Electrochemical Machining (ECM): Introduction, Diagram, Parts, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages, Applications [PDF]
Electrochemical Machining process, the combination of electrical energy and chemical energy makes the removal of material from the surface of a work-piece. It works on the principle of Faraday's law of electrolysis.
Before dive into the main topic let me give you some idea related to ECM.
Principle-Faraday's law of electrolysis:
The mass of a substance deposited or liberated at any electrode on passing a certain amount of charge is directly proportional to its chemical equivalent weight.
Electrolyte used:
NaCl (Conducting Electrolyte).
Wear Ratio:
Infinity (because of no Tool Wear)
DC Power Supply: (3-30)V
The Positive terminal is given to the Workpiece and the Negative terminal is given to the Tool.
Tool Used:
The tool used in the Electrochemical Machining Process is either Copper or Brass or Stainless steel etc.
Properties Possessed by the Tool:
It must possess high
- Thermal Conductivity
- Electrical conductivity and
- Corrosion resistance.
Optimum Gap:
The optimum gap maintained between the tool and workpiece is 0.5 to 2 mm.
MRR (Material Removal Rate):
The initial Material Removal Rate (MRR) mainly depends upon the number of Ions displaced from the workpiece.
The number of Ions displaced is directly proportional to
- The current passing through the circuit
- The gram atomic weight of workpiece materials.
- The electrical conductivity of the electrolyte.
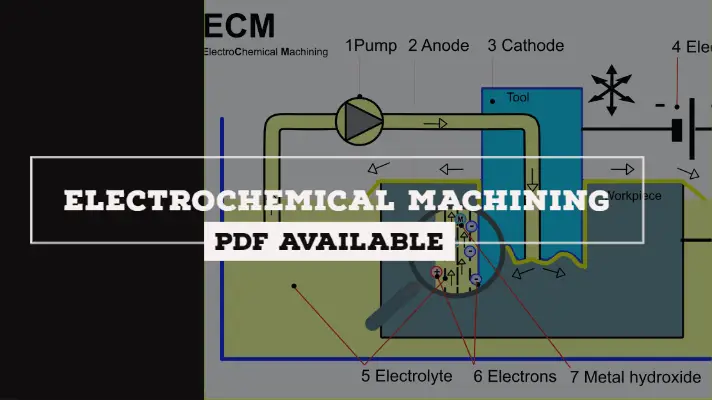
Diagram of Electrochemical Machine:
The Diagram of Electrochemical Maching Process was shown below.
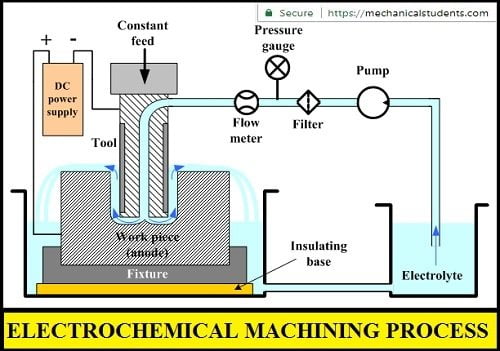
Parts of Electrochemical Machining:
The electrochemical machining setup consists of
- Fixture
- Table
- Workpiece
- Tool
- Electrolyte
- Pump
- Filter
- Pressure gauge
- Flowmeter
- Feed unit
- Power supply
An Explanation for the Parts of Electrochemical Machining Process:
The explanation is as follows.
Fixture:
The fixture is used to hold the table firmly.
Table:
The table is used to hold the work piece properly.
Workpiece:
It is the material on which machining is carried out to remove the material from the surface of the workpiece. Here, the workpiece acts as an anode.
Tool:
With the help of the tool, material removal takes place in the workpiece. Here, the tool acts as a cathode.
Electrolyte:
The electrolyte acts as a medium for the flow of ions and leads to the removal of material from the surface of workpiece.
Pump:
It pumps the electrolyte from the sump to all the parts of the system.
Filter:
It removes the impurities present in the electrolyte which is being pumped to the system or work region.
Pressure gauge:
It is used to check the pressure of the electrolyte coming from the pump via a filter to the work region.
Flow meter:
It is used to measure the discharge or mass flow rate of the fluid(electrolyte).
Feed Unit:
To give the feed to the tool, servomotor is used such that whenever material removal takes place from the workpiece, the servomotor gives the necessary amount of feed to the tool.
Power Supply:
The power supply is to be given to the machine to work properly. Here +ve supply is given to the workpiece(acts as an anode) and the -ve supply is given to the tool(acts as a cathode).
This is the explanation for the parts of Electrochemical Machining. Let's understand the working principle of it.
Working of Electrochemical Machining (ECM) Process:
The electrolyte is pumped to the work region by the pump via a filter, pressure gauge, flow meter and finally, it enters into the work region from the passage.
When the Power supply is given, an optimum gap is maintained between the tool and workpiece because of Faraday's laws of electrolysis, the ions have started displacing from the workpiece and trying to deposit over the tool.
Before the ions are depositing on the tool, the electrolyte present between tool and workpiece is pumped out. Then, the ions also moving along with electrolyte without depositing on the tool.
From the above, the mechanism of material removal is Ion displacement and because there is no disturbance taking place in the tool, the same tool can be used for producing an infinite number of components.
Hence, we can say that the wear ratio of the tool is infinity(because of no tool wear)
This is the detailed explanation of the electrochemical machining process along with the basic terms and working.
Advantages of Electrochemical Machining(ECM) Process:
The advantages of Electrochemical Machining are as follows.
- Complex Concave curvature components can be easily produced by using Complex Concave curvature tools.
- Because of ion displacement, the surface finish produced is excellent.
- Because no forces are acting, no residual stresses will be present.because of no heat generation, no thermal effects are present on the workpiece.
- Because of no tool wear, the same tool can be used for producing an infinite number of components.
Disadvantages of Electrochemical Machining(ECM) Process:
The disadvantages of Electrochemical Machining are as follows.
- Workpiece material must be electrically conductive.
- Out of all the Non-traditional machining methods, electrochemical machining requires the highest specific cutting energy Therefore, the cost of machining will be high.
- This is preferable for producing contours only but not for holes.
Applications of Electrochemical Machining Process:
The applications of Electrochemical Machining are as follows.
- It is mainly used for producing Complex concave curvature components such as Turbine blades etc.
- The ECM process is used for profiling and contouring, die sinking operation, drilling, trepanning, and micromachining.
This is the explanation of Electrochemical Machining Process with its advantages, limitations, and applications in a detailed way. If you have any doubts feel free to comment down below.
Watch the Youtube Video:How Electrochemical Machining Works
References [External Links]:
- Electro-Chemical Machining - Nptel
- Non-Traditional Machining Processes - NIT Calicut