Cooling System in IC Engine: Types, Advantages, Disadvantages [PDF]
As per the engines, the heat produced by the combustion of fuel in the engine cylinder is not converted into useful power at the crankshaft completely and the typical distribution of fuel energy is as follows:
- Useful work at the crankshaft= 25%
- Loss in exhaust gases= 35%
- The loss to the cylinders walls= 30%
- Loss due to friction= 10%
If the heat is not removed from the cylinders, it would result in the pre-ignition of the charge.
Requirements of Cooling Systems in IC Engine:
The following are some reasons, why we need cooling systems in an Engine.
- When the engine is very hot, It should need to remove the heat at a fast rate.
- Maintaining the temperature below certain limits by dissipating excess heat from the cylinder walls.
- Cooling below an optimum limit may not be recommended as it will decrease overall efficiency.
- If too much removal of heat takes place in the engines, it will lower the thermal efficiency. So it is desirable up to 30% only.
Types of Cooling System in IC Engine:
There are generally two types of Engine Cooling System are there, and those are the following:
- Air Cooling System
- Water Cooling System
Air Cooling System in the IC Engine:
The basic principle involved in this method is to have a current of air flowing continuously over the heated metal surface from where the heat is to be removed.
The heat dissipated depends upon the following factors:
- The temperature difference between the heated surface and air.
- The mass flow rate of air.
- The surface area of metal into contact with air.
- The conductivity of the metal.
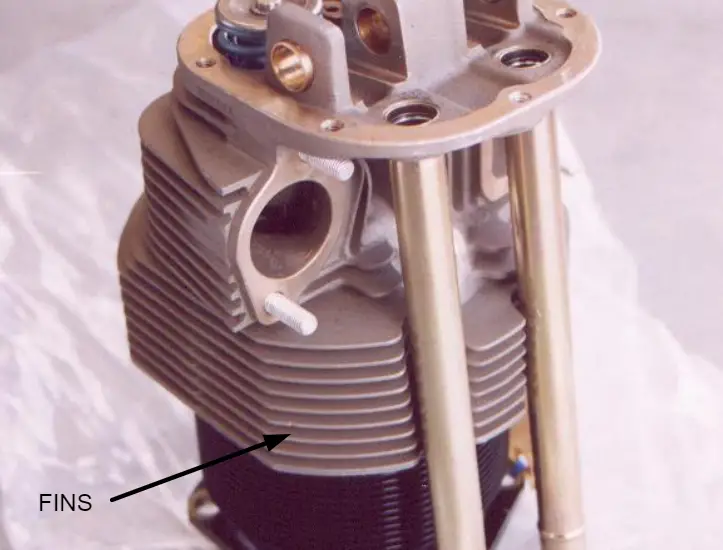
The surface area of the metal which is in contact with the air should be increased for effective cooling and this can be done by using fins over the barrels.
These fins are either cast as an integral part of the cylinder finned barrels or inserted over the cylinder barrel.
Baffles are used sometimes to increase the contact area still further.
Because of their better thermal conductivity, the usage of copper and steel alloys has also been made to improve the heat transfer.
Advantages of Air Cooling System in IC Engine:
These are some advantages of Air Cooling System:
- Air-cooled engines are lighter because of the absence of the radiator, the coolant, and the cooling jackets.
- Air cooling systems are operated in extreme climates, where there is a chance of water to be frozen.
- Maintenance is easier because the problem of leakage is not there.
- The air-cooled engine is an advantage In certain areas, where there is a scarcity of cooling water.
Disadvantages of Air Cooling System in IC Engine:
Also, there are some disadvantages of using Air Cooling System and those are:
- The fan absorbs a considerable portion of the engine power (about 5%) to drive it and is very bulky.
- Because of the absence of cooling water, Air-cooled engines are noisier.
- As the coefficient of heat transfer for water is more than that of air, there is less efficient cooling in this case.
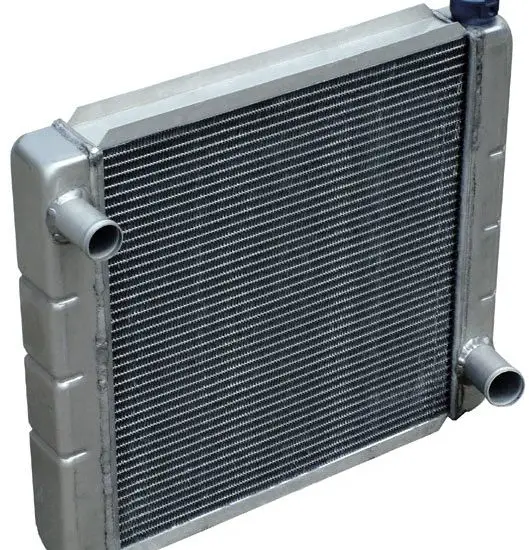
Water Cooling System in IC Engine:
The cooling medium used is "water" in the water cooling system.
In this, engine cylinders are surrounded by water jackets through which the cooling water flows. Heat flows from the cylinder walls into the water which goes to the radiator where it loses its heat to the air.

To avoid the frozen water in the engine during the winter season, antifreeze is added to the water.
By adding antifreeze, the water did not free and circulate through the system.
Note: Antifreeze + Water= Coolant
Usually, some antifreeze is added to the cooling water, due to which it is often referred to as coolant.
Classification of Water Cooling Systems in IC Engines:
Water cooling systems are of two types :
- Thermosyphon System
- Pump Circulation System
Thermosyphon Cooling System in IC Engines:
It is a cooling system that works under Gravity.
Parts of Thermosyphon Cooling System:
The parts of the Thermosyphon Cooling System are:
- Radiator
- Engine
- Filler cap or Pressure cap
- water
- Cooling Fan
- Hosepipe
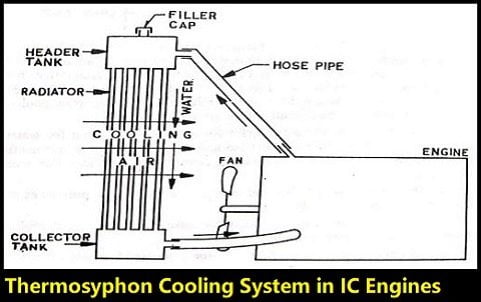
Working of Thermosyphon Cooling System:
A very simple system, which was used in many early automobiles is obsolete now. It consists of a radiator connected to the engine through flexible hoses.
In this system, the circulation of water is obtained from the difference in densities of the hot and the cold regions of cooling water.
The circulating water gets heat from the engine cylinders, thereby cooling the same.
The same heat in the water is then dissipated into the atmosphere, through the radiator, by mainly conduction and convection.
Therefore, the circulating water becomes cold by the time it reaches the collector tank of the radiator. The same water is then circulated through the engine to collect heat from the cylinders.
Some of the thermosyphon systems also had fans mounted behind the radiator and driven by belt and pulleys from the crankshaft, to assist the flow of cooling air.
Advantages of Thermosyphon Cooling System:
The advantages of Thermosyphon Cooling System are as follows:
- Simplicity.
- Low initial cost.
Disadvantages of Thermosyphon Cooling System:
The disadvantages of Thermosyphon Cooling System are as follows:
- As the circulation of coolant is maintained by natural convection only, the cooling is rather slow.
- As there is a large quantity of water in the system and due to the gravity, the pressure in the coolant is less and it takes more time for the engine to reach the operating temperature.
- Always a minimum level of coolant is to be maintained in the system else it leads to the failure of the system by the hot gases.
Pump Circulation System in IC Engine:
It is a cooling system that works with a pump.
Components of Pump Circulation System:
The Components of the Pump Circulation system are as follows.
- Engine(with Cylinders)
- Cooling Fan
- Thermostat Valve
- Radiator
- Filler cap(Pressure cap)
- Hose Pipes
- Water Pump
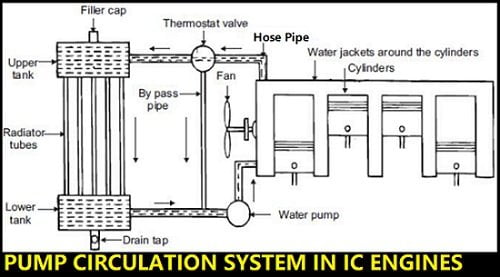
Working of Pump Circulation System:
This system is similar to the thermosyphon System described above with the only difference that a pump is used for the circulation of coolant and a thermostat is employed to control the flow of coolant. The pump is driven using a belt from the engine crankshaft.
The coolant is to be passed through the hose pipes and travel throughout the system. The thermostat plays a vital role in increasing the life of the radiator.
If the temperature of the coolant is less than 80°C, then the coolant does not enter into the radiator and it passes throughout the system with the help of bypass Pipe.
If the temperature of the coolant is more than 80°C, then the Thermostat valve opens and it sends the hot coolant into the radiator.
Now, the cooling fan is placed just before the radiator tubes and is attached to the crankshaft assembly to cool the coolant.
Due to the fan, the heat from the coolant is escaped from the tubes and after cooling the coolant, it is again underflowed through the hose pipe.
Here, the Centrifugal Pump is used to circulate the water throughout the system with high pressure so that the hot coolant cools at a faster rate.
In this way, the coolant will travels throughout the system and the hot gases do not affect the engine cylinders.
This is a detailed explanation of the Pump Circulation System in IC Engines. If you have any doubt, feel free to ask in the comments section.
References:
- Automobile - Cooling system | Britannica
- Cooling systems of ic engines - IGNOU [PDF]
Media Credits:
- All the images including feature image: Modified by Author
- Image 1: The original uploader was Ali0th at English Wikipedia. - Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons., CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1822608