During this period, the circuit becomes open and interrupts the current, flowing through the resistive element.

•By rotating the knob provided for different settings, the gap between two strips of bimetallic contact is varied.
•If the knob is rotated in an anti-clockwise direction, the gap will be small and at a lower heat, contact separation takes place.
•If the knob is rotated in a clockwise direction, the gap will be increased and requires more bend and more heat for contact separation.
•Thus it automatically interrupts the circuit when required or set heat reached.
This is the detailed explanation of House wiring systems in Electrical Engineering Workshop.
More Resources:
Engineering Fitting Workshop
Measuring Instruments used in Workshop
References [External Links]:
- Electrical Workshop-Lab manual
- lab record basic workshop - IARE

